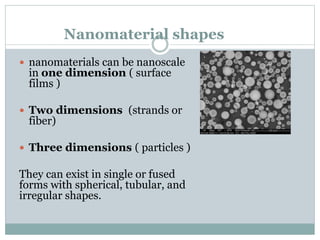
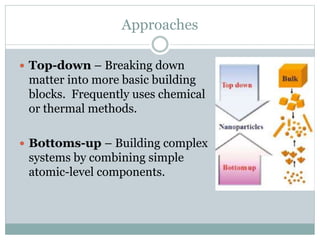
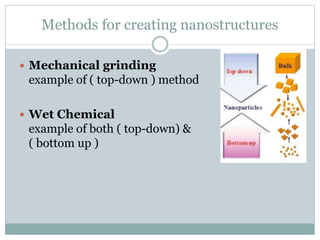
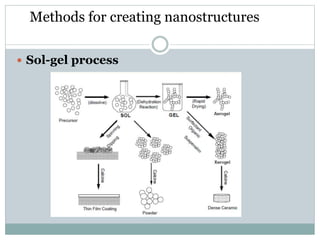
Nanomaterials are defined as materials with at least one dimension less than 100 nanometers, exhibiting unique properties such as high surface area and reactivity. They have diverse applications in fields like energy, electronics, and optics, offering advantages over bulk materials, including improved efficiency and tailored properties. However, concerns about health risks and manufacturing complexities pose challenges for their widespread use.