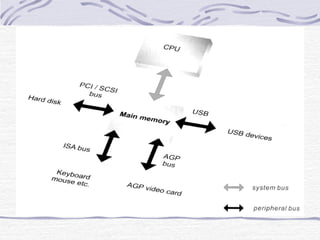
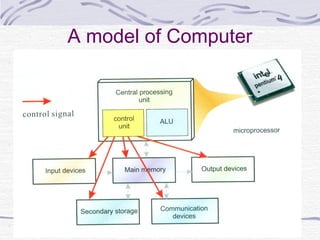
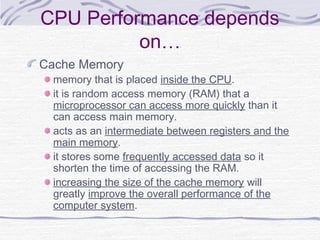
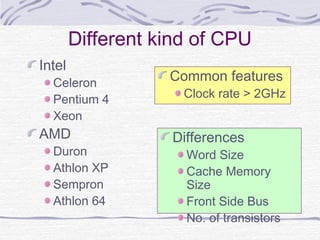
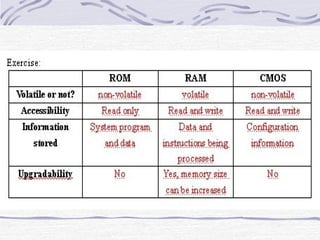
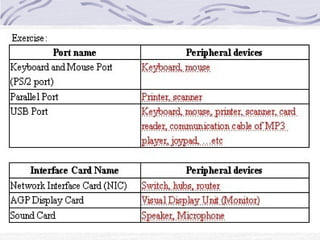
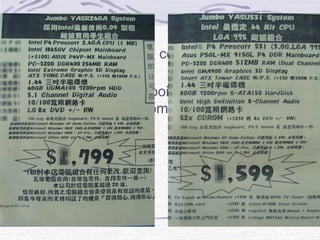
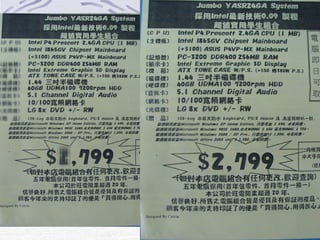
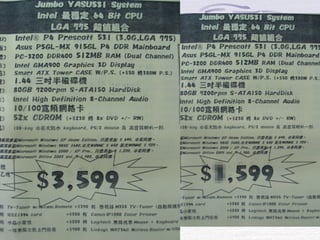
This document provides an overview of common computer hardware components, including the motherboard, CPU, RAM, hard disk, optical drives, display and sound cards, and network cards. It describes the functions of these components and how they connect and communicate via bus lines like the system bus and peripheral buses. Specific components like Intel and AMD CPUs are compared based on factors like clock rate, cache size, and number of transistors. Ports and interface cards are explained as the connection points between peripherals and the CPU. Two case studies with pictures are provided to illustrate real computer configurations.