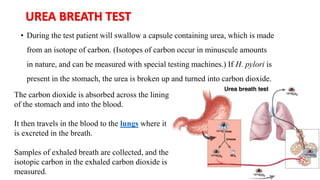
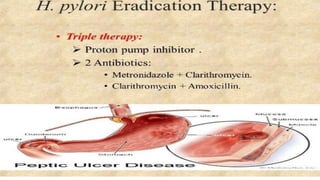
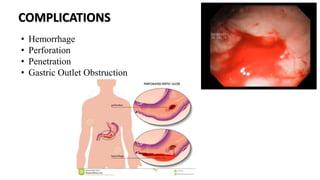
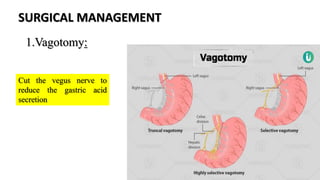
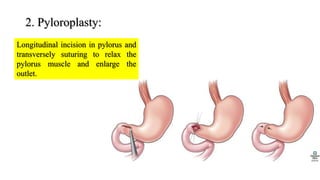
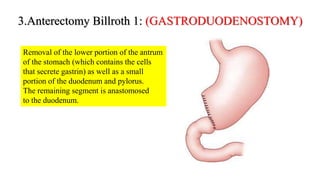
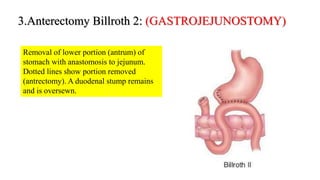
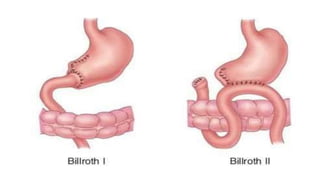
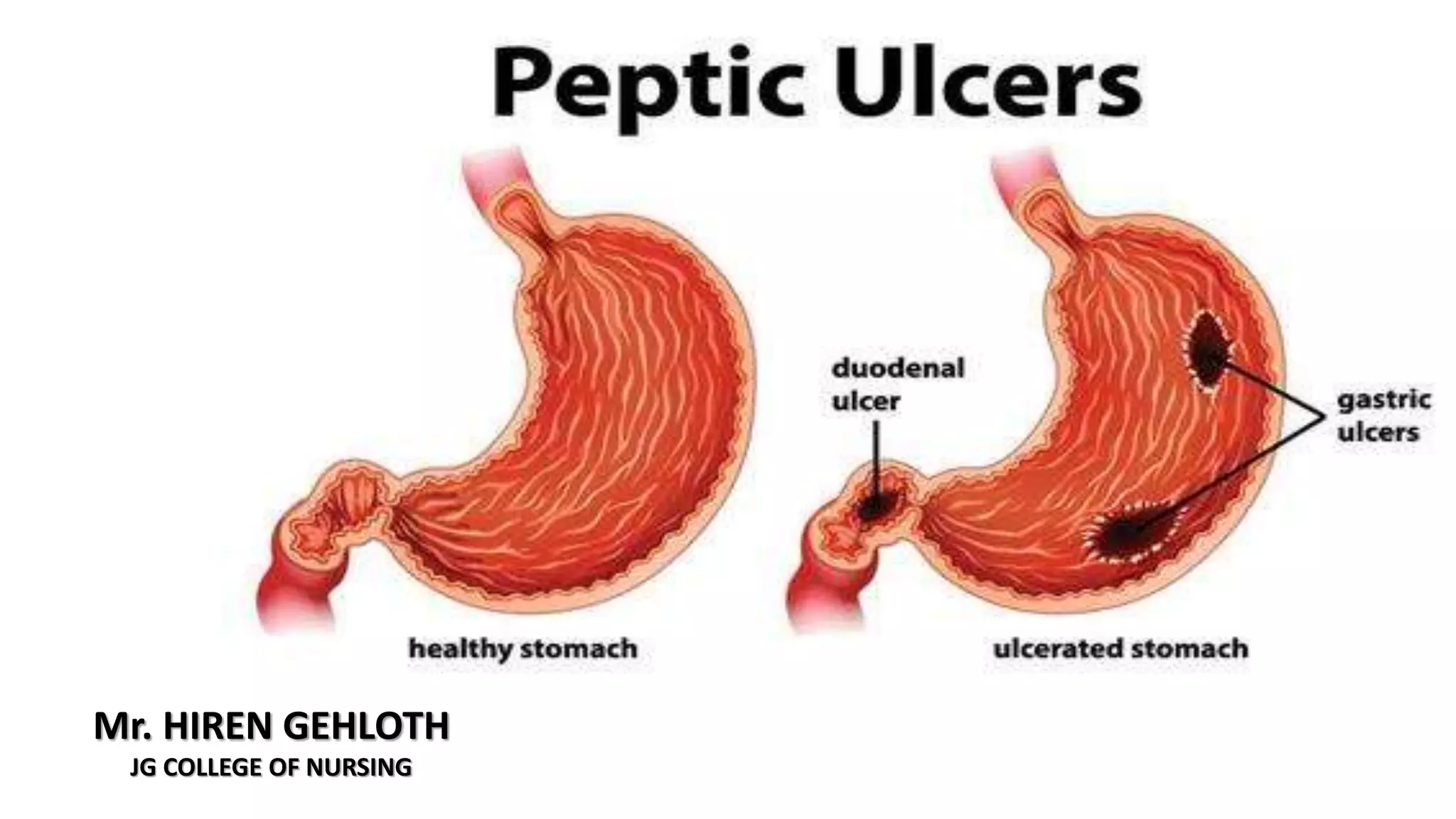
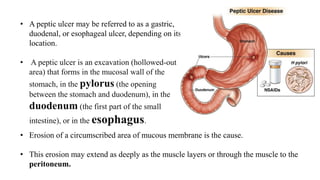
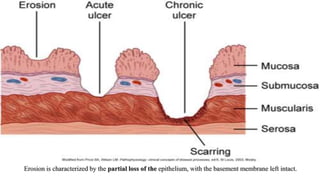
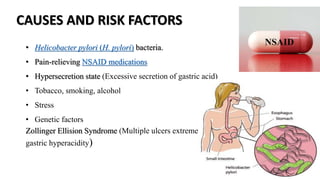
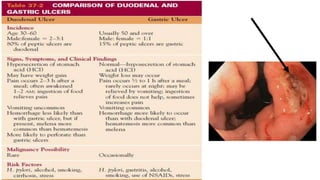
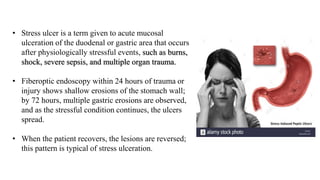
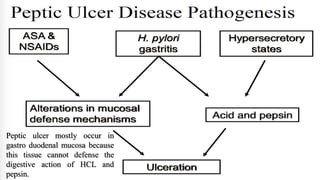
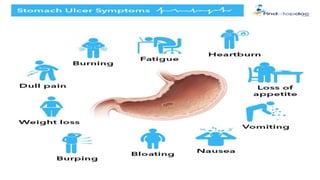
Peptic ulcers form in the lining of the stomach, esophagus, or duodenum due to erosion caused by gastric acid. Risk factors include H. pylori bacteria, NSAIDs, smoking, alcohol, and stress. Diagnosis involves endoscopy, stool tests, or a urea breath test to detect H. pylori. Treatment consists of antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, and lifestyle changes. Complications include hemorrhage, perforation, and gastric outlet obstruction. Nursing care focuses on pain relief, nutrition, anxiety reduction, and monitoring for complications.
![• Peptic ulcers are more likely to occur in the duodenum than in the
stomach.
• As a rule they occur alone, but they may occur in multiples.
• Chronic gastric ulcers tend to occur in the lesser curvature of the
stomach, near the pylorus.
• Esophageal ulcers occur as a result of the
backward flow of HCl from the stomach
into the esophagus (gastroesophageal reflux
disease [GERD]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pepticulcerdisease-210724050958/85/Peptic-ulcer-disease-4-320.jpg)

![ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION
• Physical examination (epigastric tenderness,
abdominal distention).
• Endoscopy (preferred, but upper gastrointestinal
[GI] barium study may be done).
• Diagnostic tests include analysis of stool
specimens for occult blood, gastric secretory
studies, and biopsy and histology with culture to
detect H. pylori (serologic testing, stool antigen
tests, or a Urea breath test may also detect H.
pylori).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pepticulcerdisease-210724050958/85/Peptic-ulcer-disease-11-320.jpg)