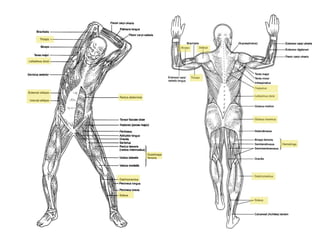
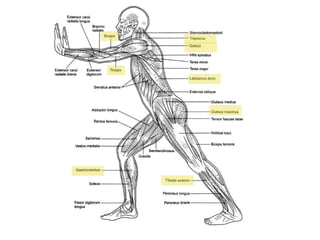
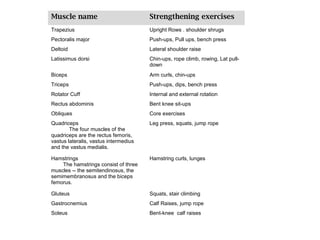
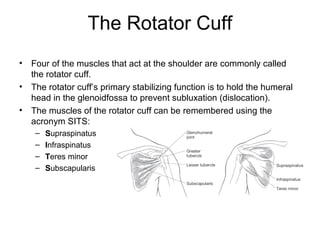
The document discusses the muscular system and provides information about specific muscles. It notes that there are three types of muscular tissue - smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle. It then focuses on skeletal muscle, stating there are over 600 muscles in the body but the class will learn just a few. The rest of the document lists important muscles like the trapezius, pectoralis major, and deltoid. It provides strengthening exercises for each and describes muscles groups like the quadriceps, hamstrings, gluteus, and rotator cuff.