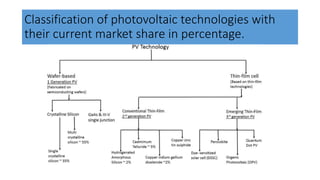
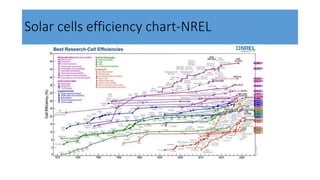
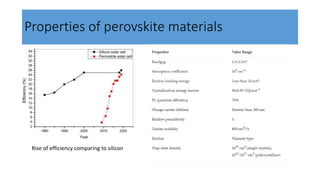
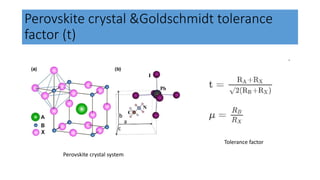
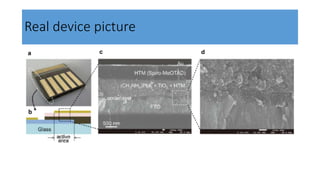
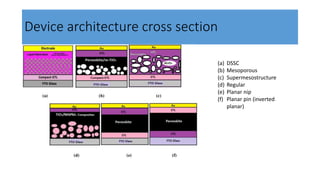
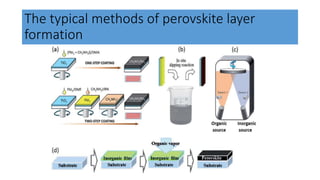
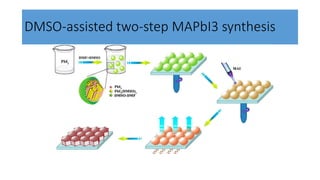
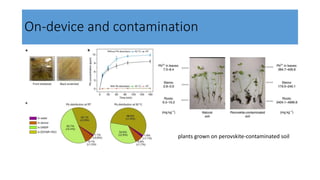
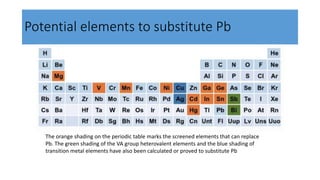
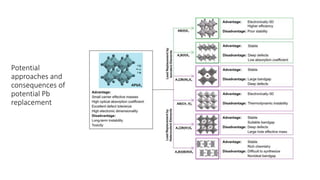
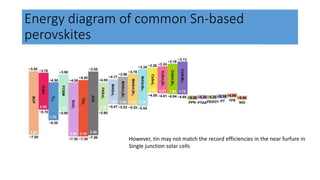
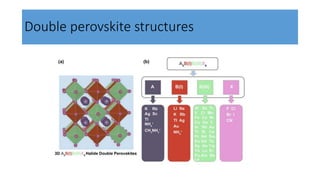
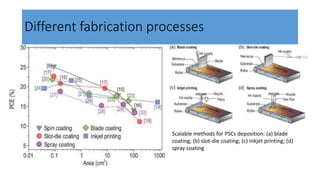
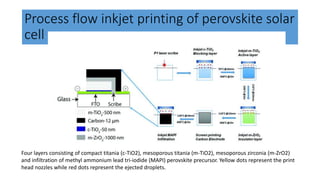
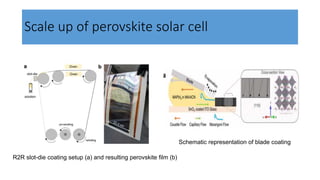
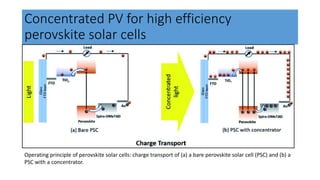
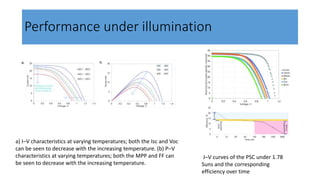
This document discusses perovskite solar cells. It begins with an overview of different photovoltaic technologies and efficiency charts. It then discusses the properties of perovskite materials and various device architectures for perovskite solar cells. The document outlines fabrication methods for perovskite solar cells, including potential replacements for lead and printed or roll-to-roll approaches. It concludes with a discussion of the commercialization potential and future outlook of perovskite solar cells.