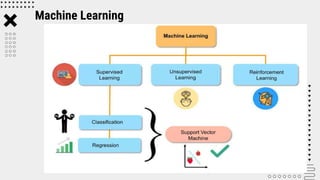
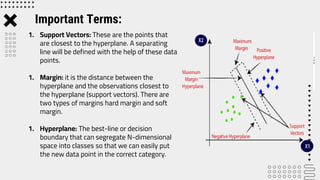
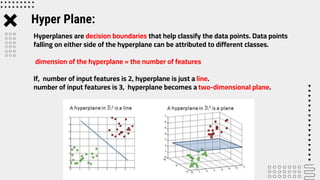
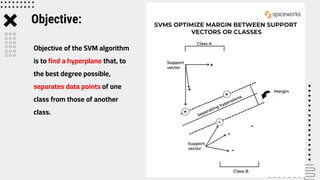
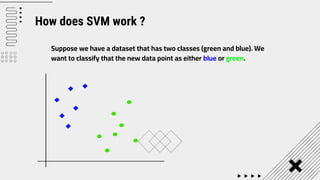
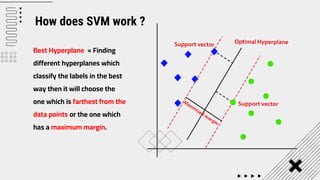
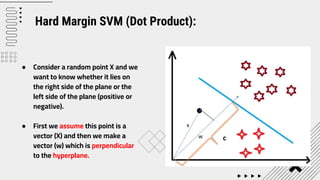
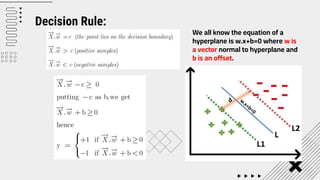
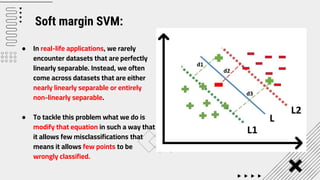
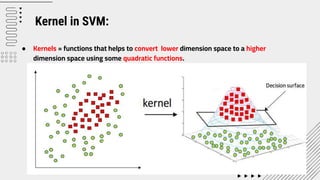
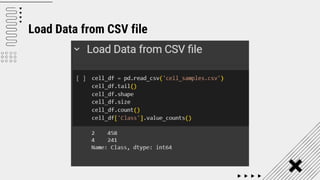
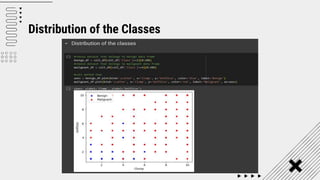
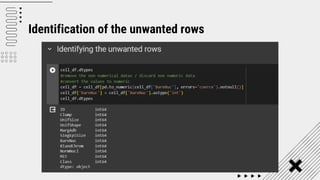
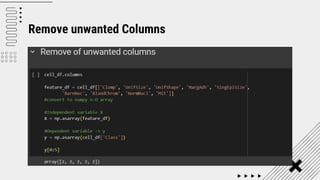
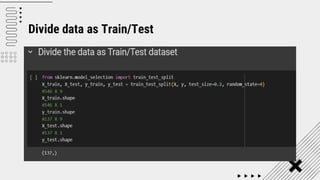
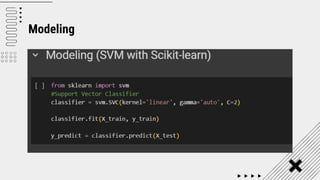
Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression analysis. It finds a hyperplane in an N-dimensional space that distinctly classifies data points. SVM is effective in high-dimensional spaces and with limited training data, and can perform nonlinear classification using kernel tricks. The objective is to find the hyperplane that has the largest distance to the nearest training data points of any class, since these are the hardest to classify correctly.