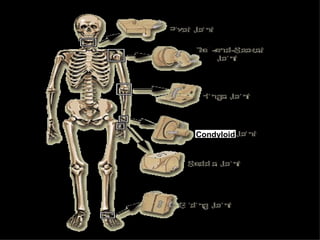
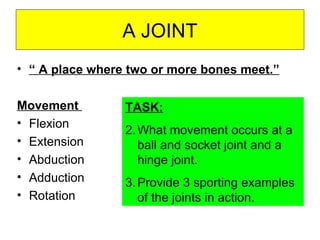
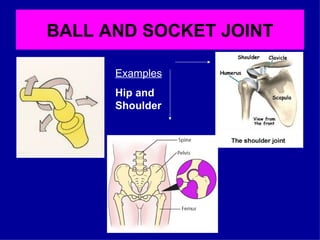
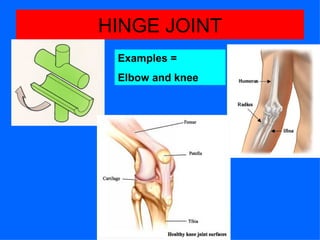
The document provides instructions for a homework assignment on the skeletal system. Students are asked to identify 10 bones of the skeleton from head to toe, circle joints on a labelled skeleton, and define the 6 types of freely moveable joints. For each joint type, examples of sporting movements are requested. Definitions are also requested for different types of movements at joints like flexion, extension, and rotation. The parts of a synovial joint are defined, including cartilage, joint capsule, synovial membrane, synovial fluid, and ligament.