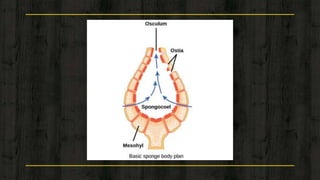
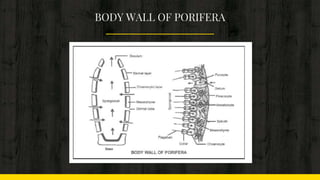
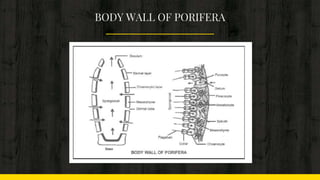
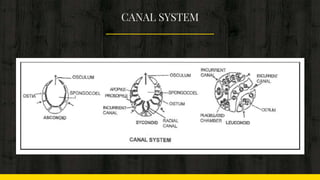
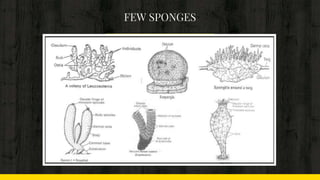
This document provides an introduction to the phylum Porifera, commonly known as sponges. It discusses their key features and cellular organization, including their canal system for circulation, skeleton structure, and asexual and sexual reproduction processes. The document also lists some important sponge organisms such as the largest known sponge, a hypothetical simple sponge, and a crustacean that shows commensalism with certain sponges.