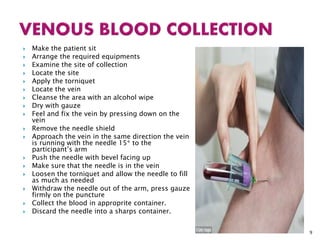
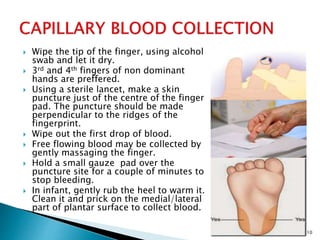
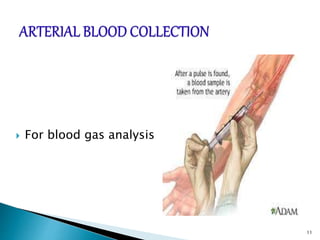
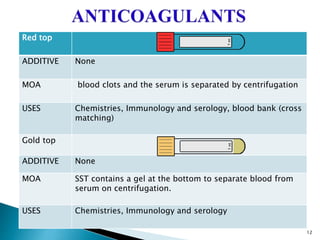
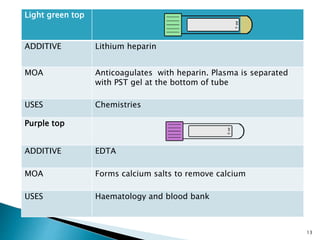
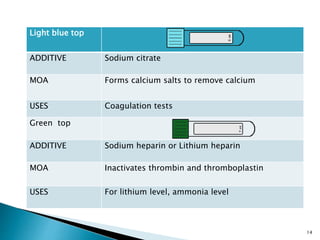
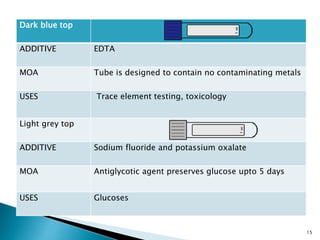
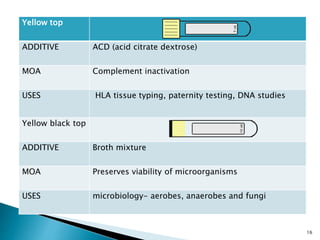
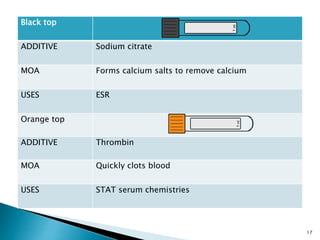
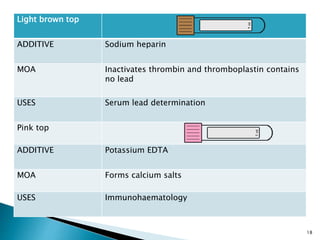
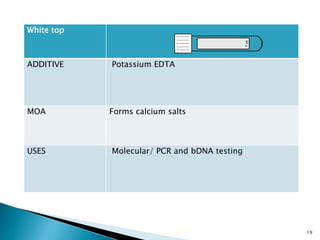
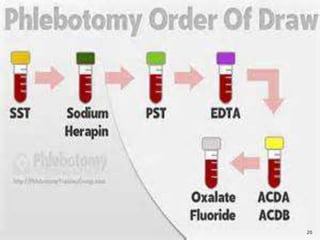
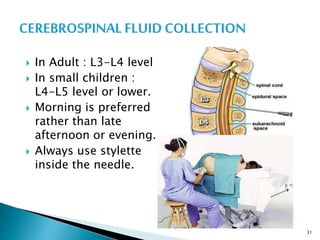
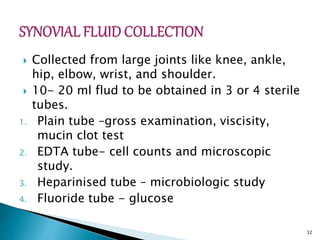
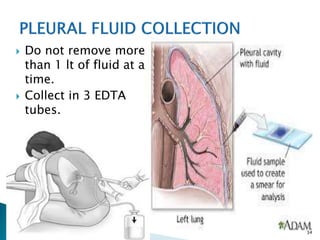
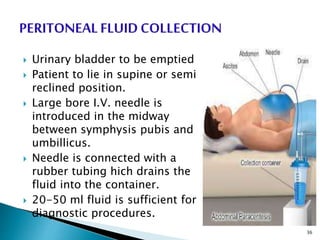
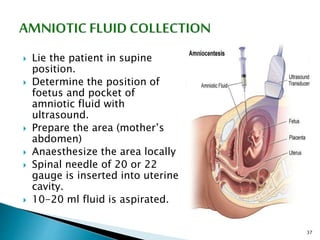
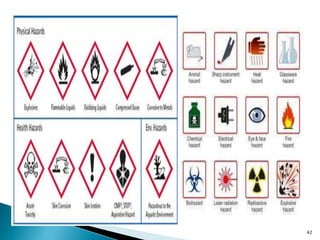
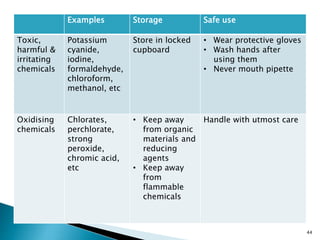
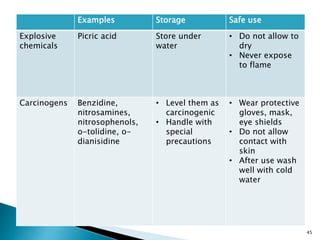
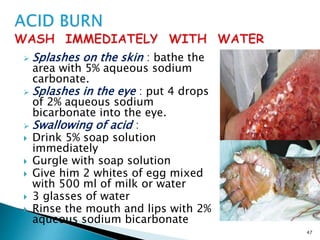
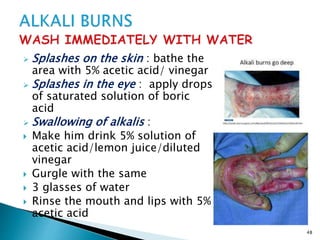
This document provides an overview of laboratory procedures for collecting and handling various clinical specimens. It discusses the appropriate collection containers, requirements, and procedures for collecting blood, urine, stool, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, and other specimens. Specific topics covered include blood collection by venipuncture and fingerstick, urine collection and testing parameters, stool collection for culture and ova/parasite examination, and safety practices for handling hazardous materials in the laboratory.