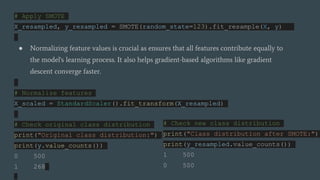
The document discusses improving diabetes prediction accuracy through machine learning and data analysis techniques, emphasizing the importance of early detection to prevent complications. It reviews various machine learning approaches, particularly ensemble learning methods like boosting and stacking, and highlights the significance of model interpretability for clinical utility. The findings indicate that enhanced data preprocessing, handling imbalanced datasets, and effective hyperparameter tuning can significantly improve model performance, while future work should focus on diversifying datasets and integrating models into clinical systems.







![Data Preprocessing
● Handling missing values
print("Null values in features")
print(data.isnull().sum())
(No Missing values found, so no samples removed/imputed)
● Splitting the dataset into features and target variables
# Separate features and target
X = data.drop('Outcome', axis=1)
y = data['Outcome']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mldiabetes-240725043734-a492966c/85/Diabetes-prediction-using-Machine-Leanring-and-Data-Preprocessing-techniques-8-320.jpg)