The document discusses Stephen Krashen's theory of second language acquisition, specifically:
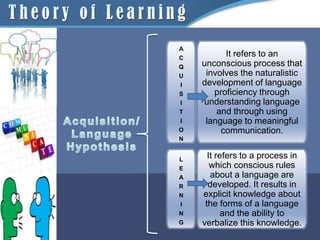
1) It distinguishes between acquisition, which is a subconscious process of developing proficiency through meaningful communication, and learning, which is a conscious process of developing explicit grammatical rules.
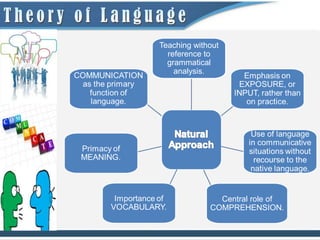
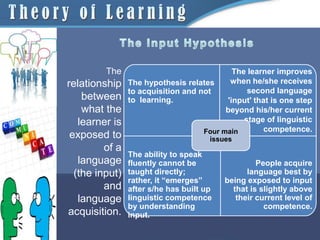
2) Krashen's Input Hypothesis states that language is acquired by understanding input that is slightly beyond one's current linguistic competence.
3) The Affective Filter Hypothesis proposes that acquisition requires a low affective filter, meaning low anxiety, high motivation, and high self-confidence.