This document provides an overview of Medicare, including:
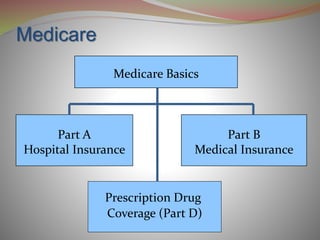
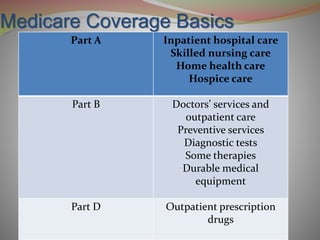
- Medicare has different parts (A, B, D) that provide different types of coverage such as hospital insurance, medical insurance, and prescription drug coverage.
- People qualify for Medicare if they are 65 or older, or under 65 with certain disabilities. It is administered by CMS.
- Medigap plans are private insurance policies that help cover gaps in Original Medicare costs. There are standardized Medigap plans A through L.
- Medicare Advantage plans are run by private insurers and provide Medicare benefits through HMOs, PPOs, and other plans.
- Medicaid provides additional coverage for some low-income individuals beyond what Medicare covers. Eligibility