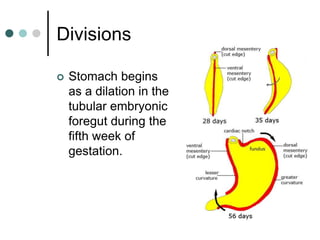
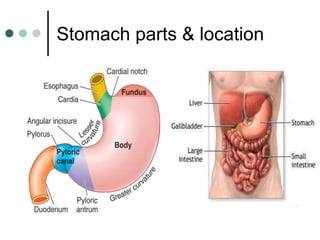
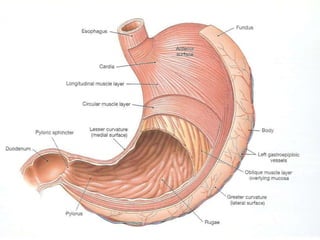
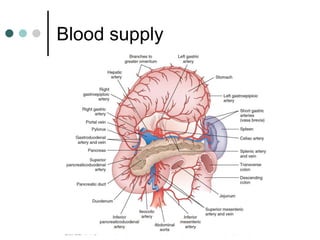
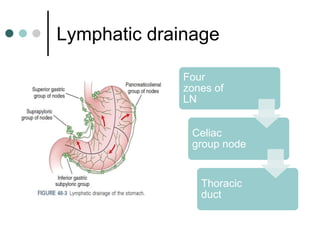
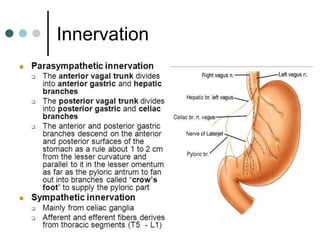
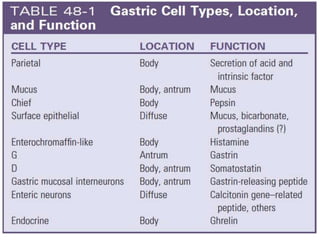
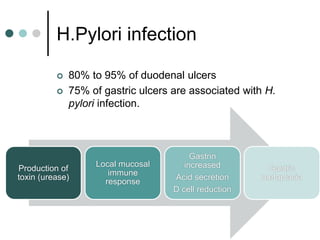
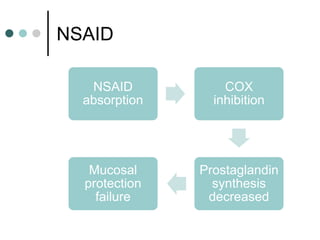
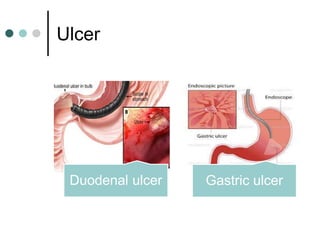
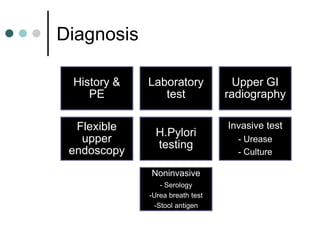
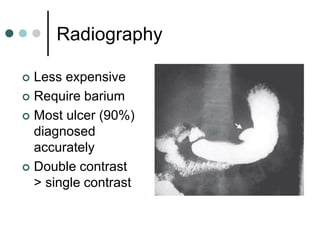
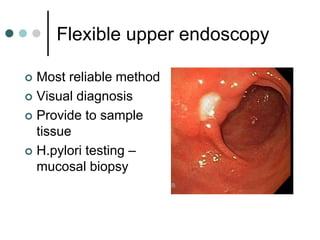
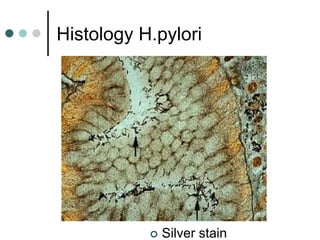
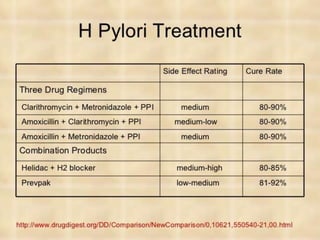
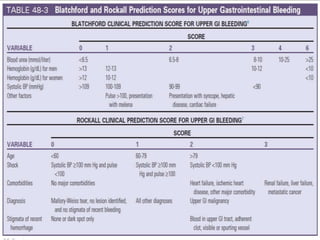
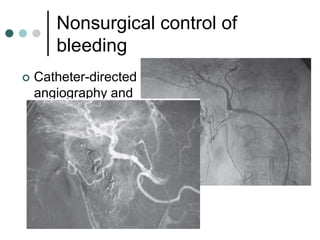
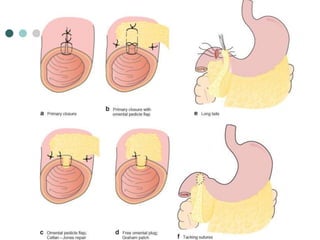
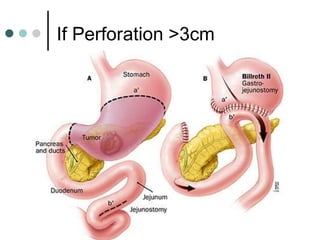
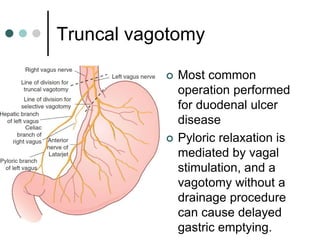
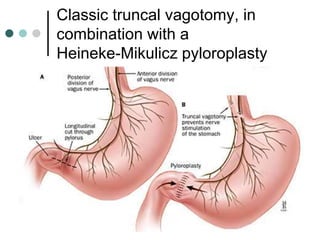
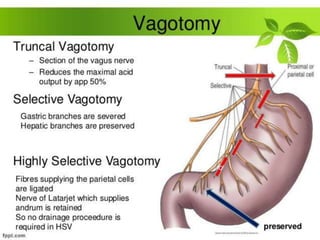
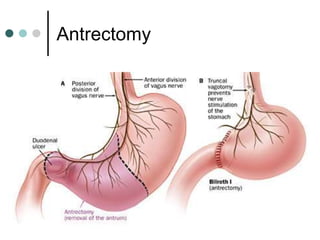
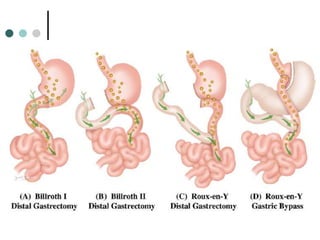
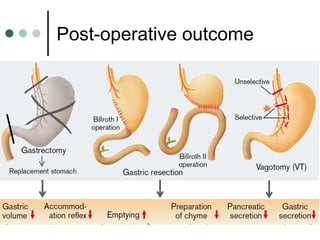
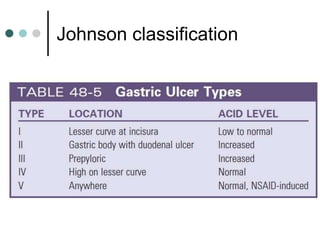
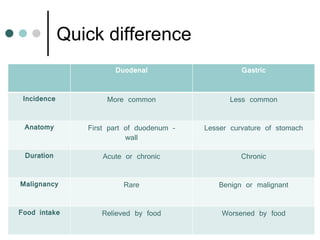
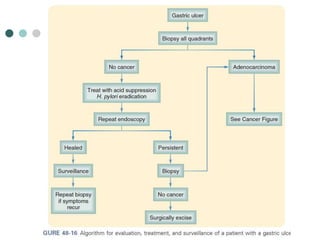
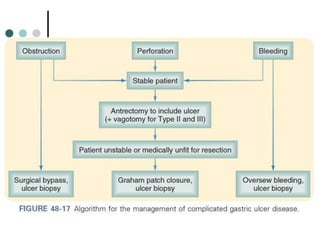
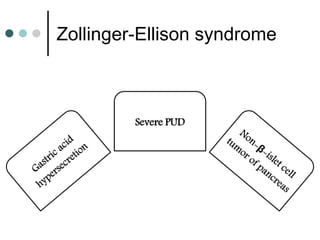
Peptic ulcer disease is defined as erosions in the gastric or duodenal mucosa that extend through the muscularis mucosae. Lifetime prevalence of peptic ulcer disease is 10% of Americans. Common causes include H. pylori infection, NSAID use, smoking, and alcohol consumption. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, upper endoscopy with biopsy, and tests for H. pylori. Treatment focuses on eradicating H. pylori, reducing acid with PPIs, and lifestyle changes. Complications include bleeding, perforation, and gastric outlet obstruction.