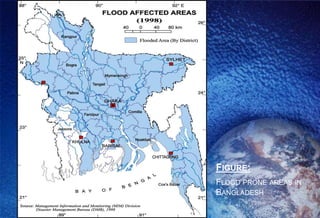
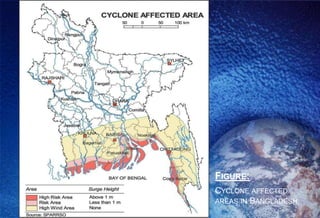
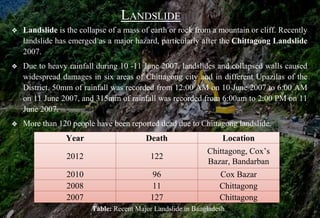
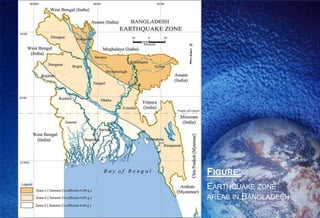
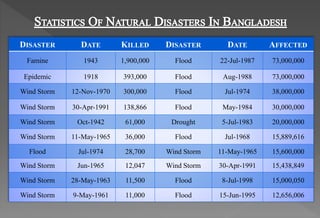
This document discusses natural disasters that commonly occur in Bangladesh. It notes that Bangladesh is highly vulnerable to natural disasters like floods, cyclones, landslides, droughts, and earthquakes due to its geography and climate. Major floods have occurred in 1954, 1987, 1988, 1998 and caused loss of life and property. Cyclones in 1991 and 2007 also killed over 100,000 people. Landslides in Chittagong in 2007 killed over 120 people. Earthquakes are another hazard, with one in 1997 causing damage. Droughts regularly affect parts of Bangladesh and have humanitarian impacts. The document outlines damage from various natural disasters and calls for mitigation efforts.