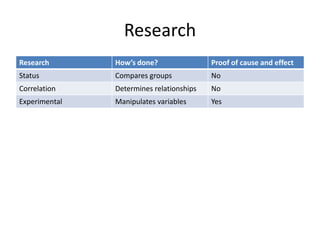
This chapter introduces sports physiology for coaches by defining key terms like anatomy, physiology, and sports physiology. It discusses how the body responds both immediately and long term to exercise through training stimuli. The chapter emphasizes that understanding sports physiology provides a foundation for developing effective athlete training programs and satisfying coaching success. It advises coaches to choose reliable sources for sports physiology information and favors experimental research.