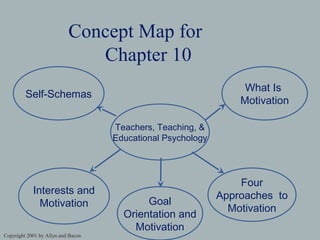
This chapter discusses motivation from multiple perspectives: behavioral, humanistic, cognitive, and sociocultural. It covers key topics like goal orientation, interests and emotions, and self-schemas. The chapter defines motivation and the differences between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. It also examines factors that influence motivation such as needs, attributions, self-efficacy, and beliefs about ability. The chapter provides guidance for teachers on applying motivation concepts in the classroom.