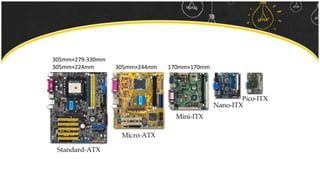
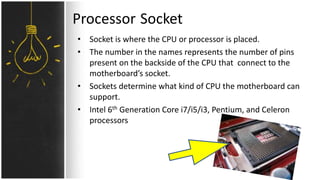
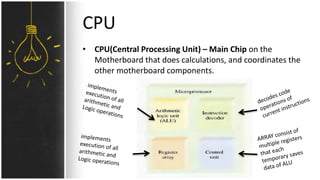
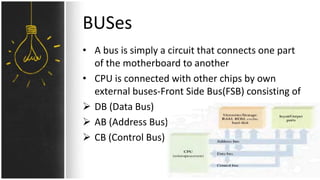
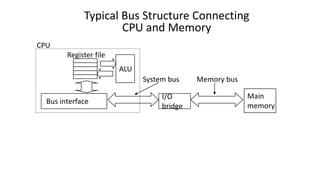
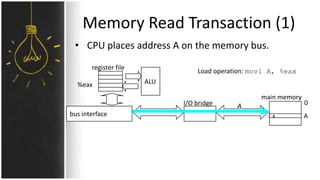
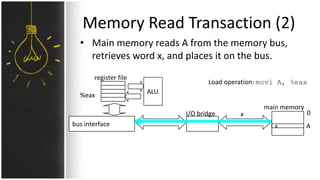
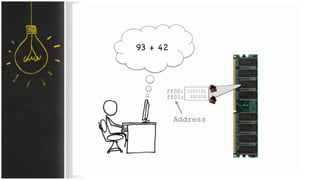
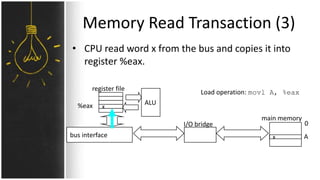
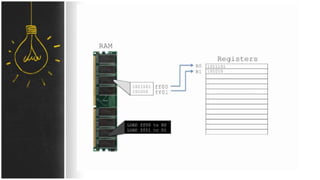
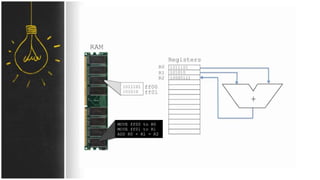
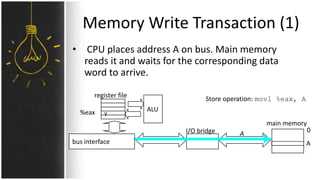
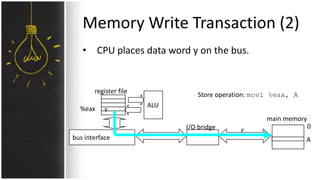
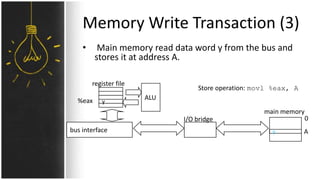
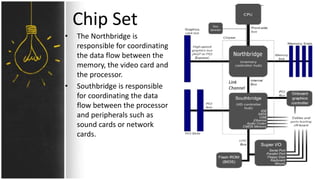
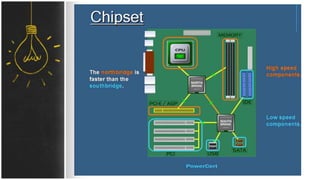
The motherboard connects and allows communication between all components of a computer. It has standardized dimensions and connectors defined by form factors like ATX. Key components include the CPU socket which determines supported processors, RAM slots for memory, expansion slots for graphics and storage, and chipsets which connect the CPU to other components. The motherboard uses buses to transfer data and instructions between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices.