This document discusses characteristics and types of mutations, as well as the molecular basis and mechanisms of mutation. Some key points:
1. Mutations are generally recessive and harmful, but a small proportion are beneficial. They are random and recurrent events. Induced mutations often show pleiotropic effects.
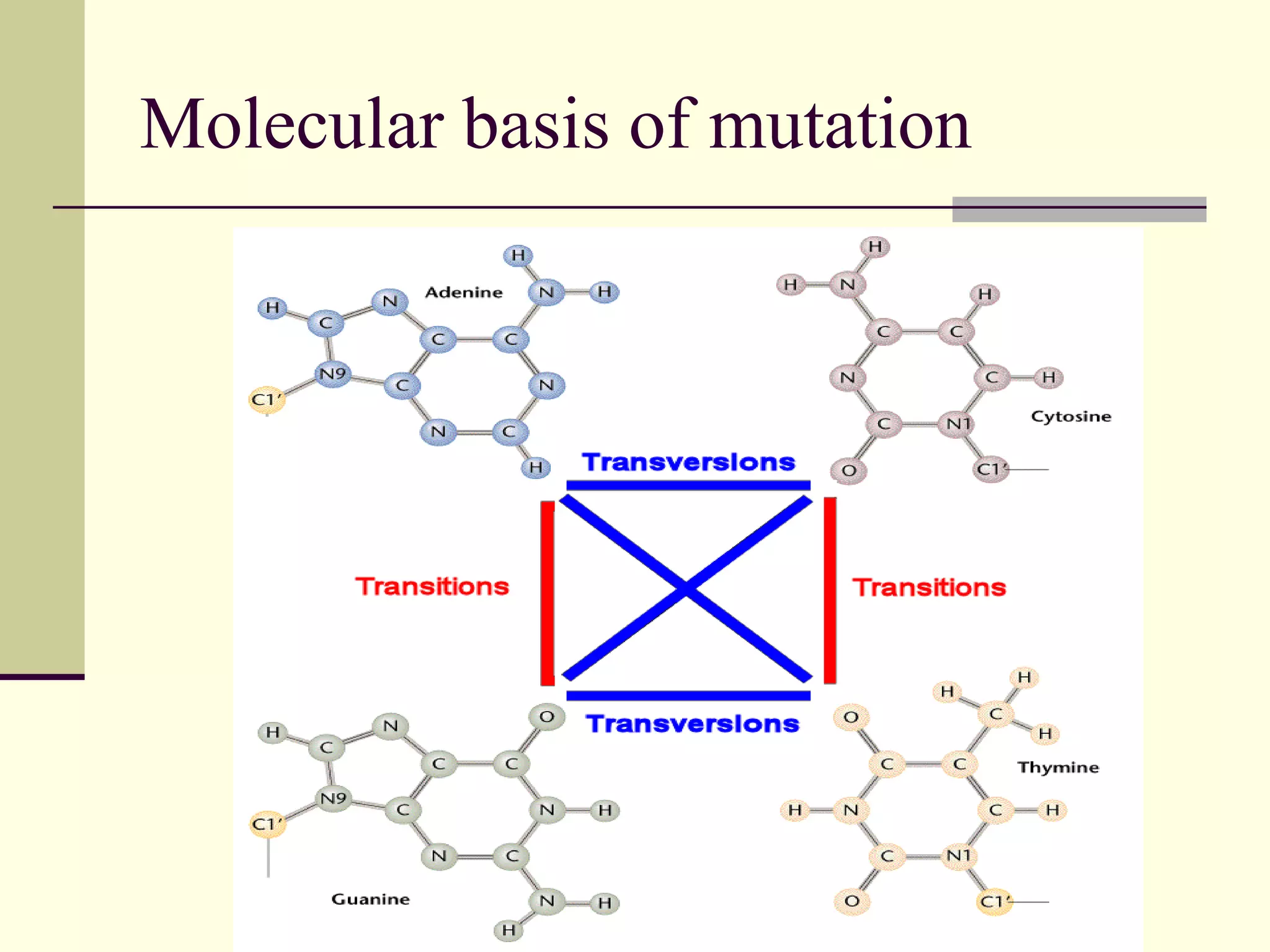
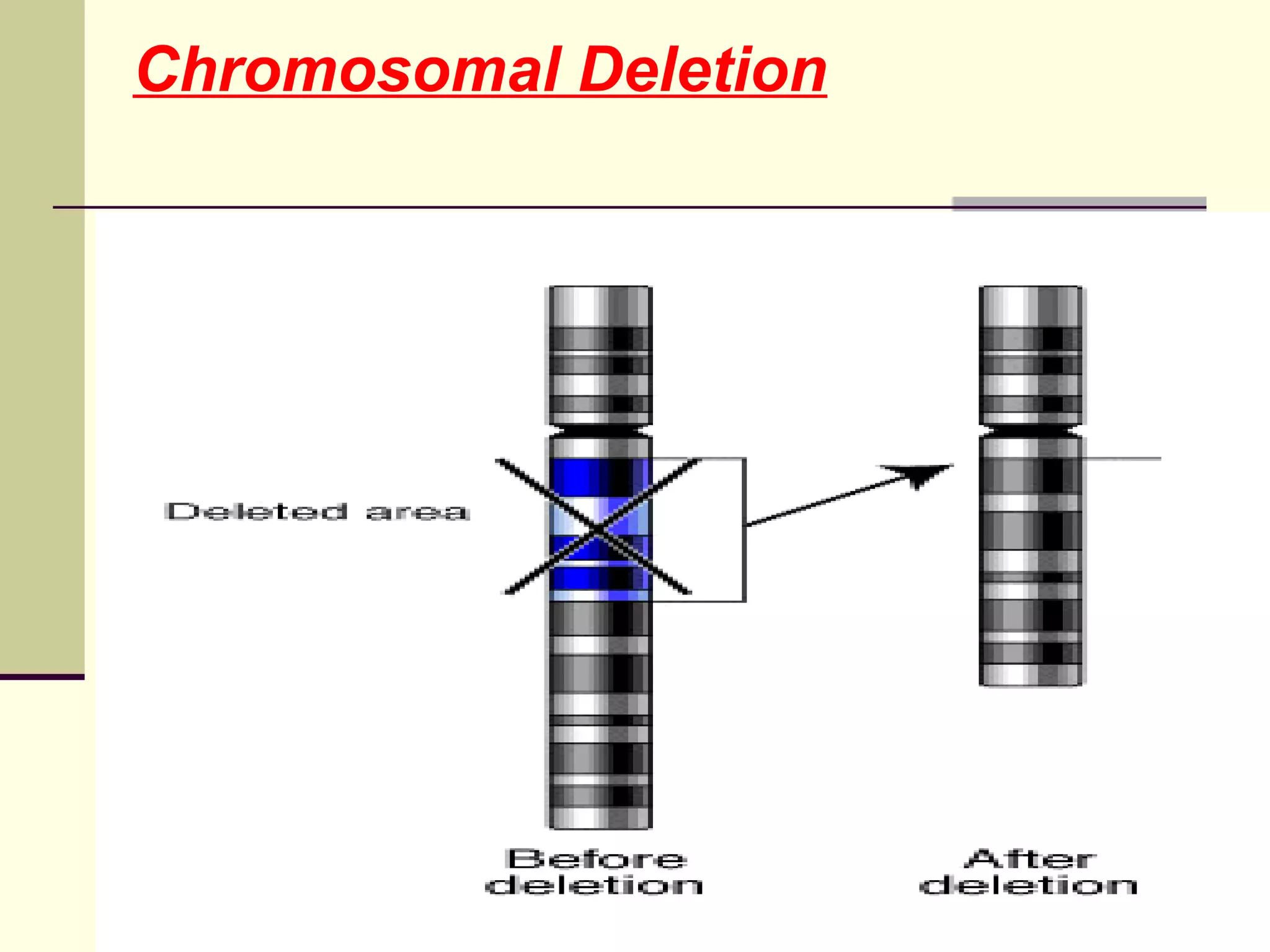
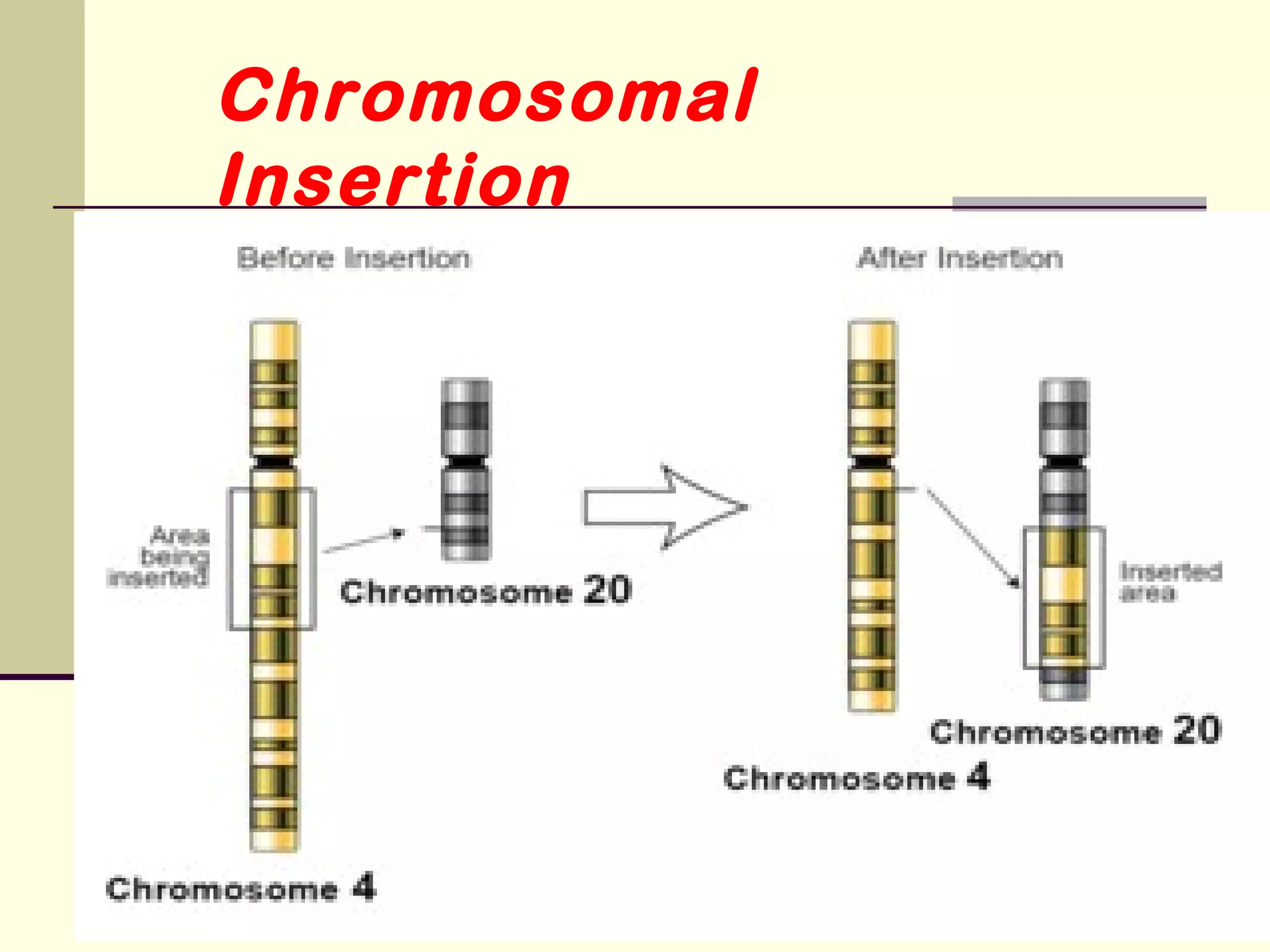
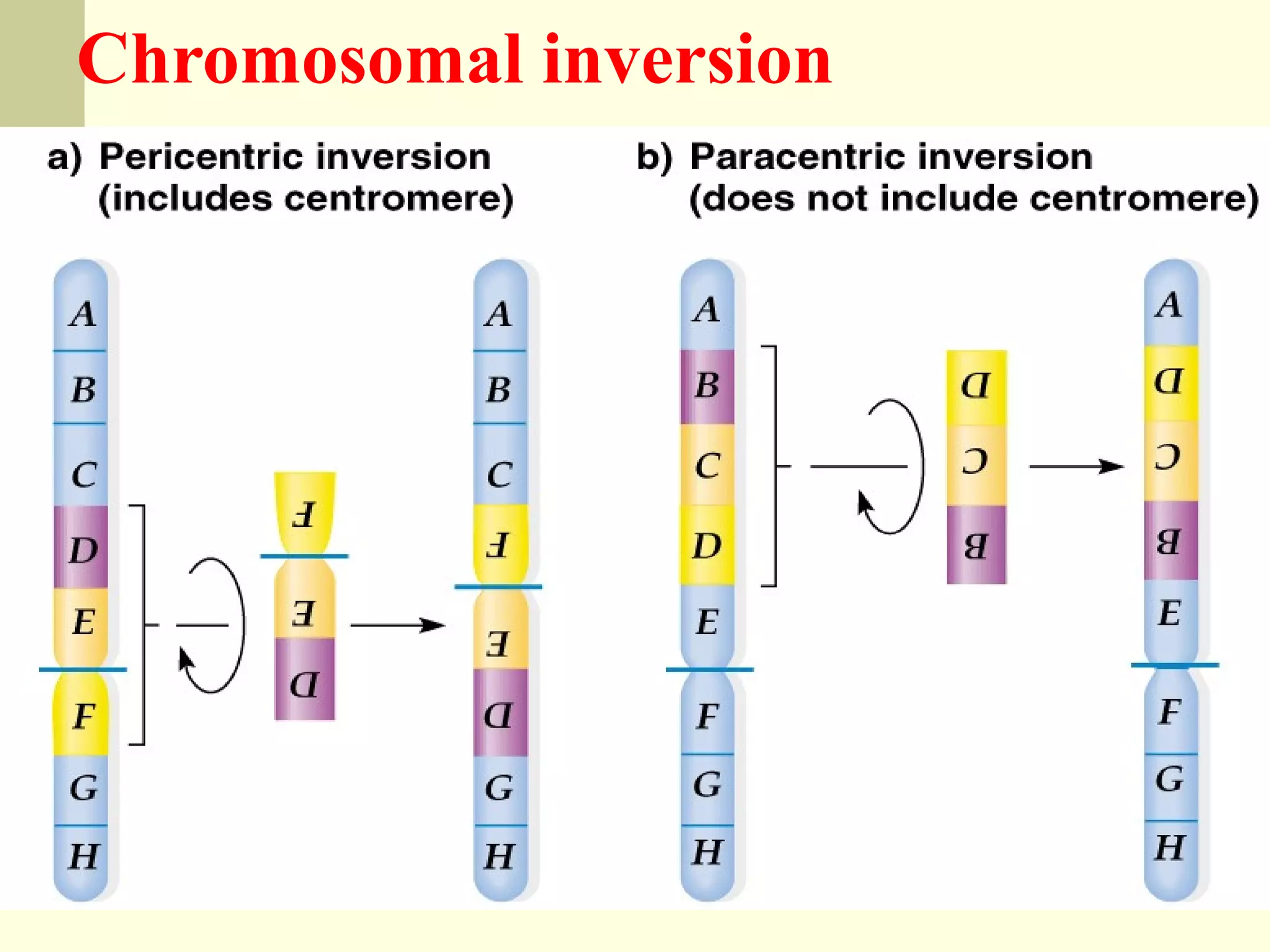
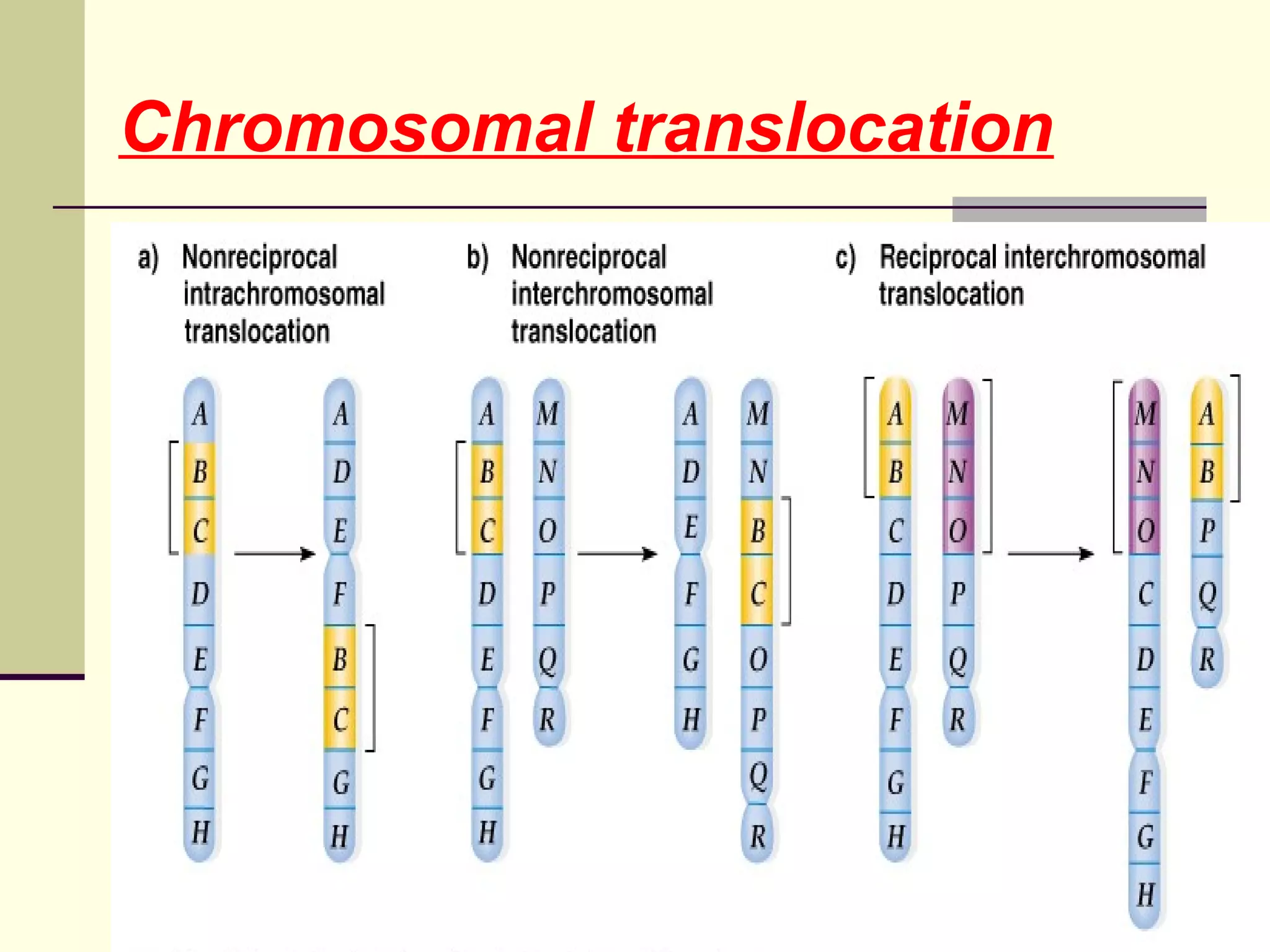
2. Types of mutations include point mutations, chromosomal mutations, and cytoplasmic mutations. Chromosomal mutations involve changes in structure like deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations.
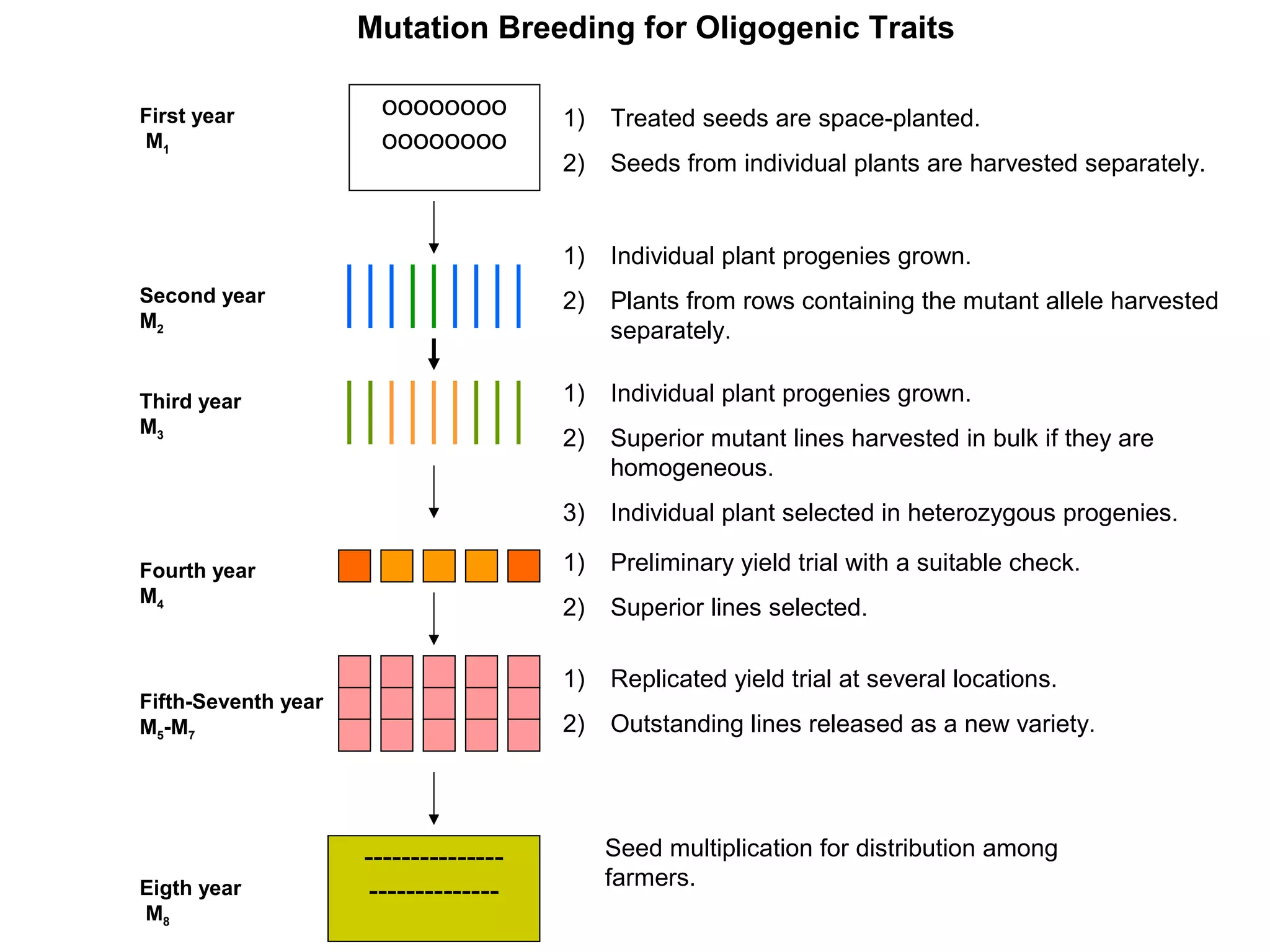
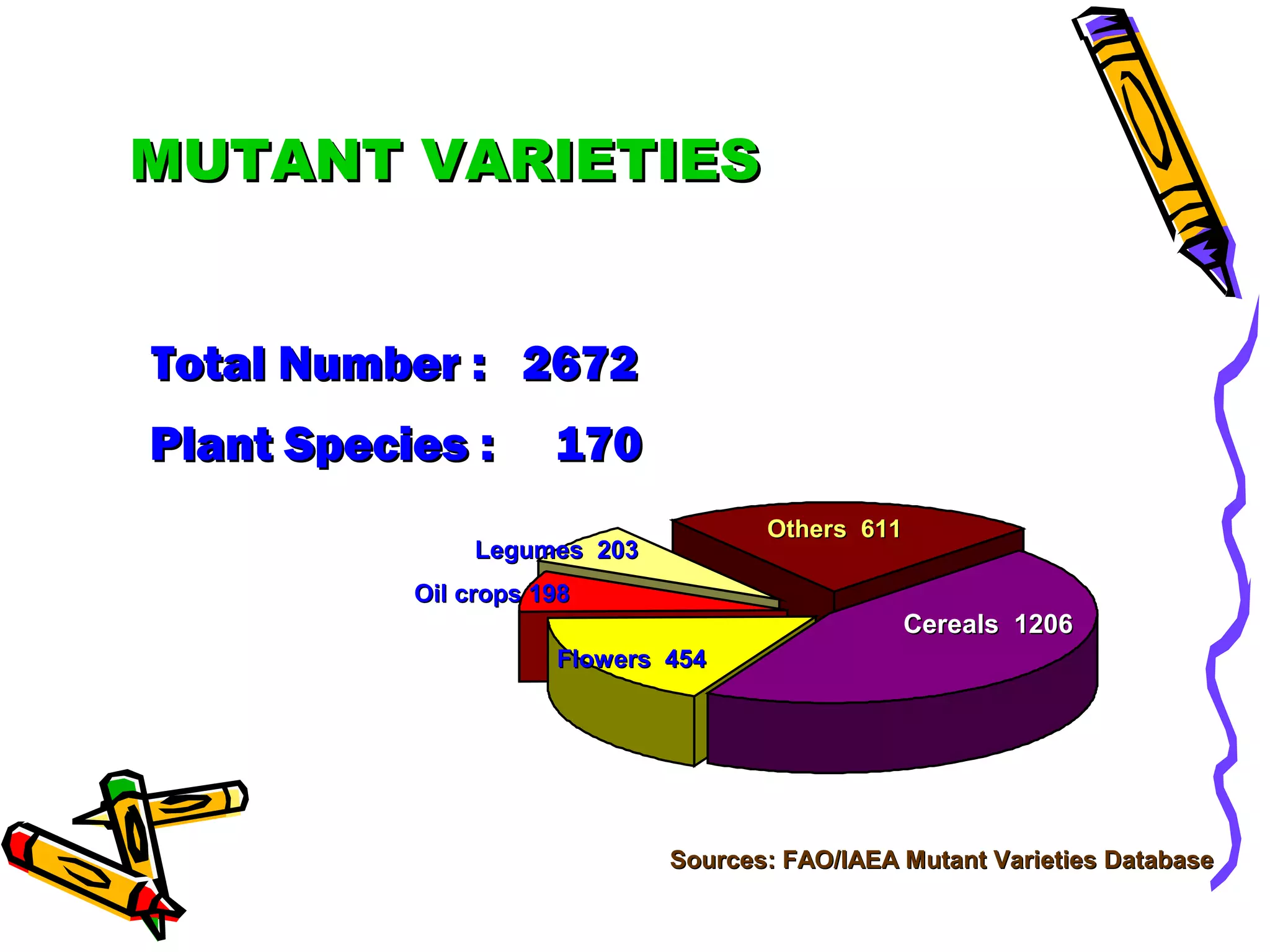
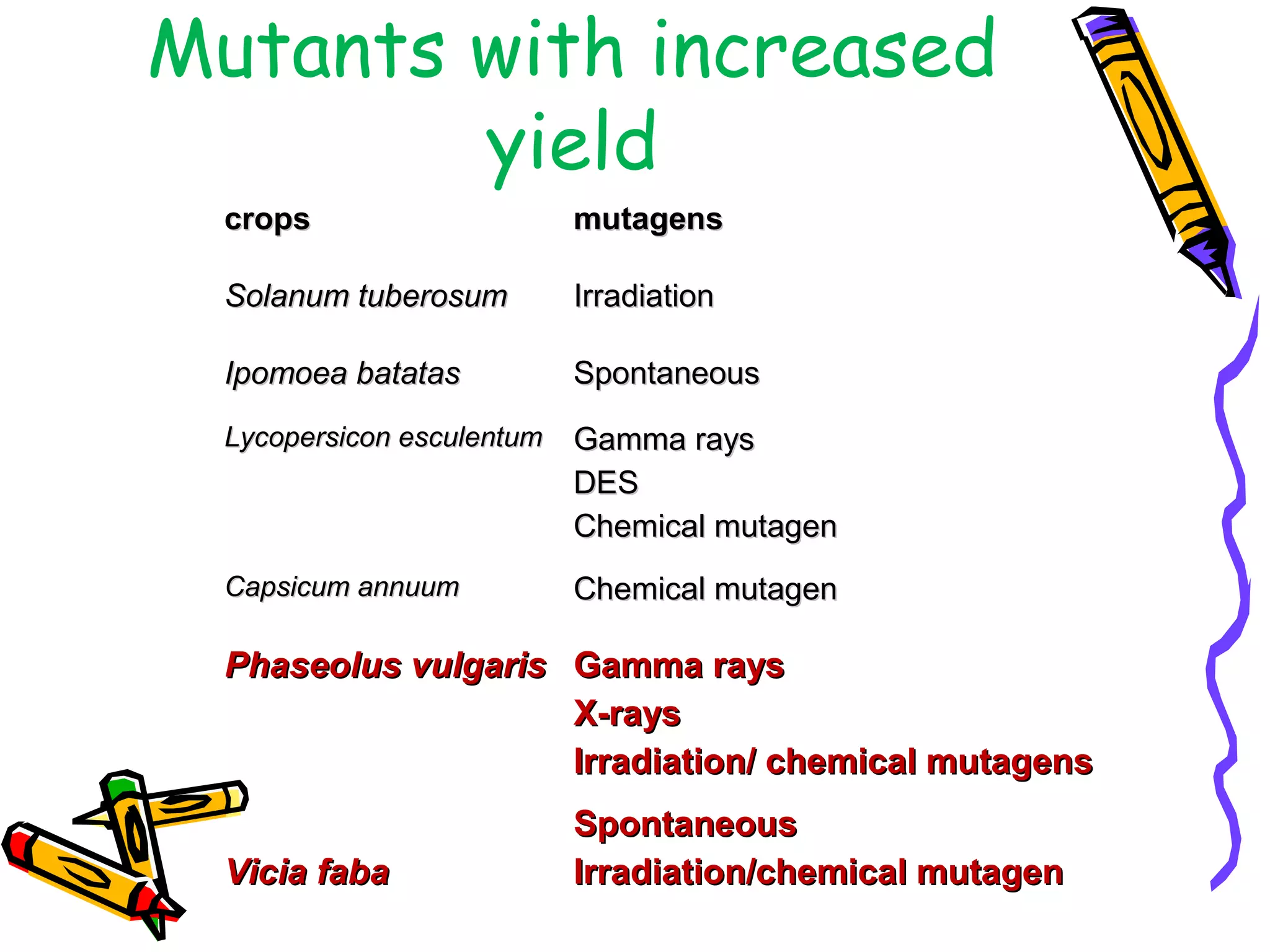
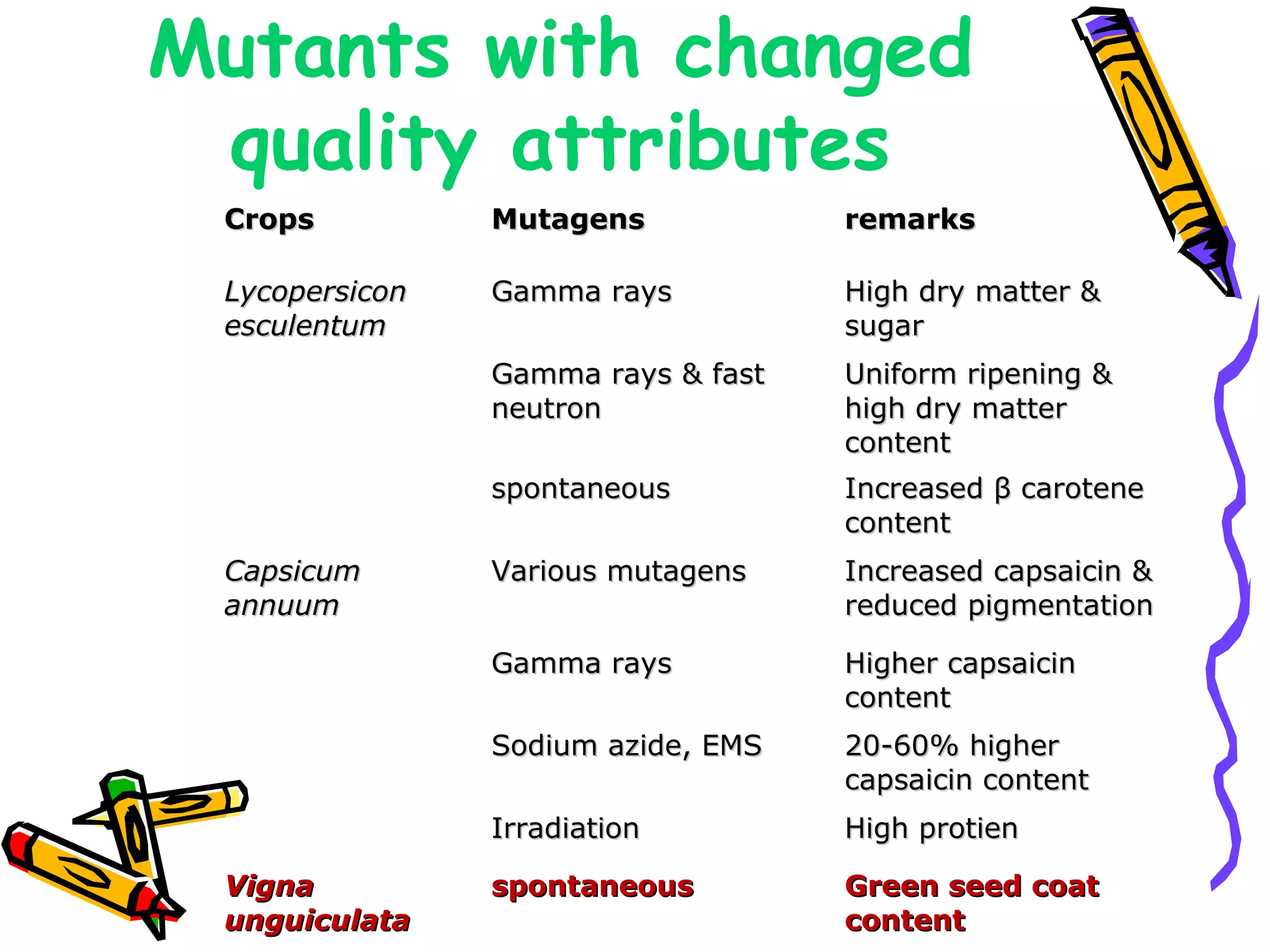
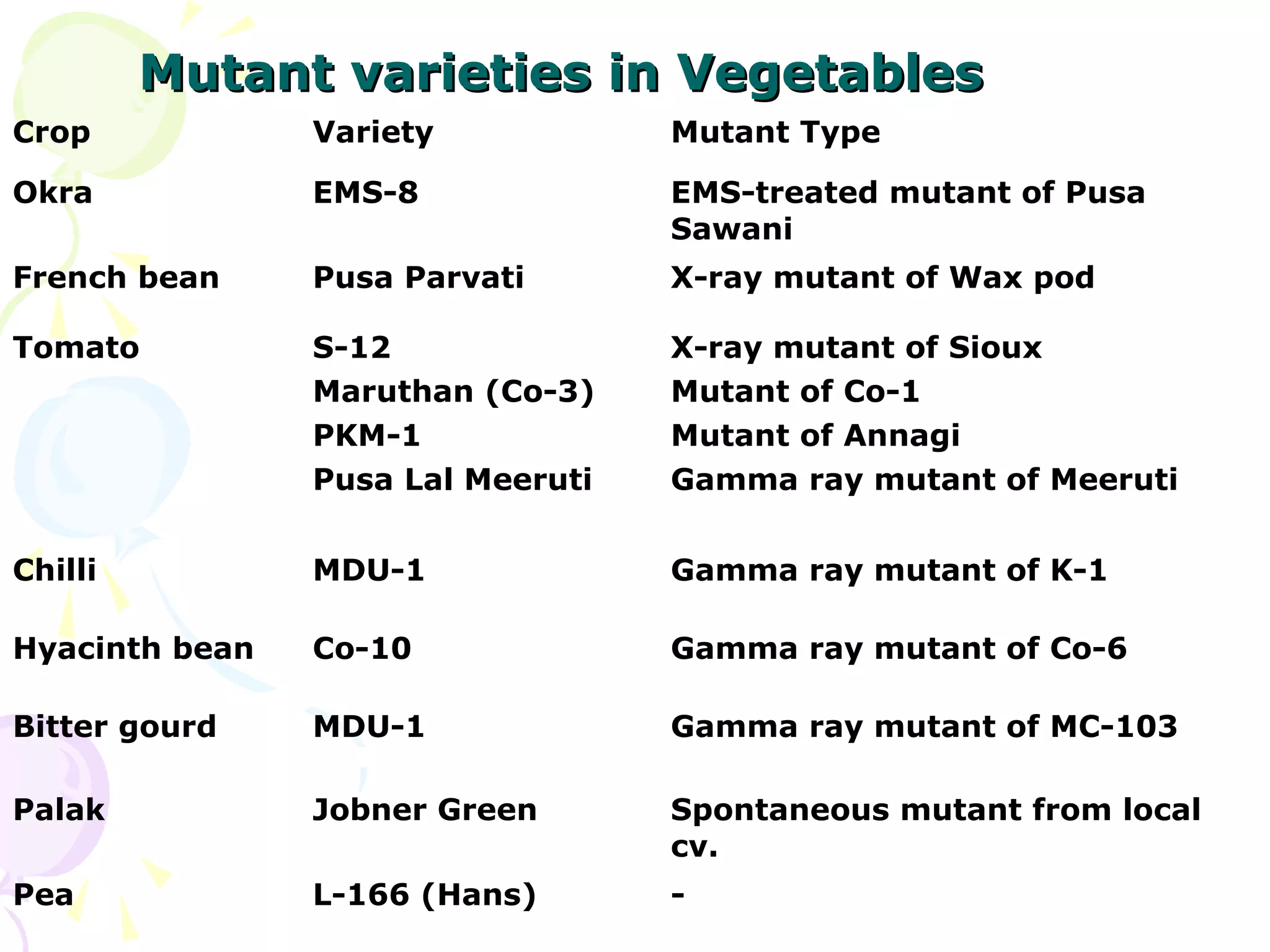
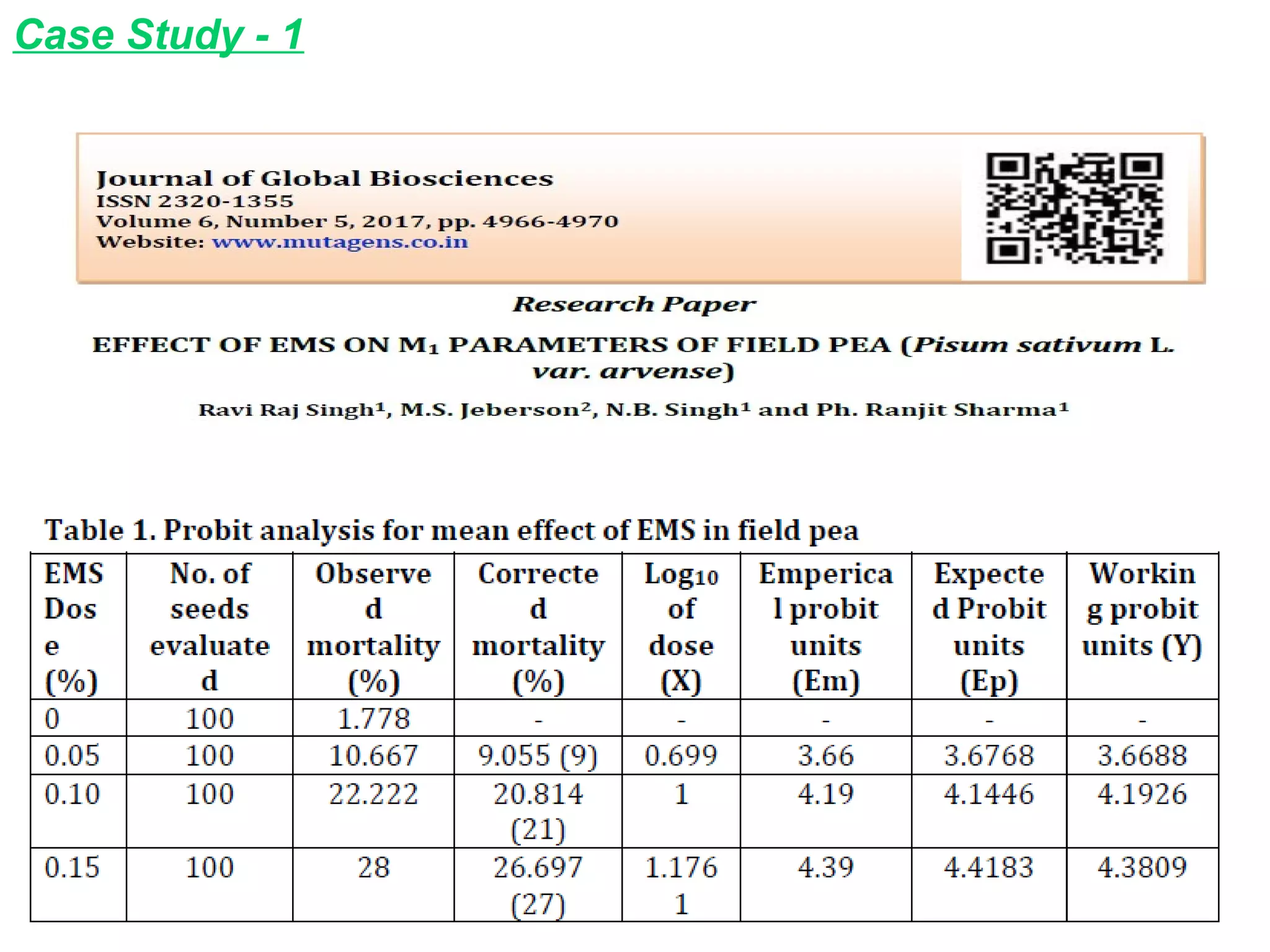
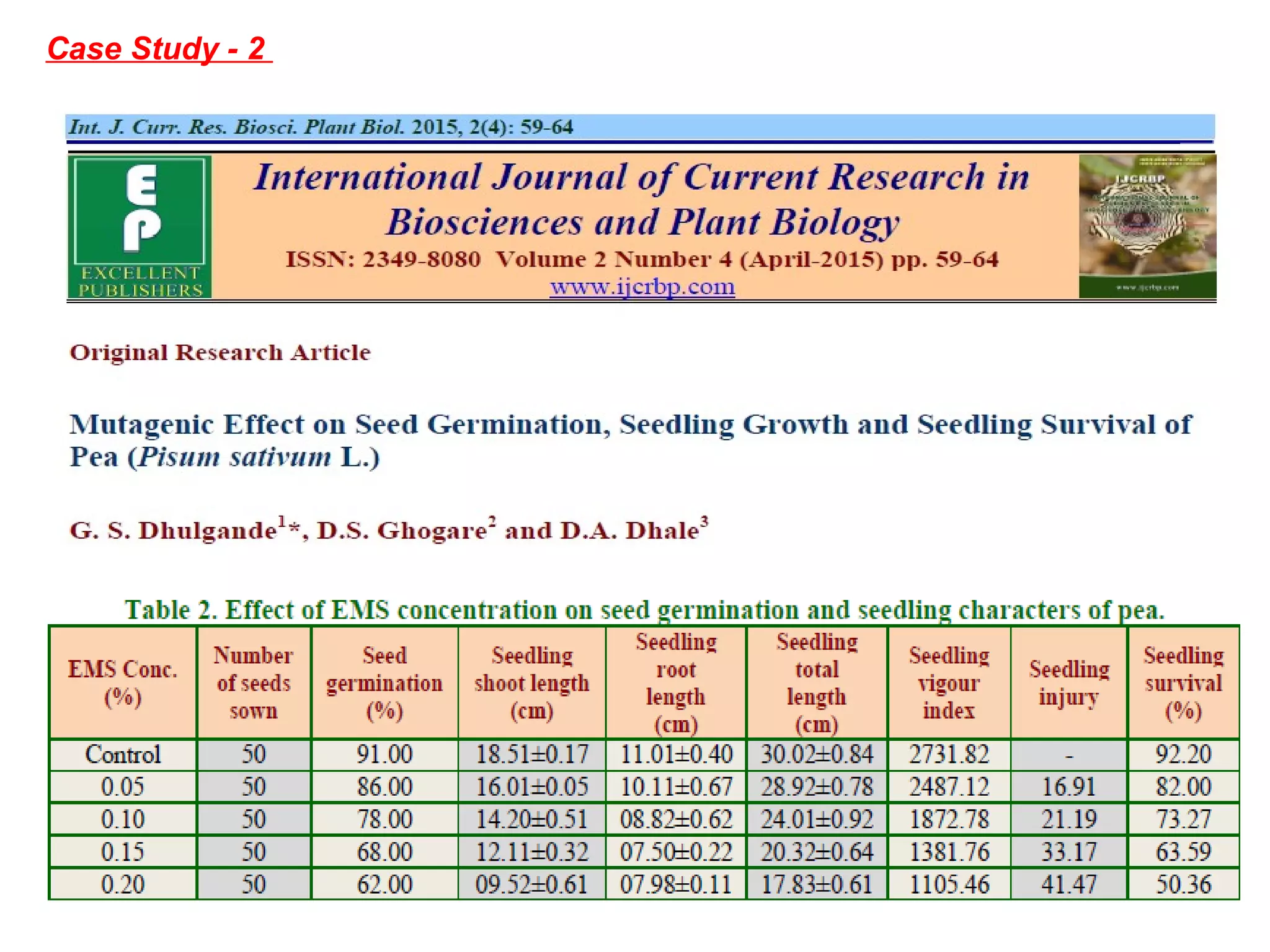
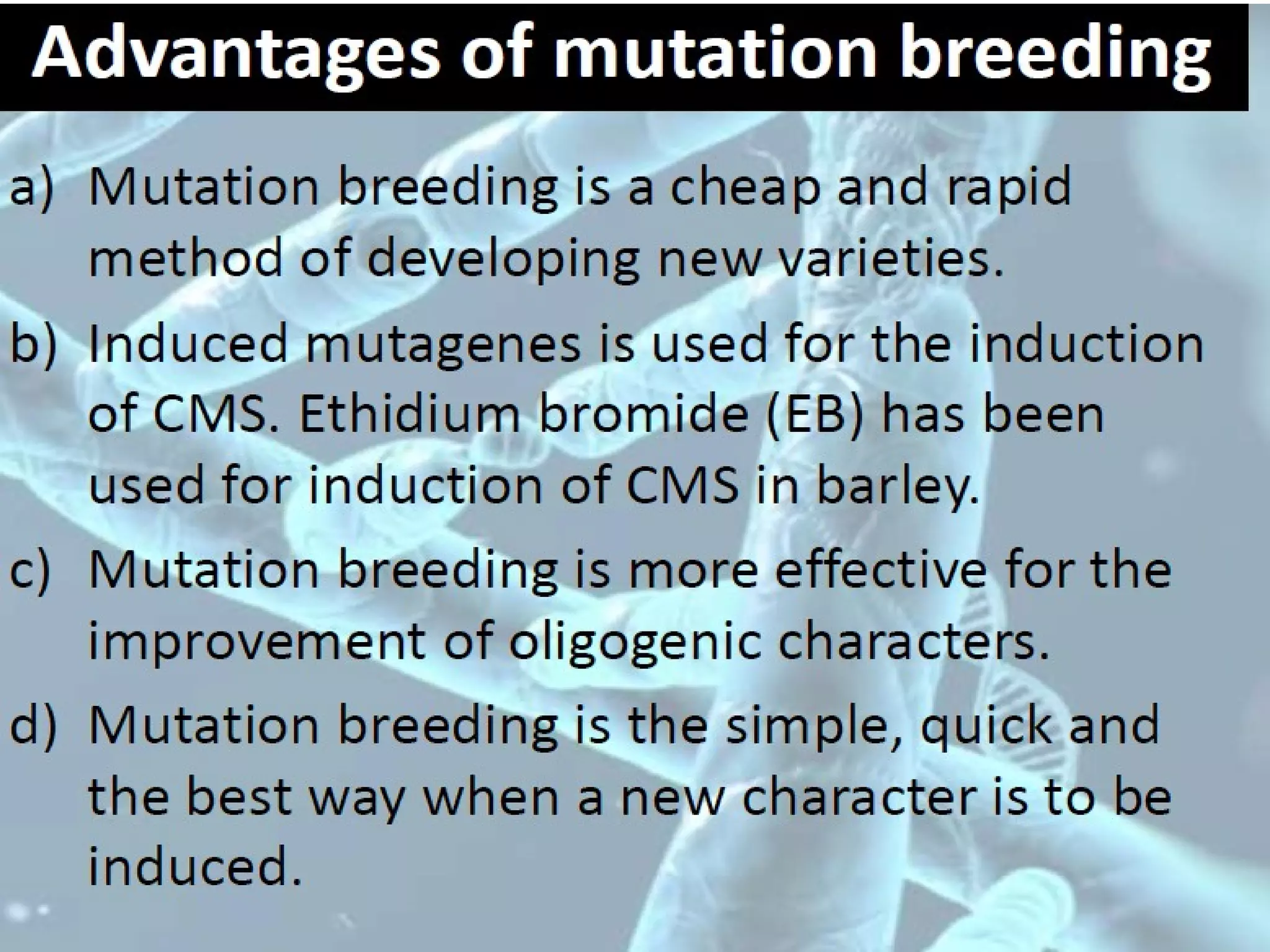
3. Mutation breeding techniques have been used to develop mutants with desirable traits like increased yield, disease resistance, or altered quality attributes in many crop species. Over 2,600 mutant varieties have been developed globally across