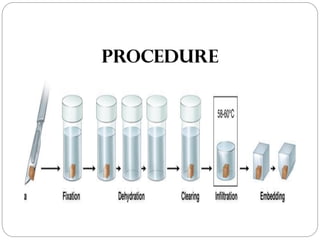
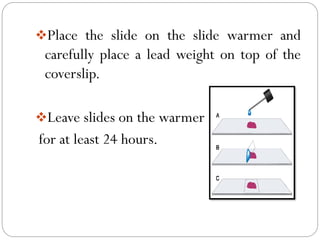
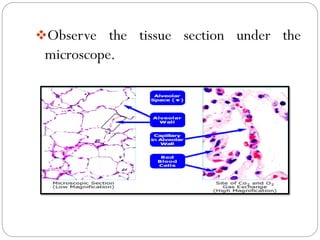
Histology techniques involve permanently mounting tissue specimens on slides for microscopic examination. There are two main types of mounting media: resinous and aqueous. Resinous media are hydrophobic and adhesive, using solvents like benzene to harden. They are most commonly used. Aqueous media are hydrophilic and non-adhesive, using water-based solutions. When preparing slides, mounting media is applied before lowering a coverslip onto the specimen to avoid bubbles and allowing it to harden under warmth. Permanent mounting preserves tissue samples for long-term examination.