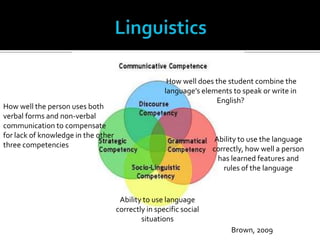
This document discusses the background and key principles of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT). It describes how CLT emerged in response to the need for language teaching to focus on communicative proficiency. CLT is not based on any single model and draws from theories of communicative competence, language functions, and the purposes of language. Central to CLT is that the goal of language teaching is communicative competence and that language learning involves developing skills for communication. Accuracy and fluency are both important aims.














![Brown, P. (2009). What’s CTL? [Blog en linea]
Language Matters. Disponible: http://language
instinct.blogspot.com/2006/09/what-is-clt-language-
competencies.html [Consulta: 2011, Octubre 25]
Richards, J. (2006). Communicative Language Teaching
Today. NewYork: Cambridge Press.
Richars & Rodgers (1986). Approaches and Methods in
Language Teaching. NewYork: Cambridge Press.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communicativelanguageteachingclt2-111121121913-phpapp01/85/Communicative-language-teaching_-clt-2-16-320.jpg)