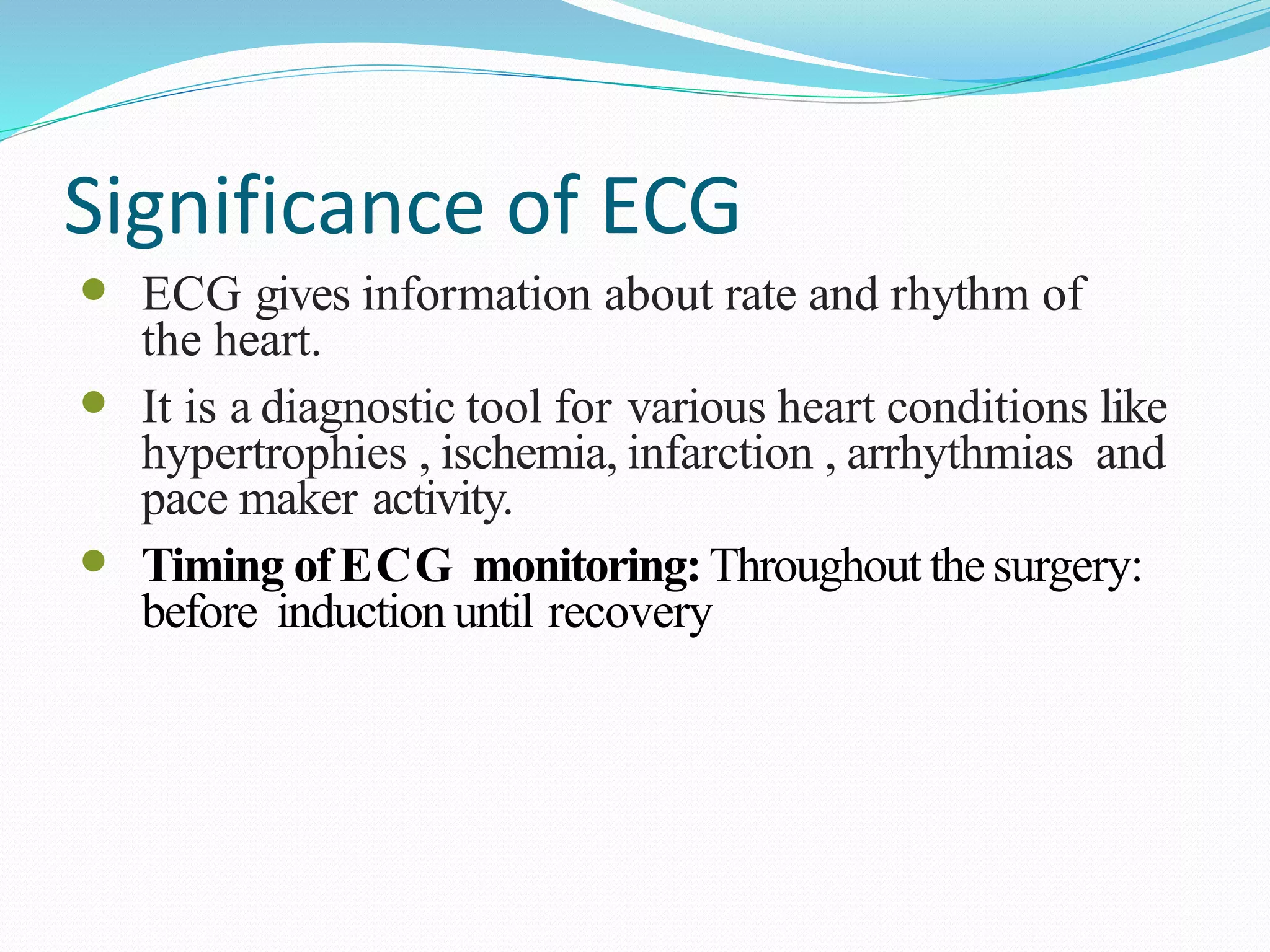
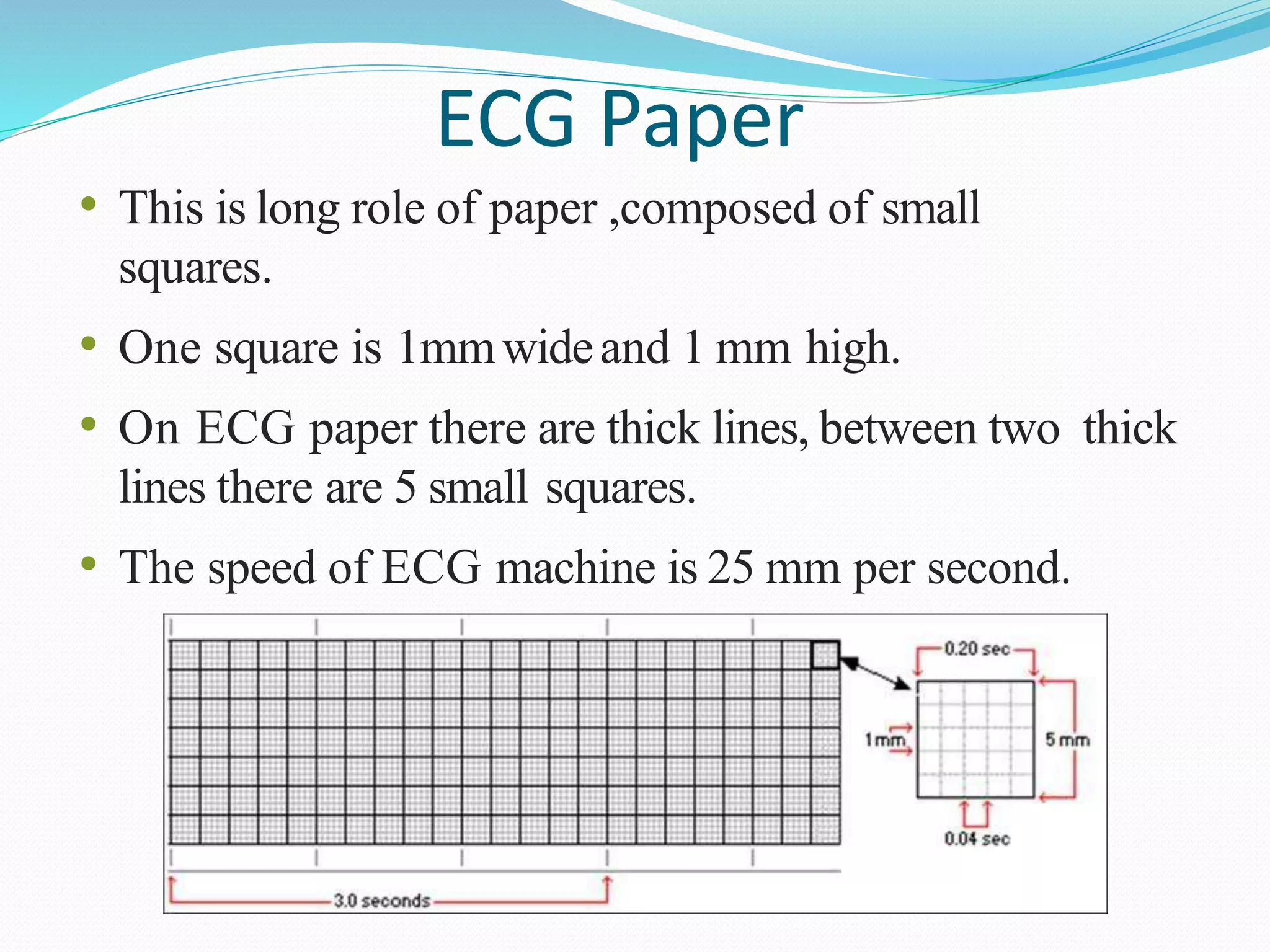
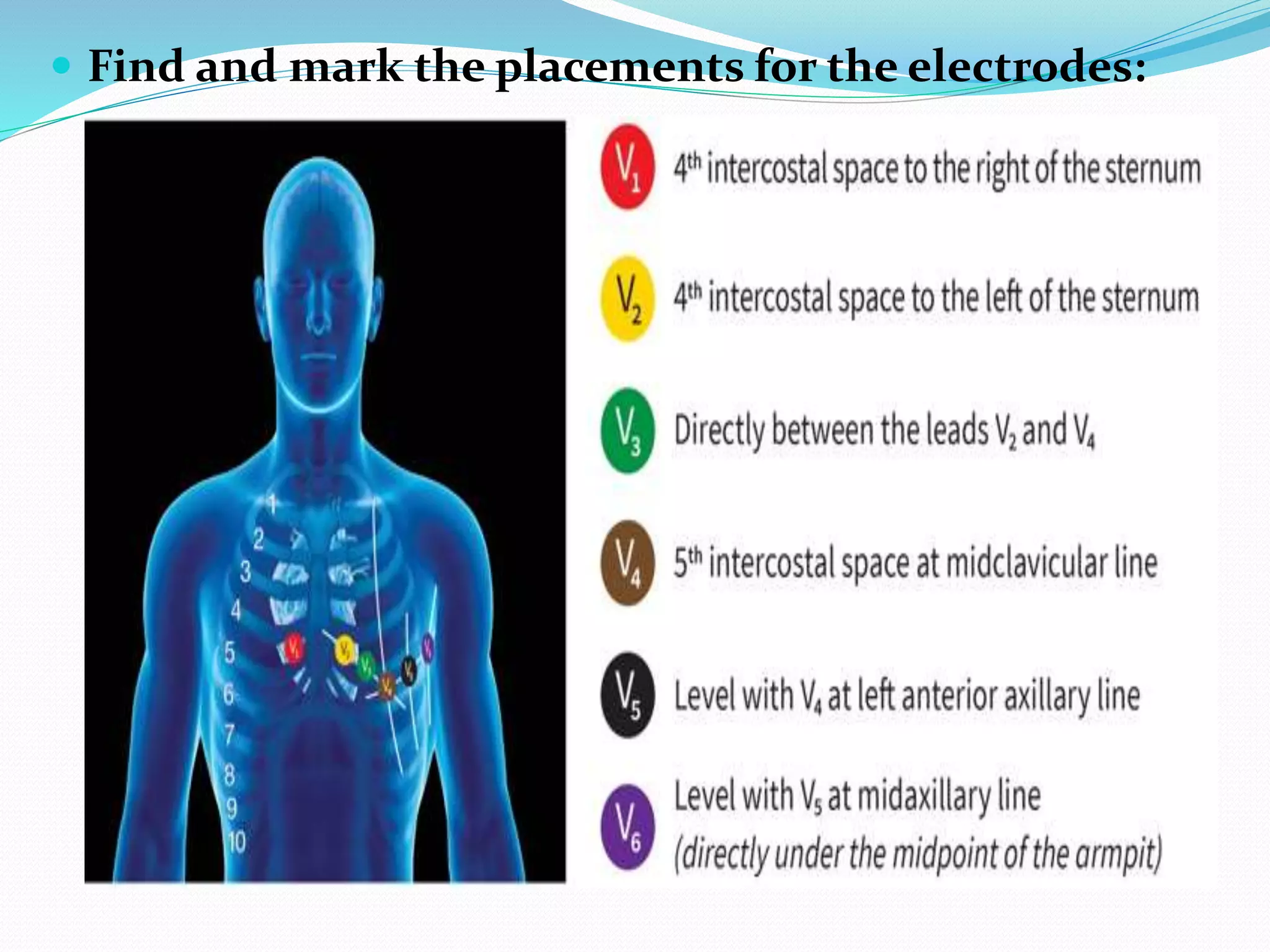
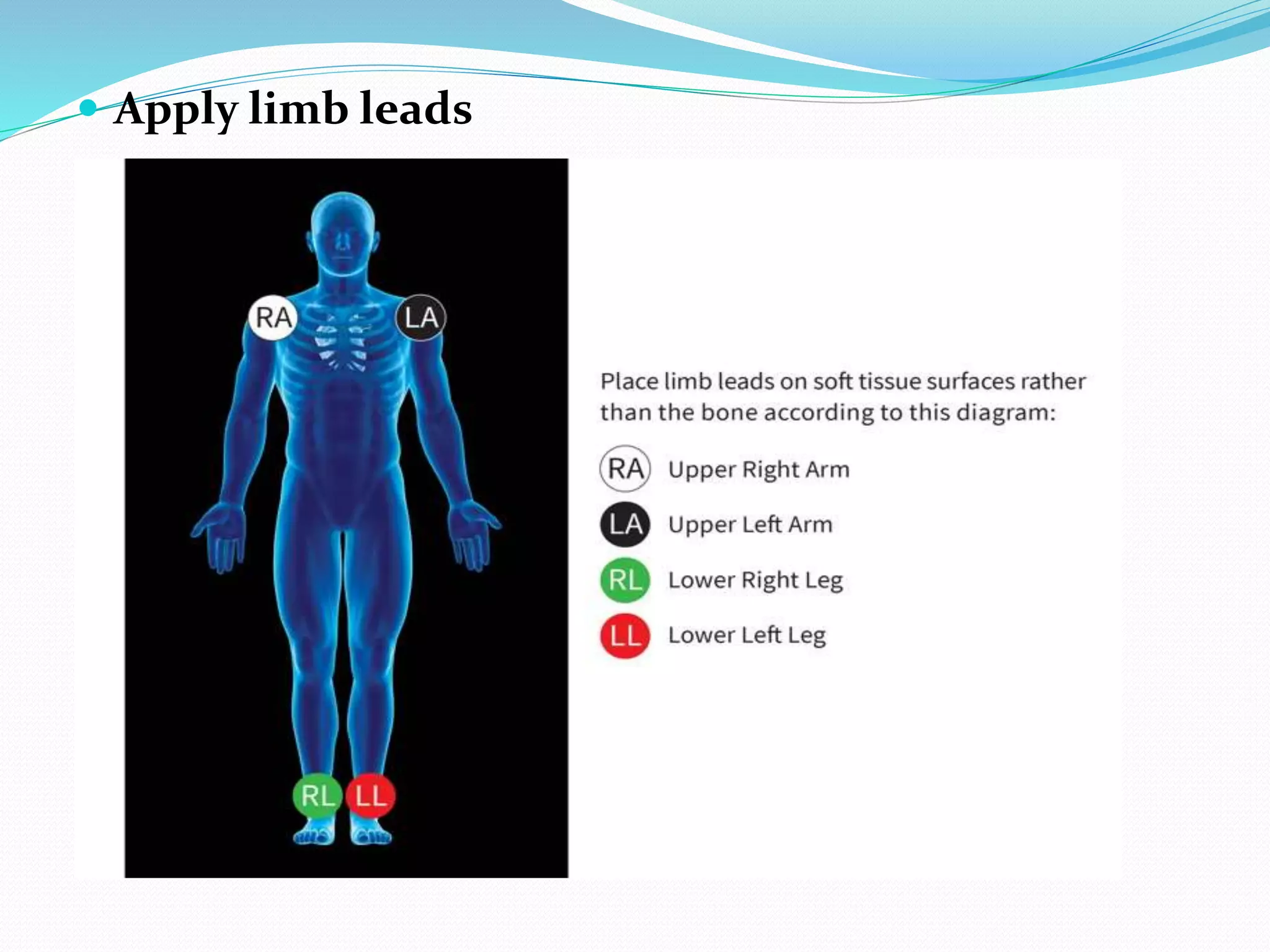
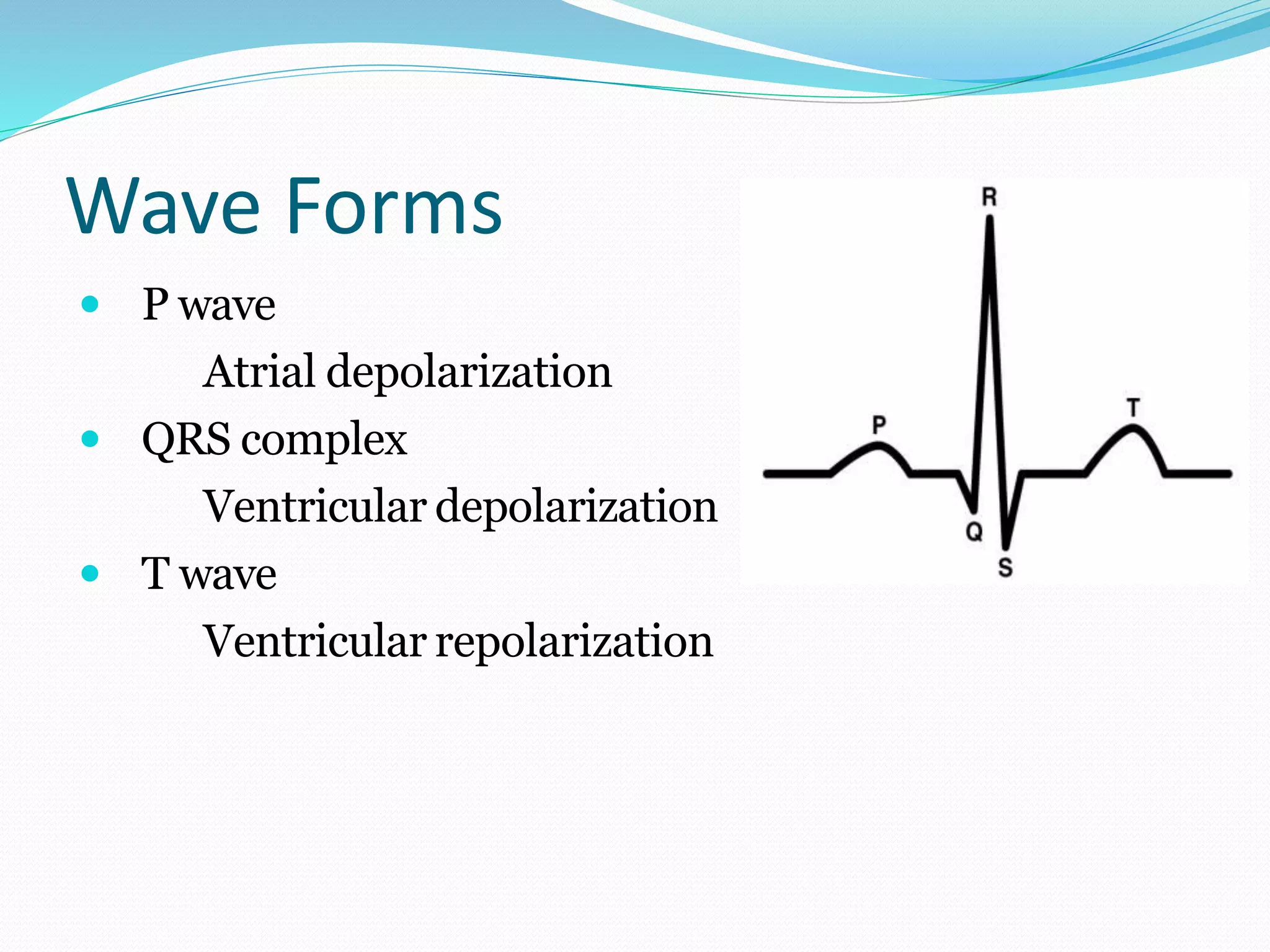
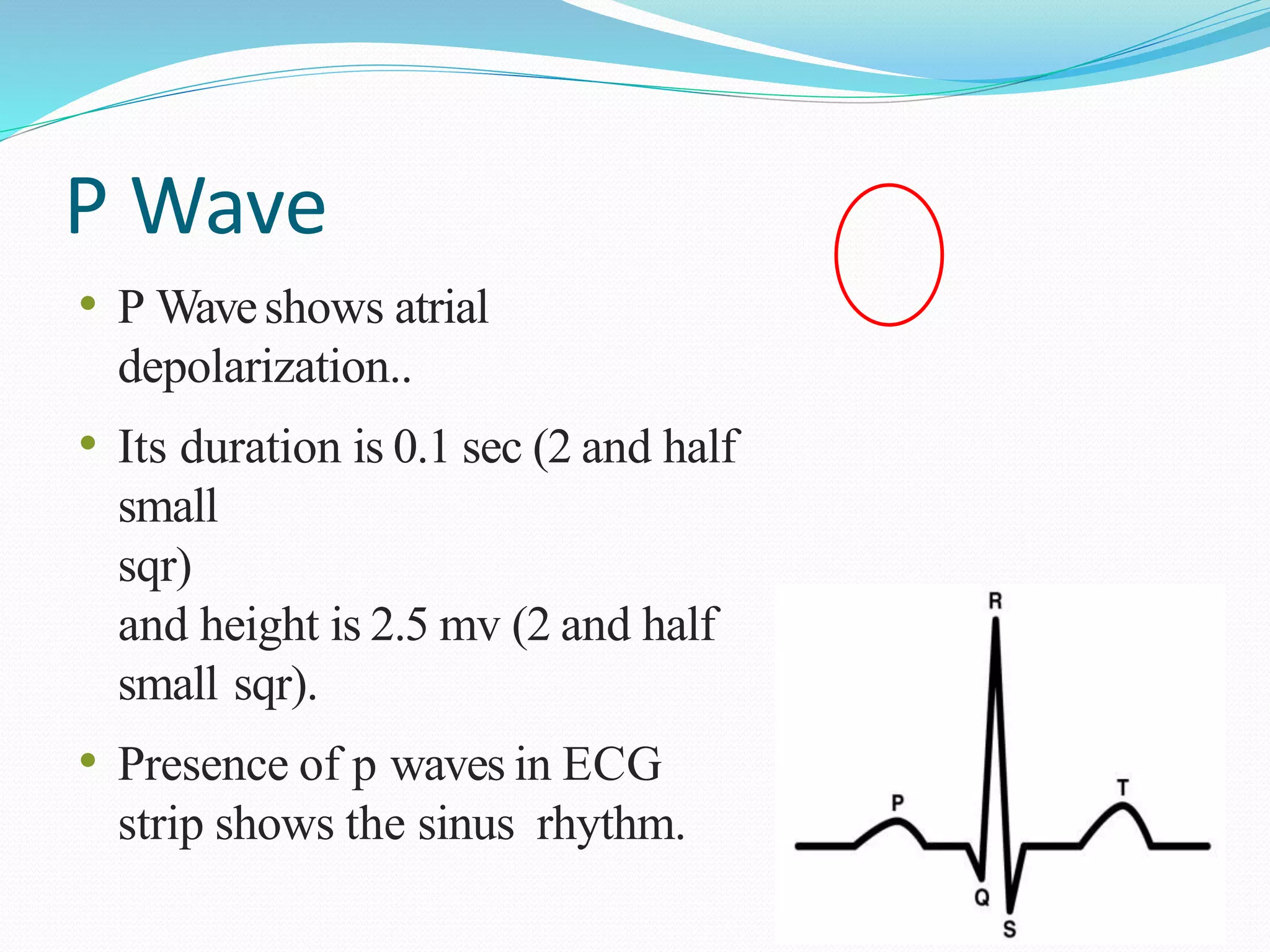
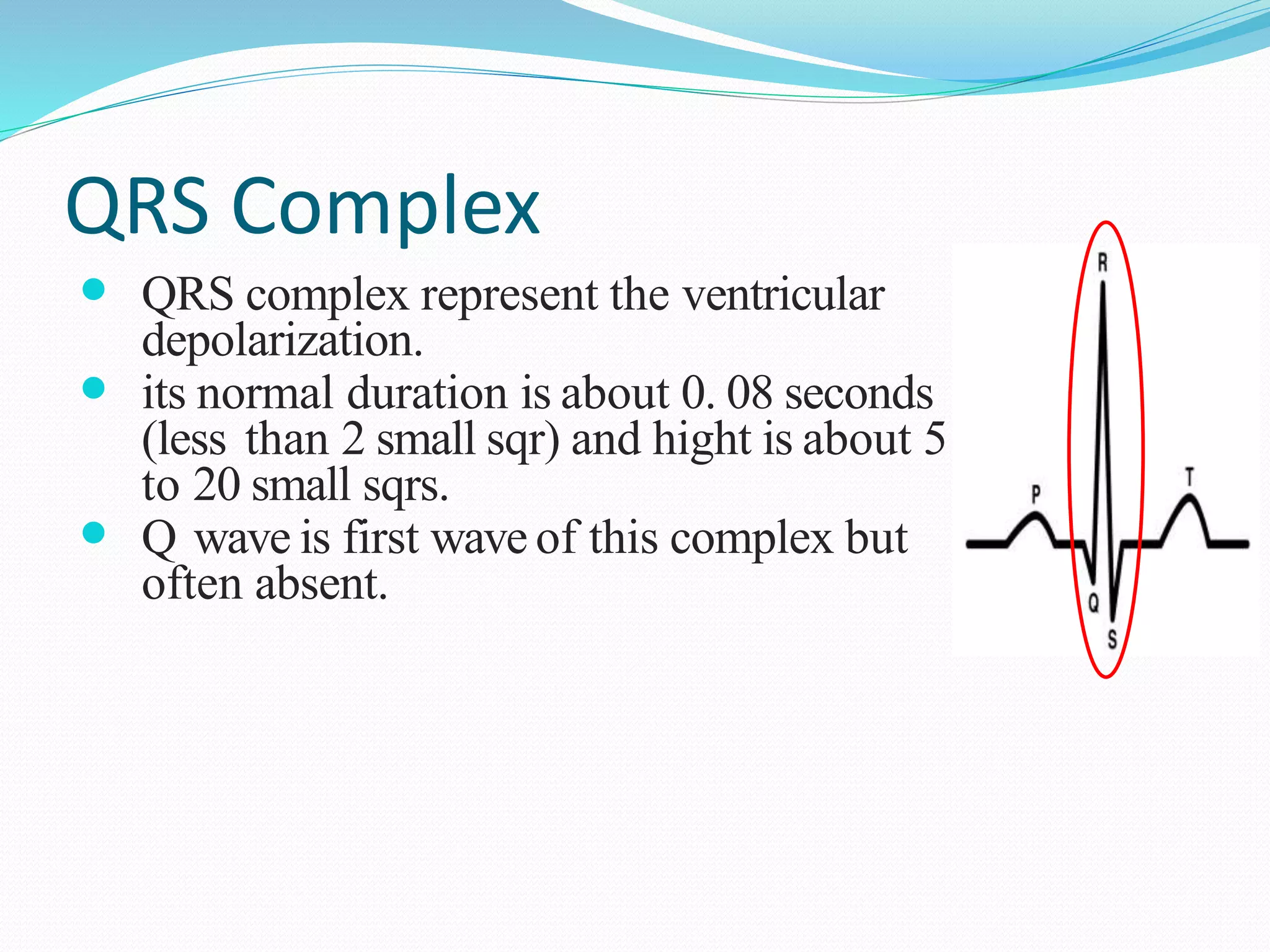
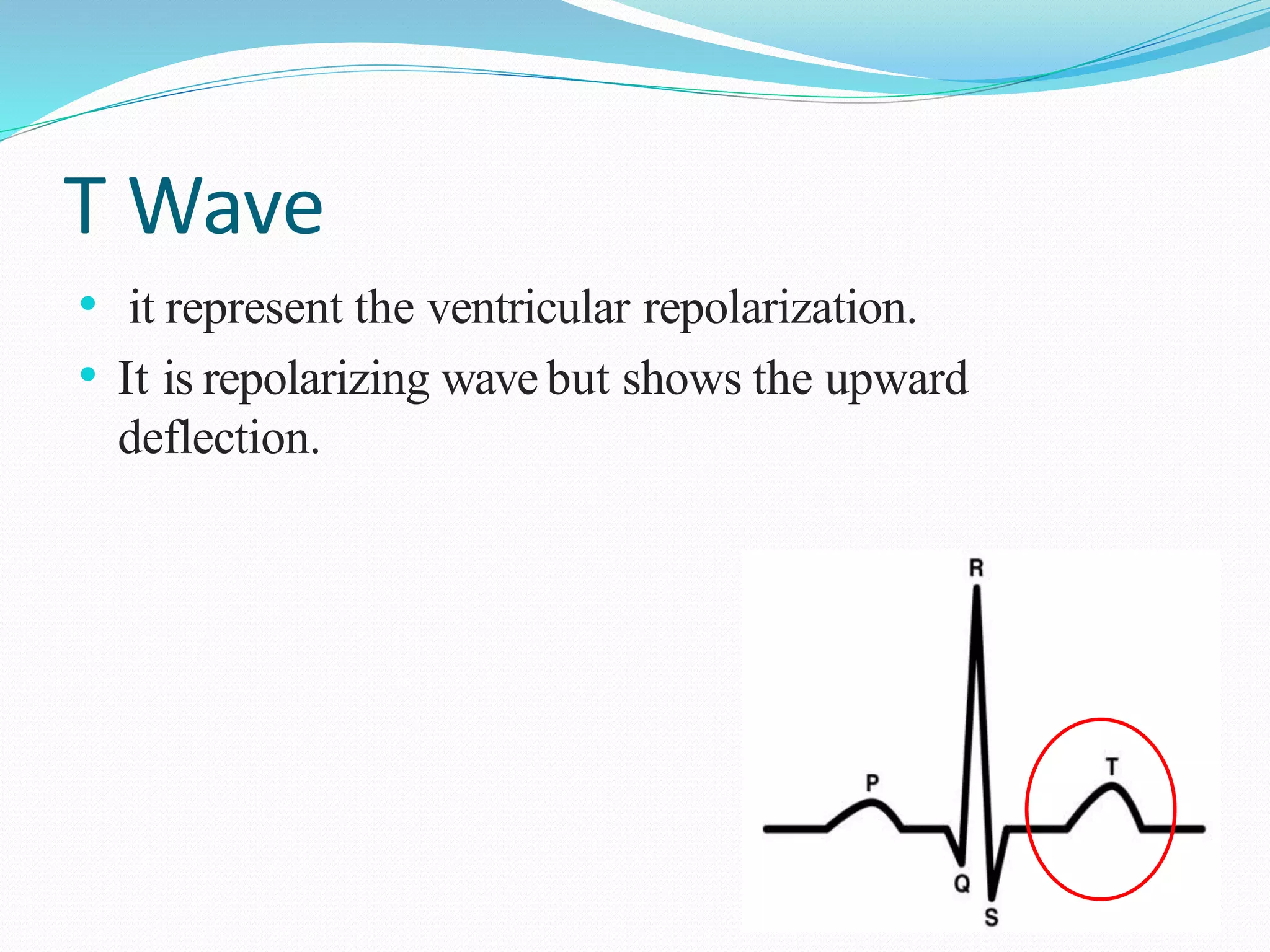
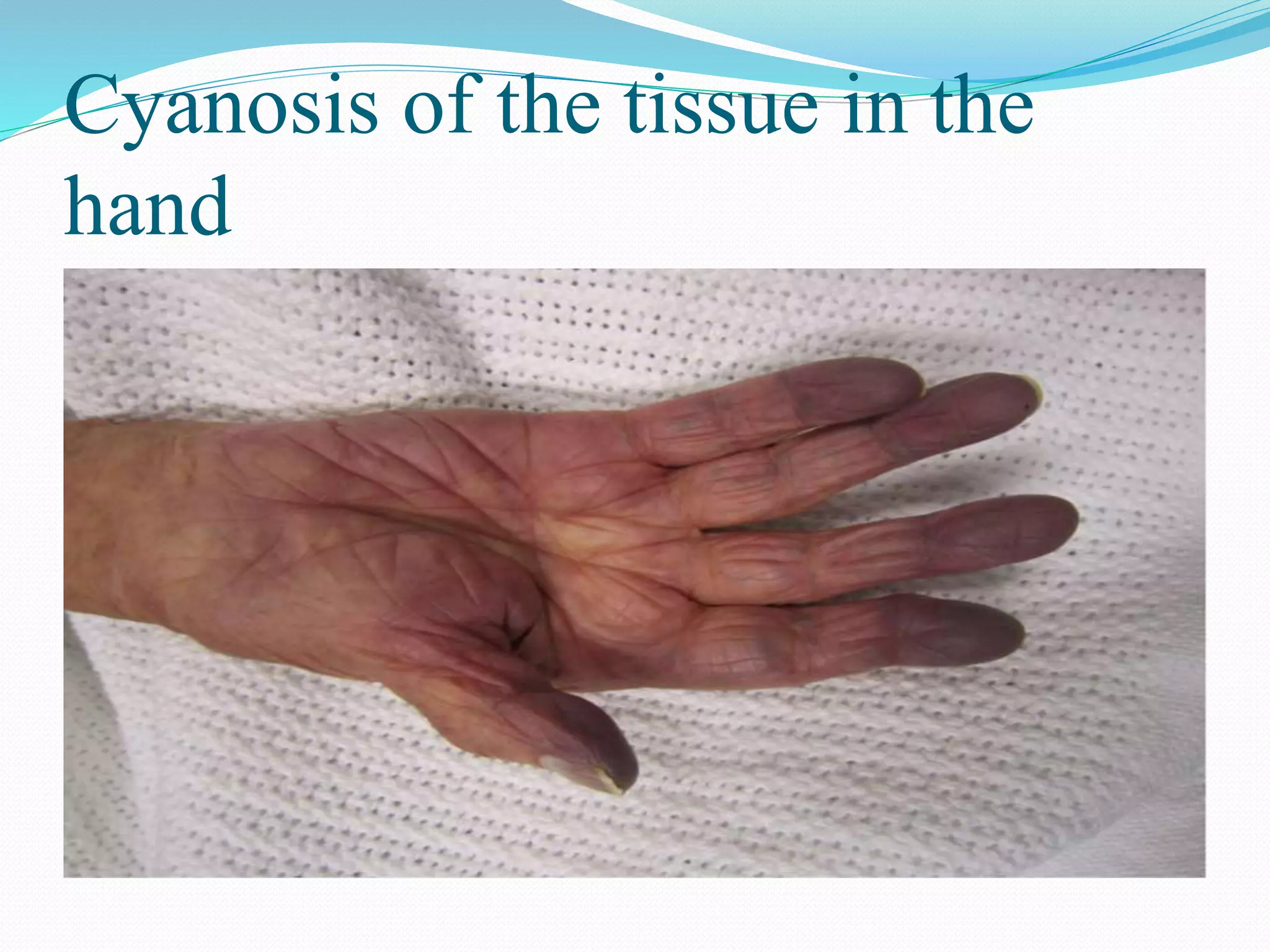
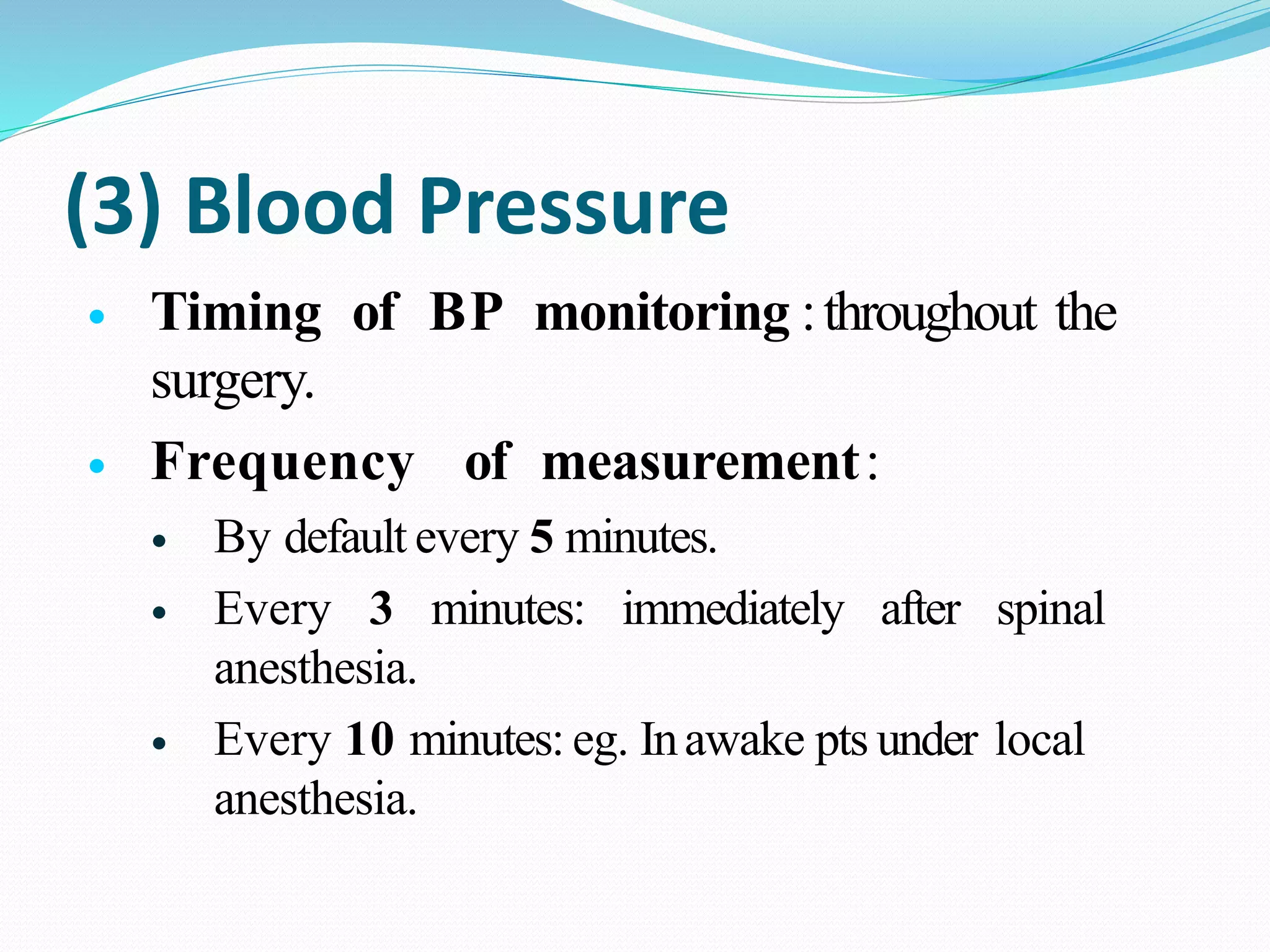
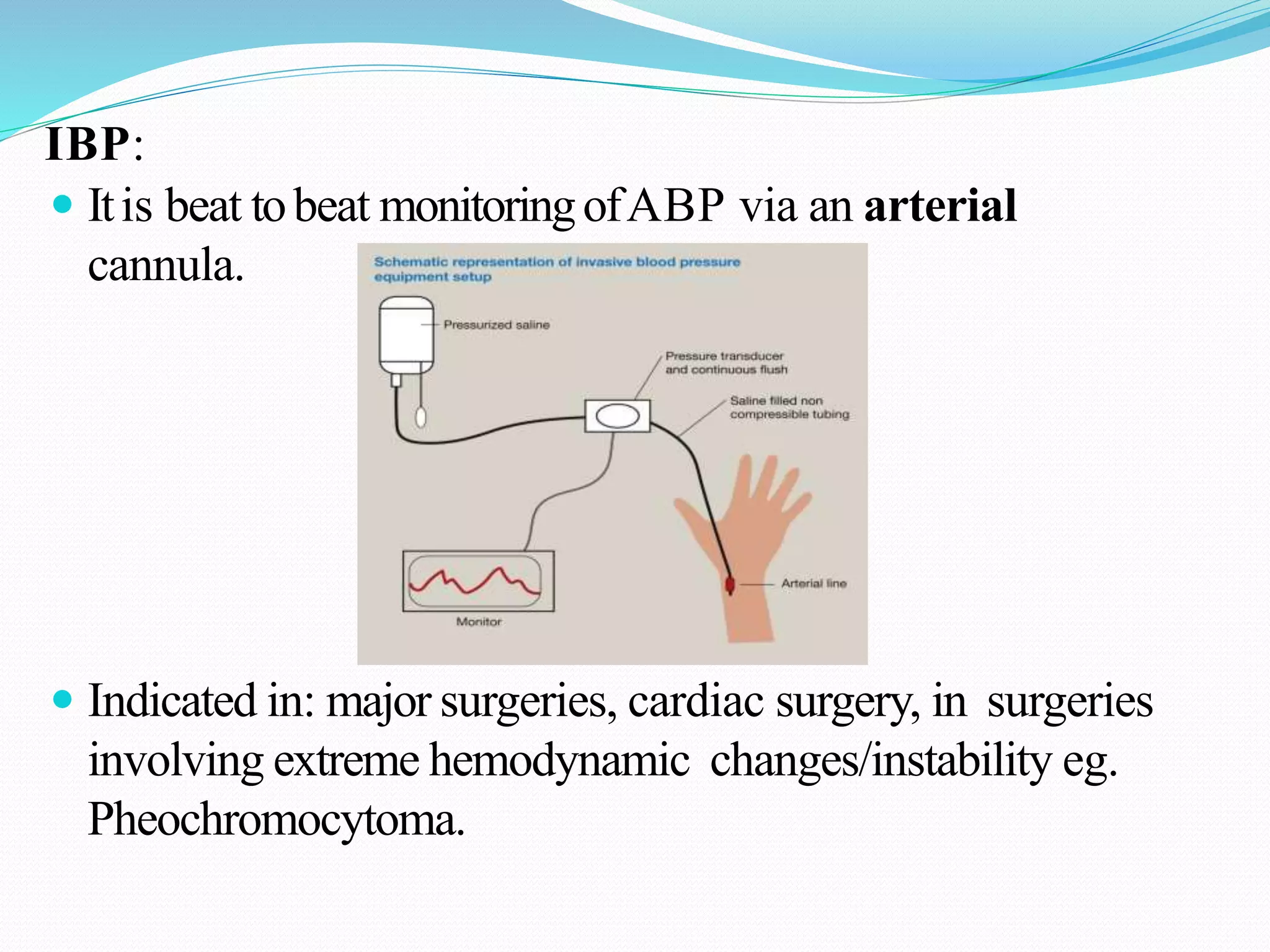
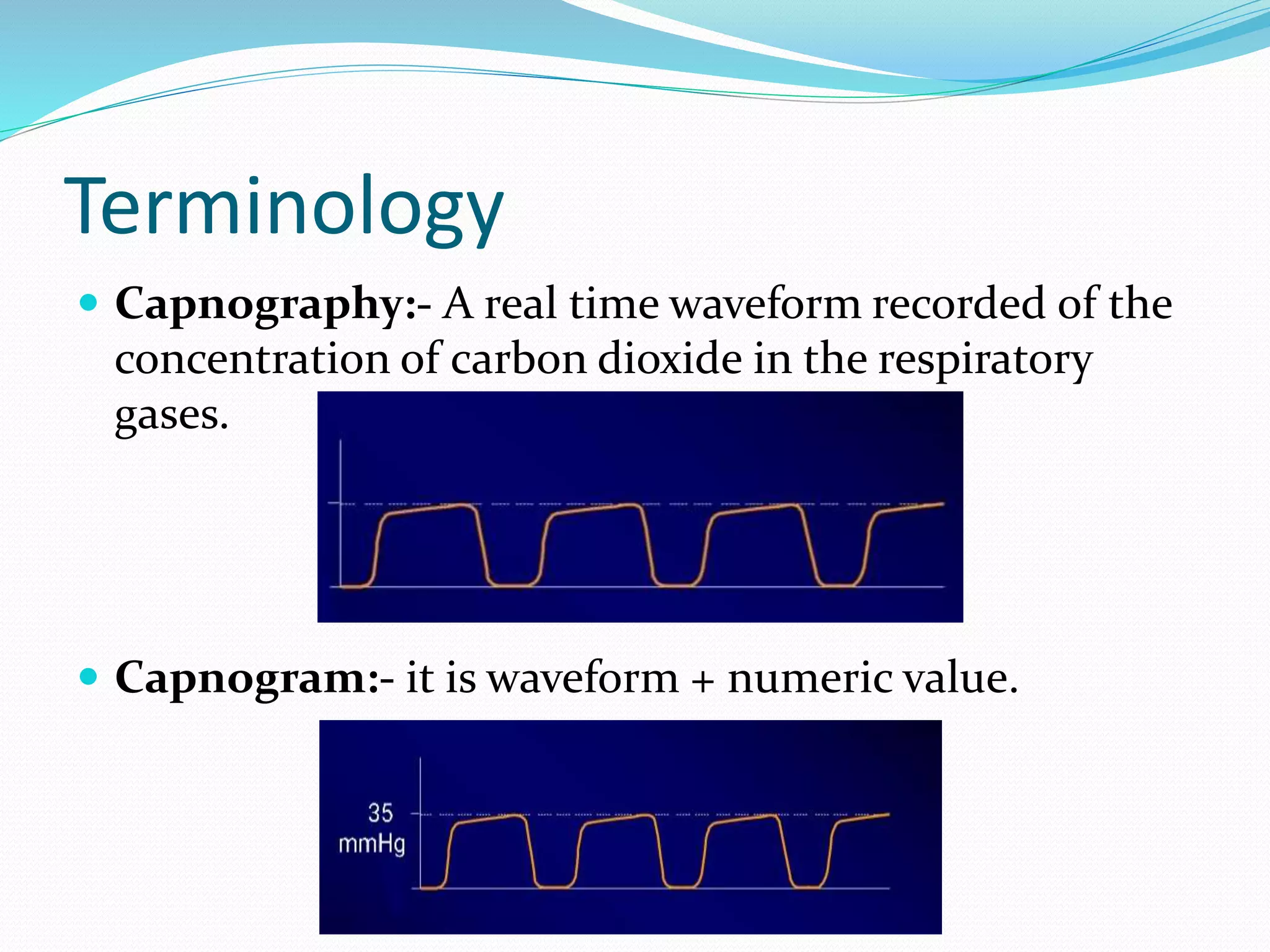
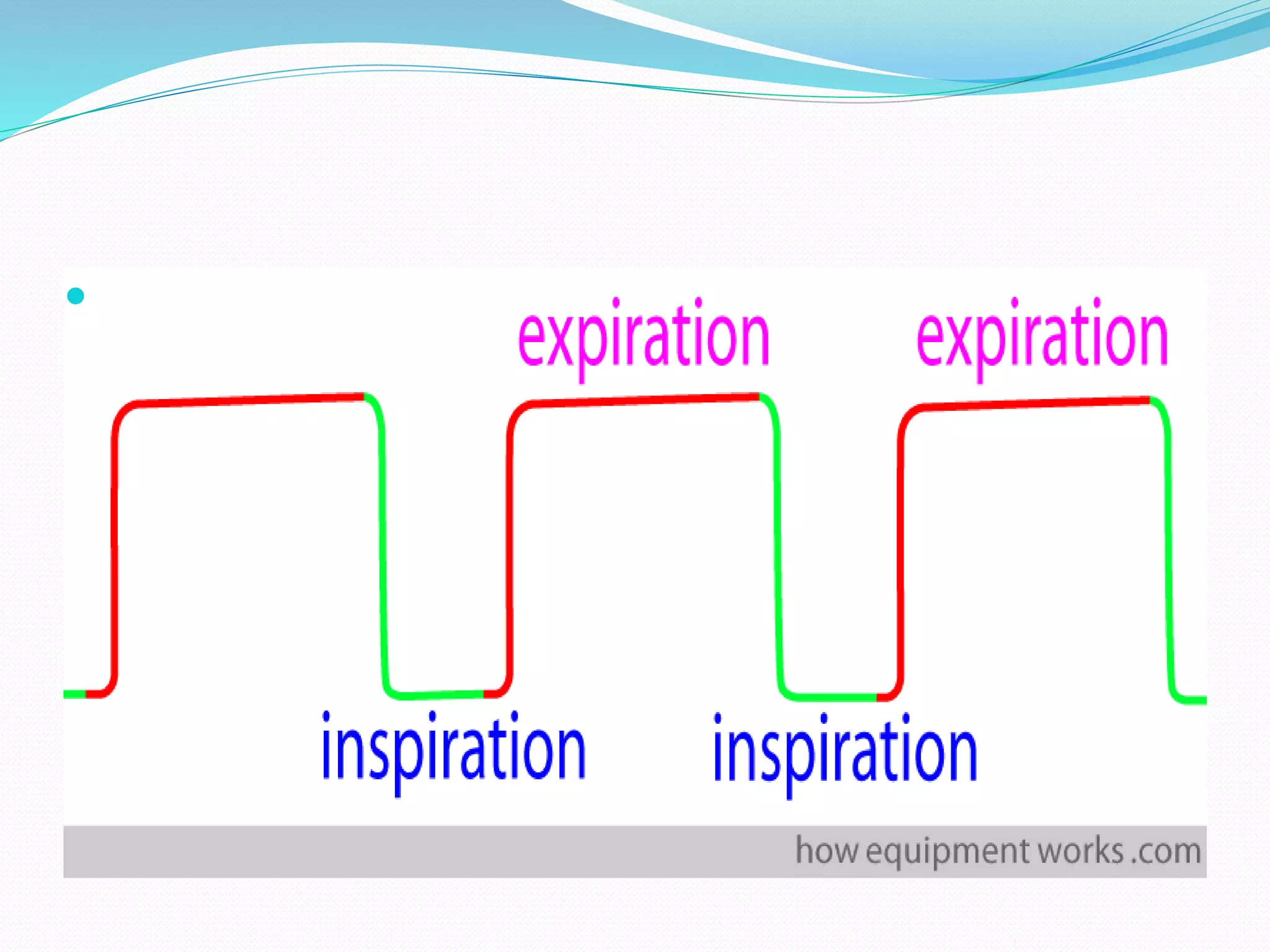
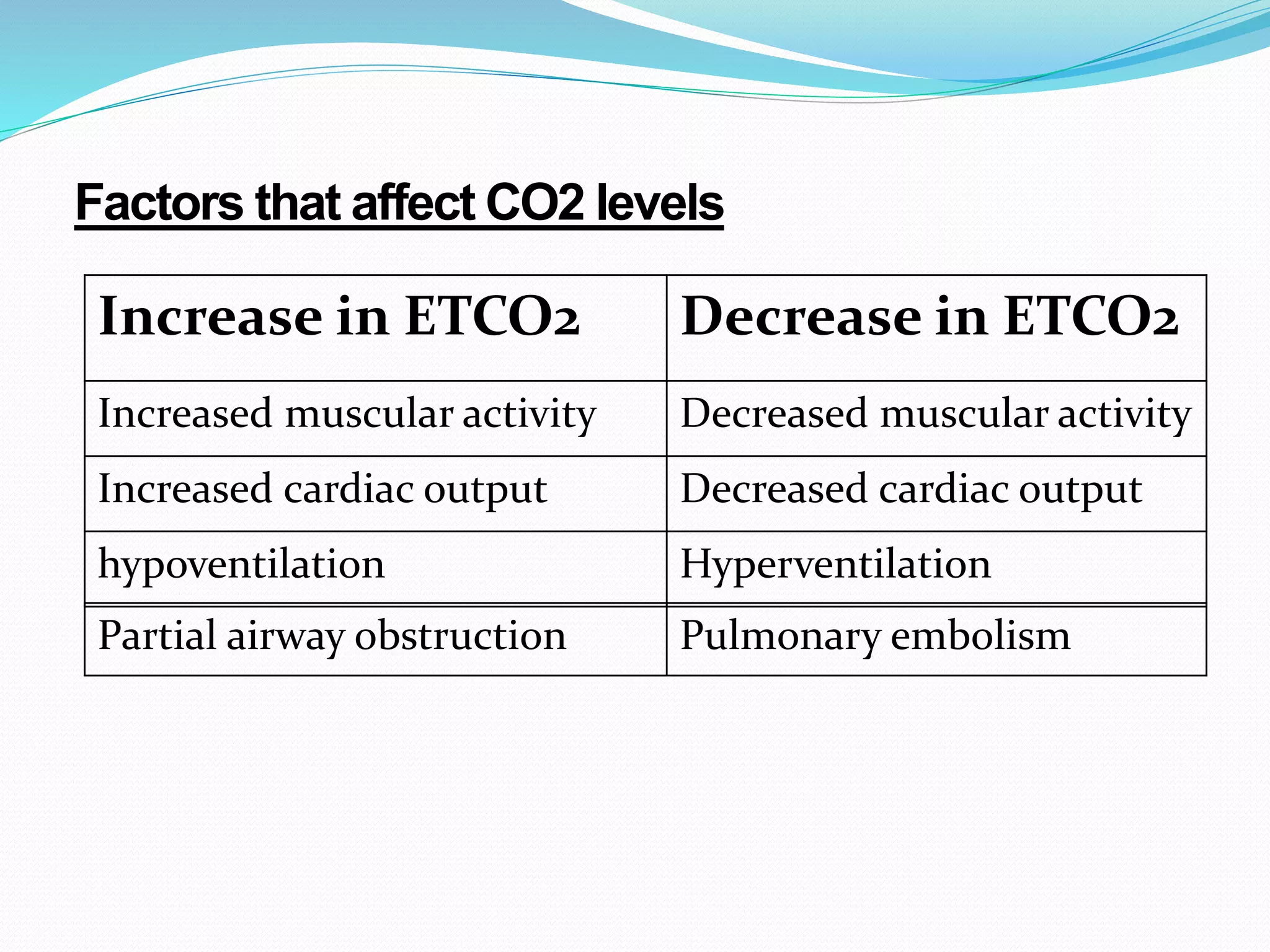
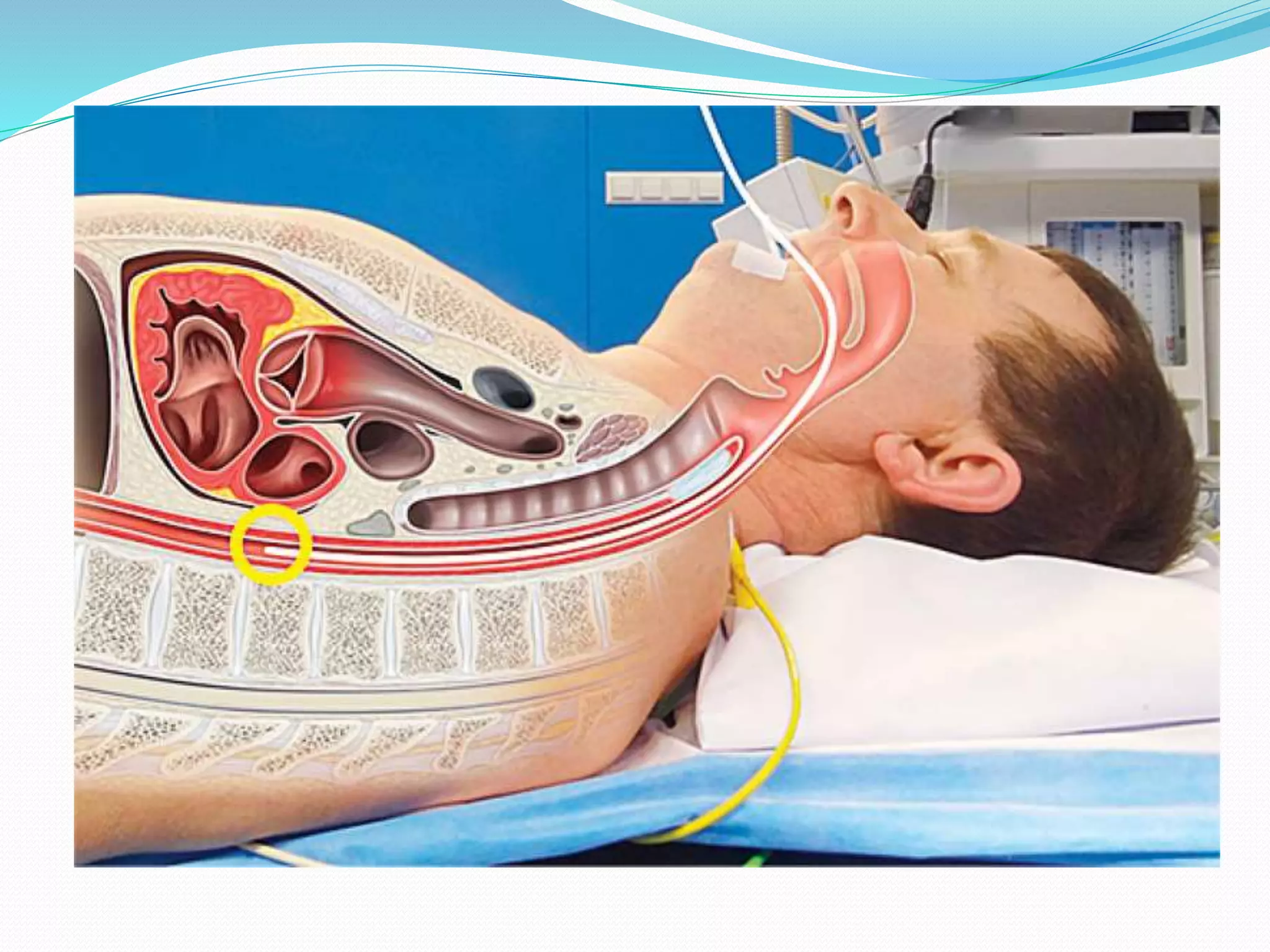
This document discusses parameters that are routinely monitored during surgical procedures, including electrocardiography (ECG), blood oxygen saturation levels (SpO2), blood pressure, end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), and temperature. Key parameters like ECG, SpO2, and blood pressure must be monitored throughout surgery. Precise measurement requires properly attaching sensors and being aware of potential errors from issues like loose or misplaced sensors. Monitoring continues in recovery to track patient status after the procedure.




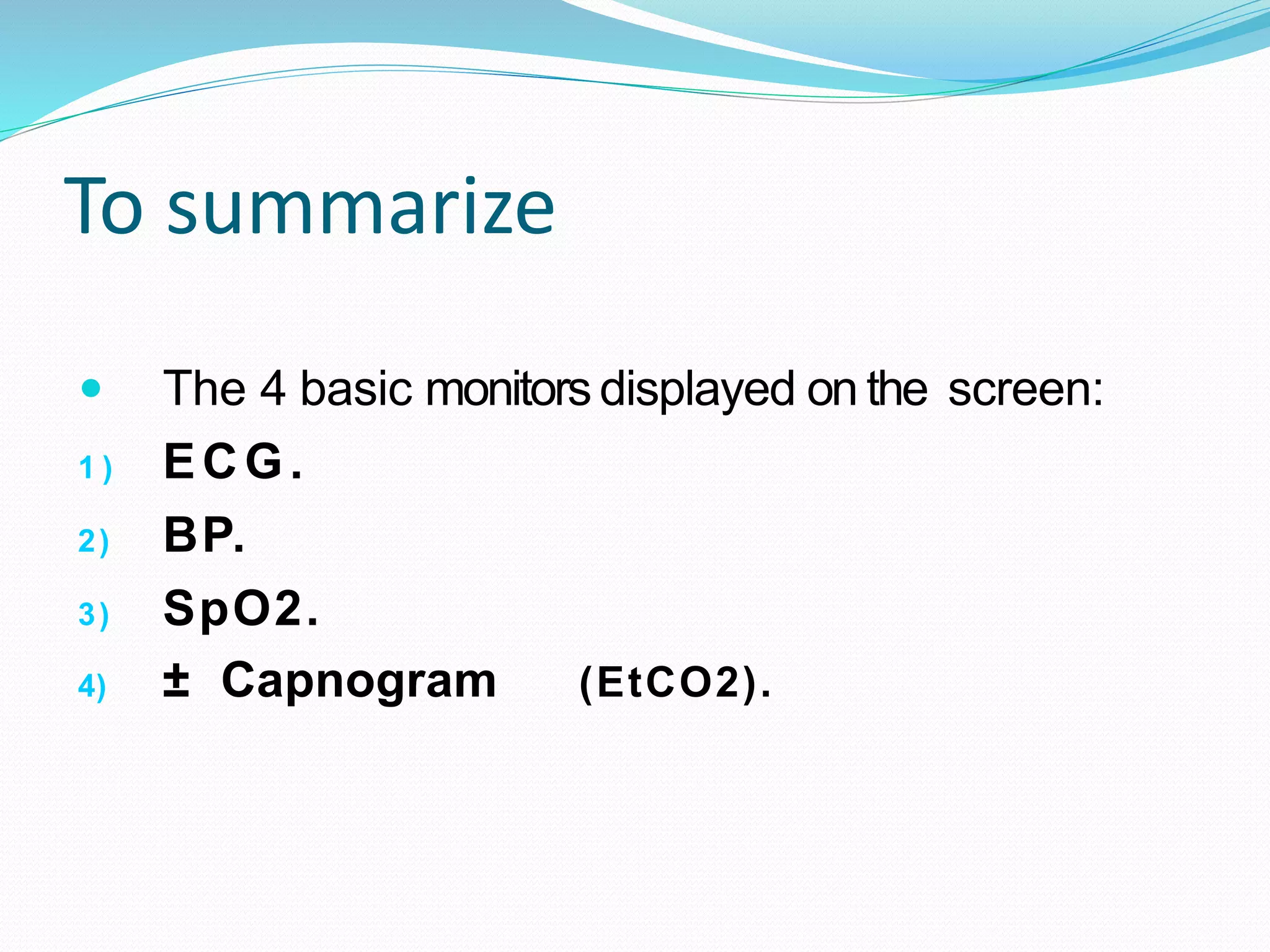
![The FOUR basic monitors.
We are not authorizedto starta surgeryinthe absence ofany
ofthesemonitors:
ECG.
SpO2: arterial O2 saturation.
Blood Pressure: NIBP (non-invasive), IBP (invasive).
± [Capnography].
The mostcritical 2 timesduringanesthesiaare:
INDUCTION - RECOVERY.
Exactly like “flying aplane ” induction(= take off) &recovery
(= landing). The aimis to achieve a smooth induction&a
smooth recovery &a smooth intraoperative course.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iom2-230728162528-24002ae1/75/IntraOperative-Monitoring-8-2048.jpg)