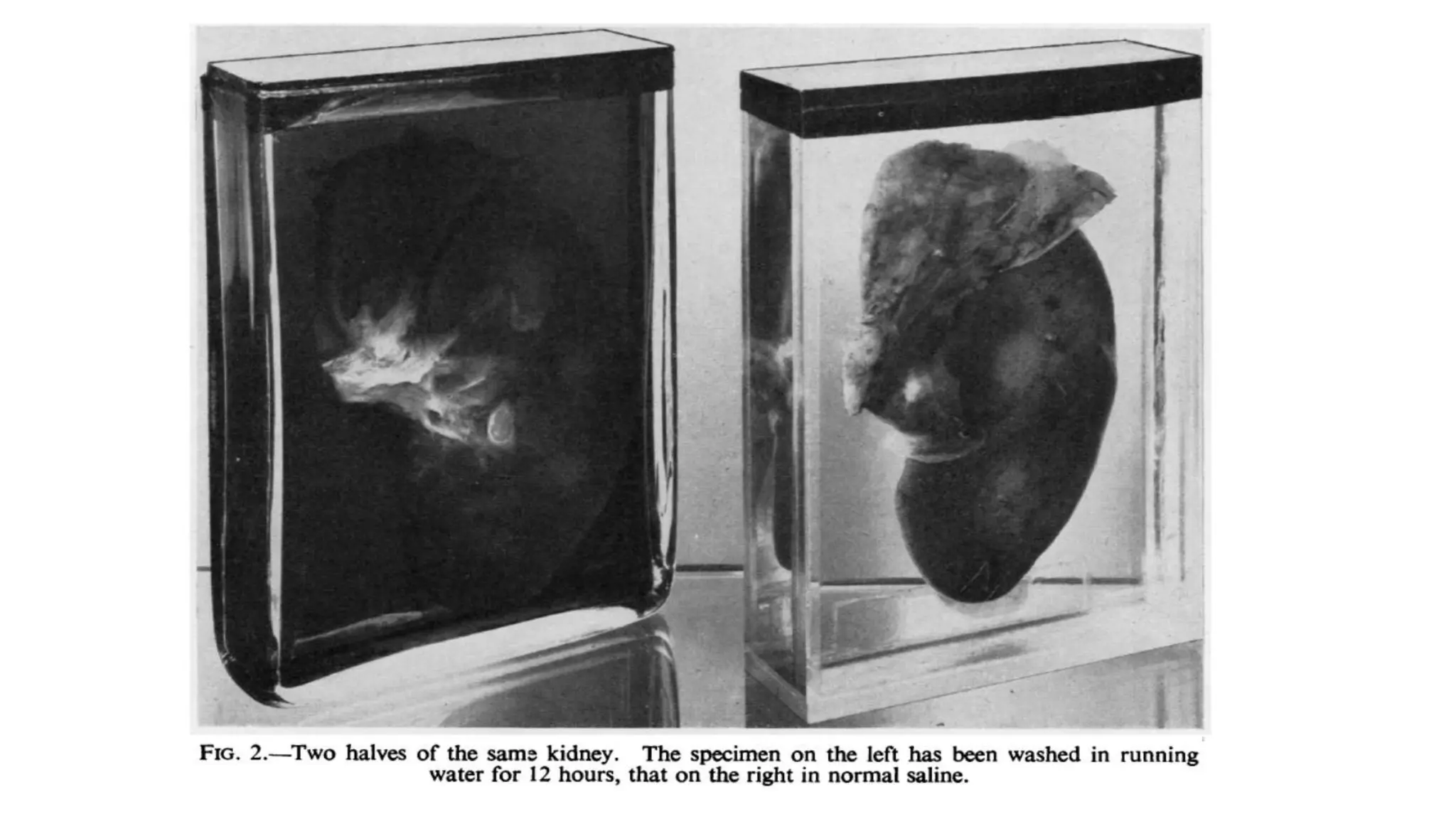
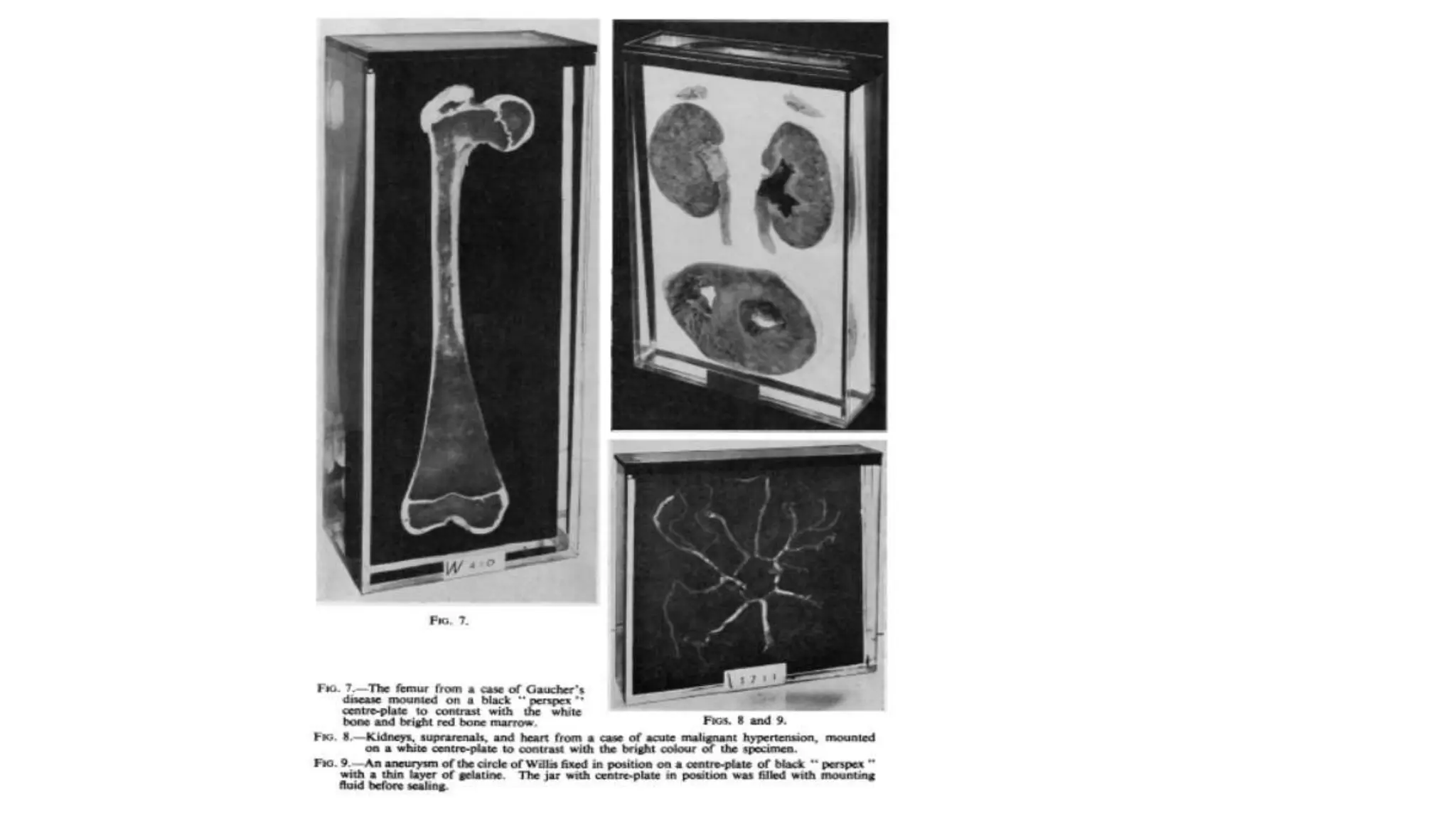
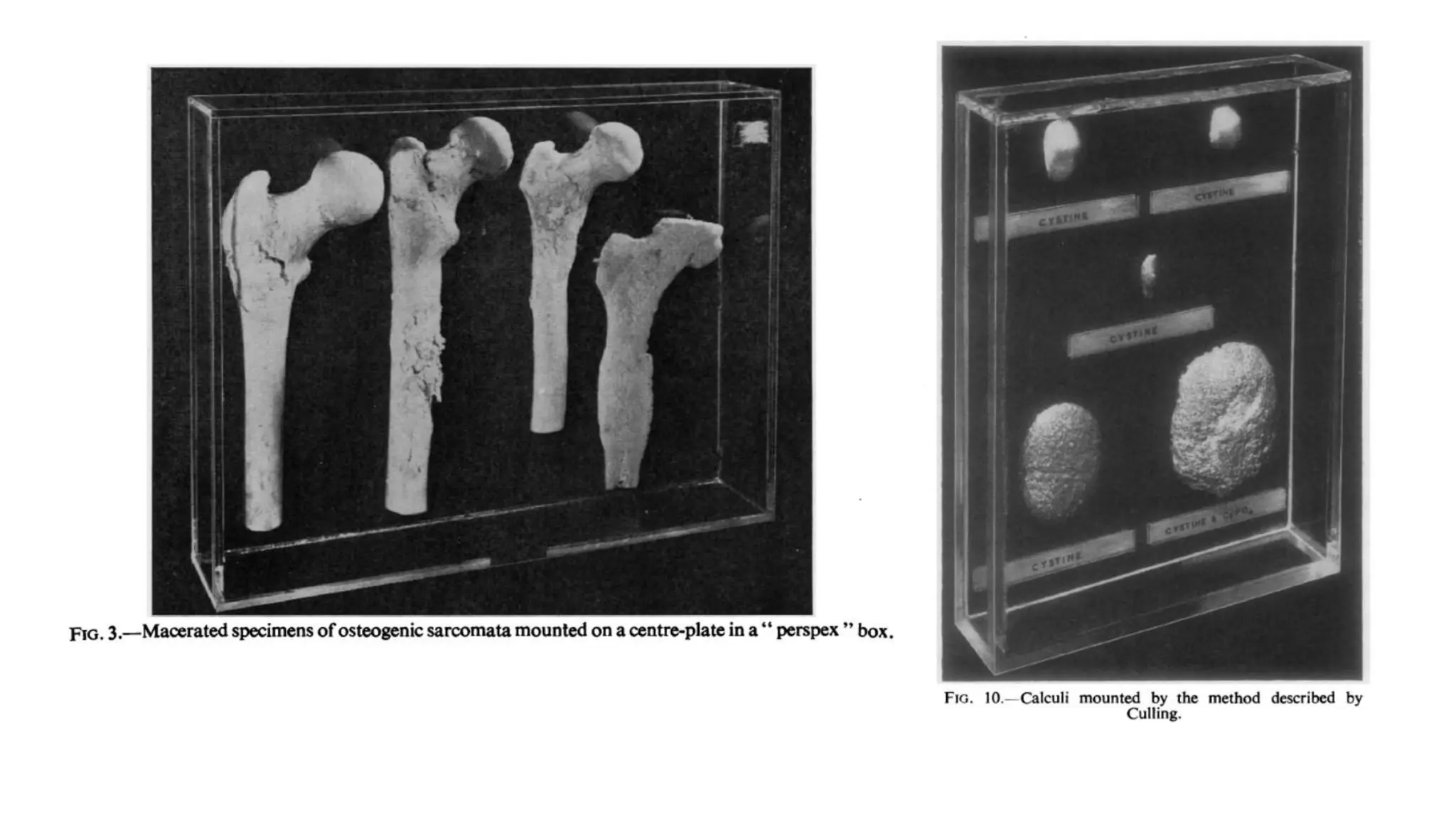
This document describes techniques for preparing and preserving pathological specimens for museum collections. It discusses receiving specimens from hospitals and laboratories, preparing them by washing in saline and fixing in formalin-based solutions, restoring color using alcohol, and long-term preservation by mounting in glycerin-based solutions. Special techniques are described for hollow organs, maceration of bone specimens, and labeling and cataloging finished museum pieces. The goal is to preserve tissue in a life-like state for teaching and research over long periods of time.