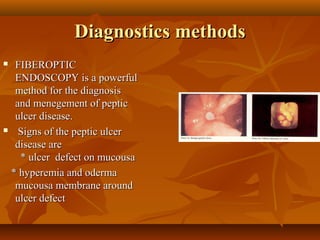
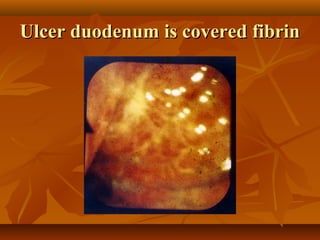
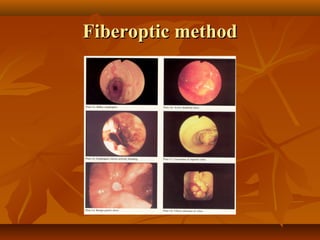
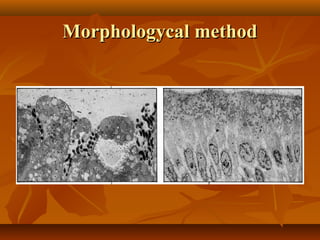
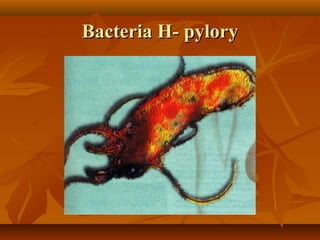
Peptic ulcer disease is a condition that causes sores, or ulcers, in the lining of the stomach or duodenum. The main causes are acid hypersecretion and infection with the bacteria H. pylori. Common symptoms include a burning pain in the upper abdomen that occurs hours after eating and is relieved by food or antacids. Diagnosis is typically made through endoscopy or imaging tests. Treatment involves lifestyle changes, medications to reduce acid production or kill H. pylori, and sometimes surgery for complications.