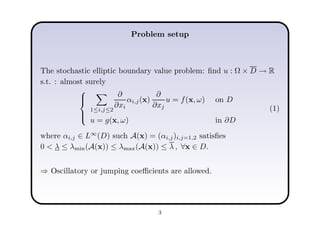
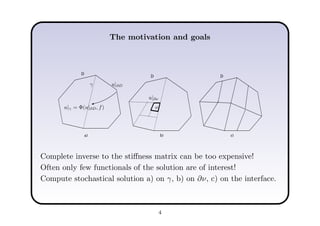
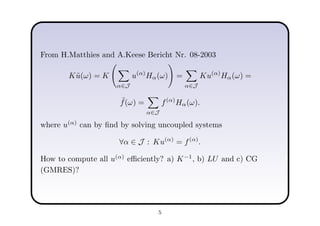
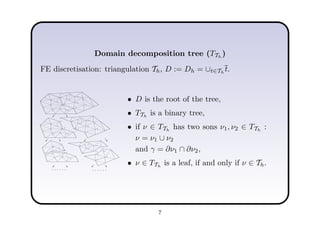
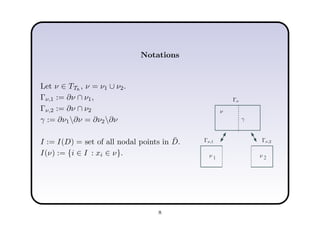
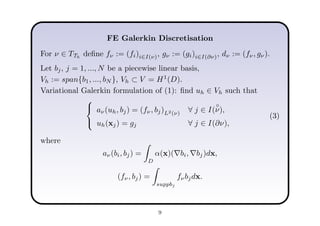
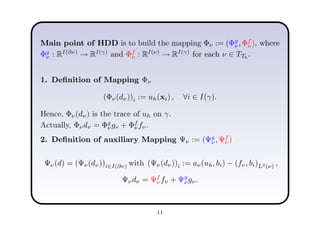
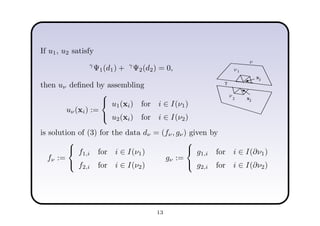
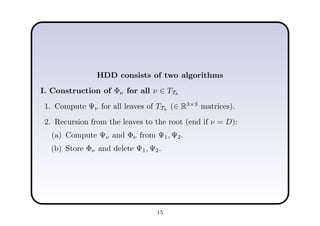
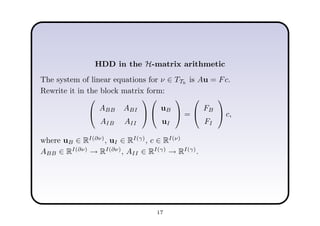
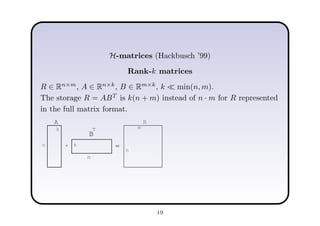
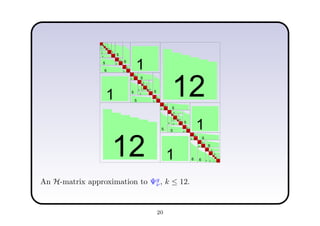
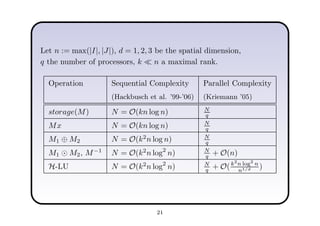
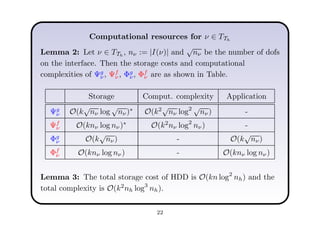
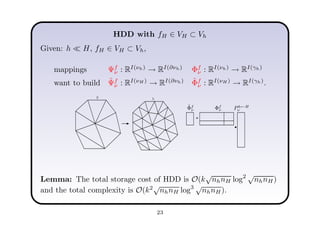
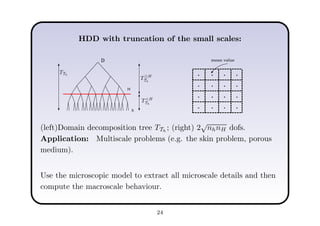
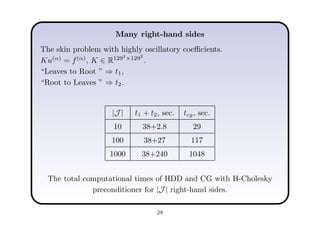
This document describes a hierarchical domain decomposition (HDD) method for solving stochastic elliptic boundary value problems with oscillatory or jumping coefficients. HDD constructs mappings between boundary and interface values that allow the solution to be computed locally in each subdomain. These mappings are represented as H-matrices to reduce computational costs. The total storage cost of HDD is O(kn log2nh) and complexity is O(k2nh log3nh), where n is the number of degrees of freedom, k is the H-matrix rank, and h is the mesh size. HDD can also be used to compute solutions when the right-hand side is represented on a coarser grid.