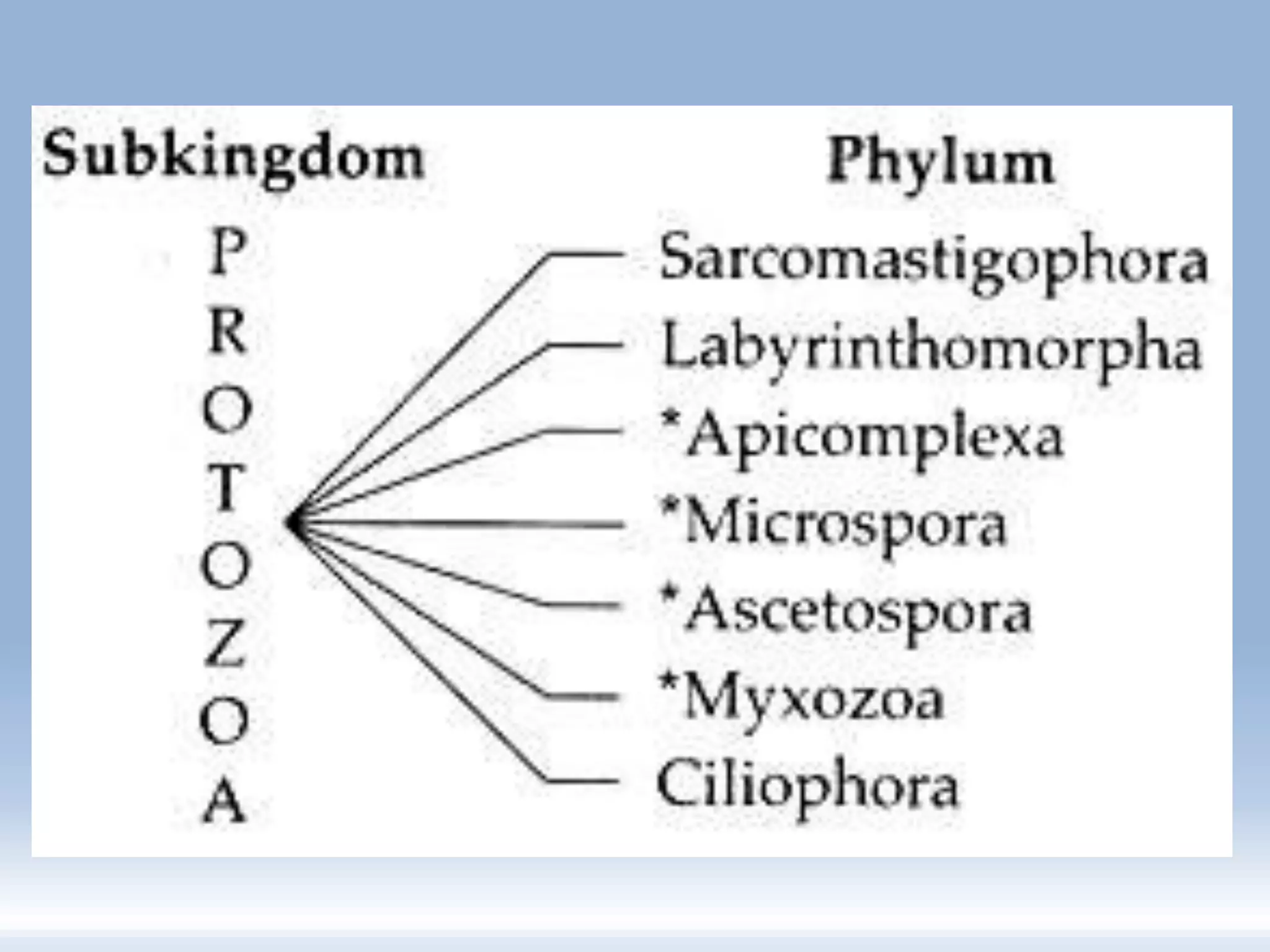
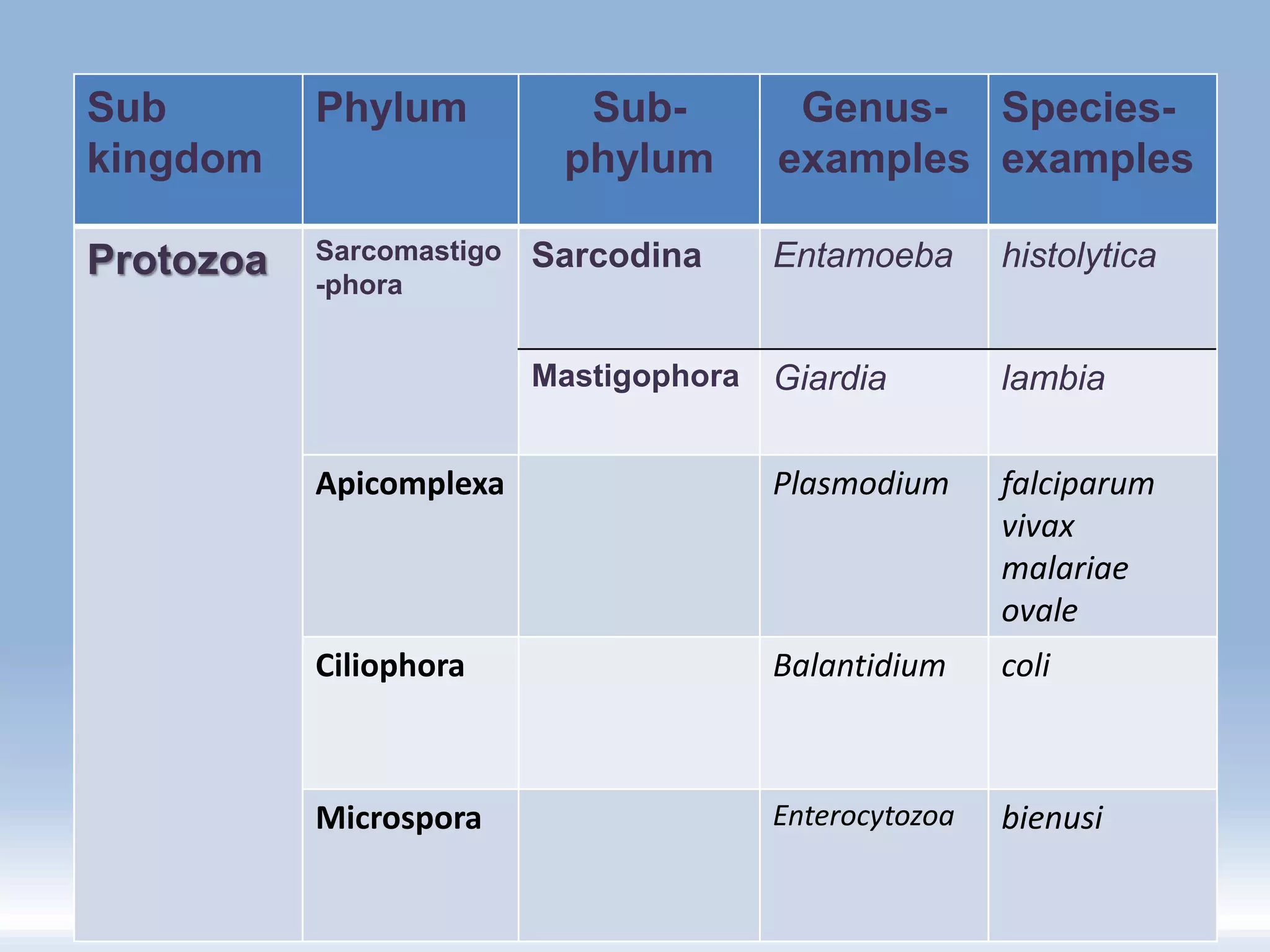
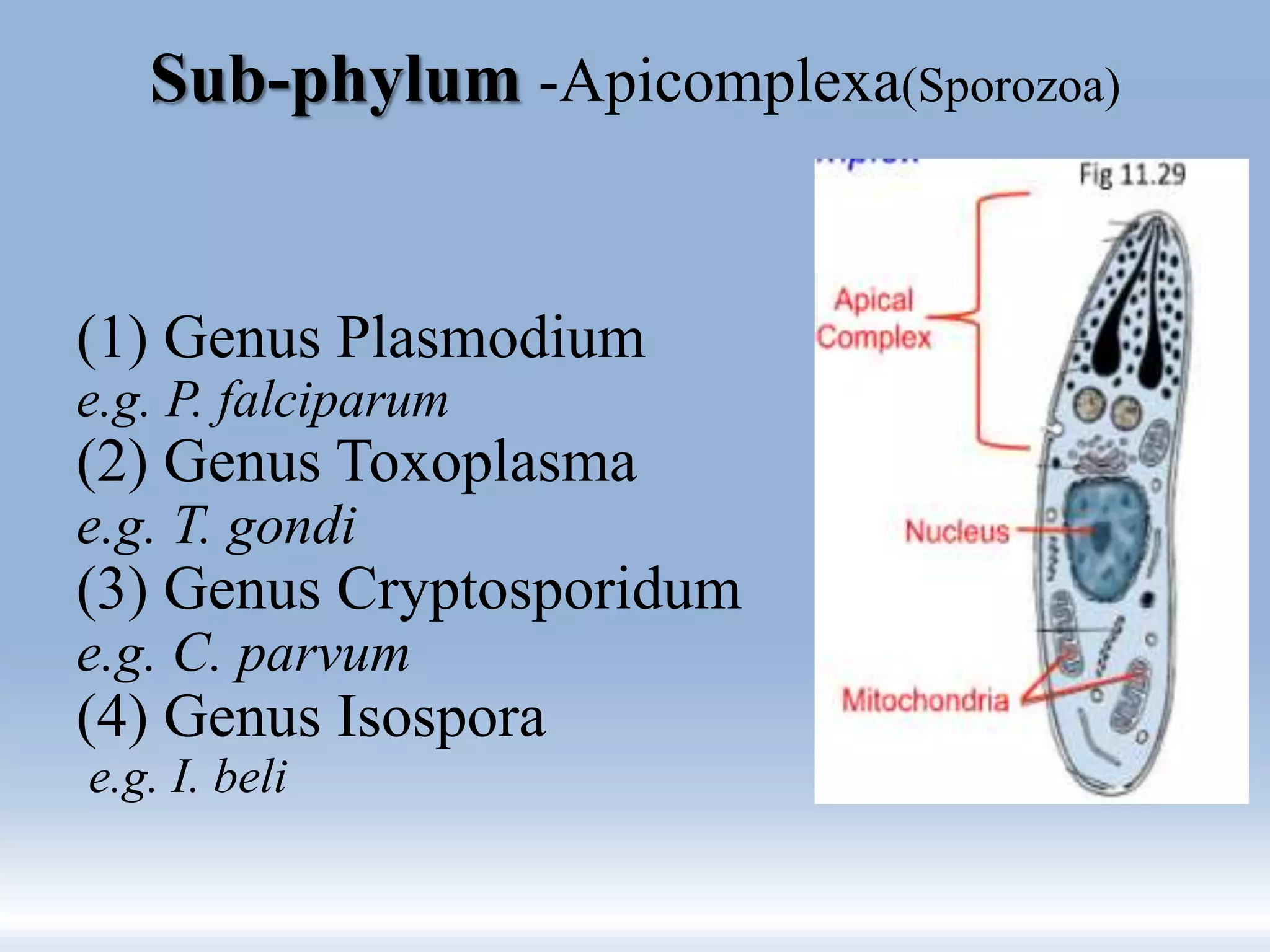
This document summarizes the classification of protozoa. It defines protozoa as microscopic, eukaryotic, unicellular organisms. Protozoa are classified into 7 phyla, with the most common human pathogens belonging to the phyla Sarcomastigophora and Apicomplexa. The document provides examples of genera and species within these phyla, including Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia, and Plasmodium falciparum. It describes key characteristics of protozoa such as locomotion, digestion, and reproduction.



![Locomotion takes place by finger like
pseudopodia[e.g.Amoeba],or hair like
cilia[e.g.paramecium] and whip like
flagella[e.g.Euglena].
Digestion is intracellular.
Respiration takes place by general body surface
by the process of diffusion.
Reproduction mainly occur asxually by
budding(Vorticella),binary fission(Amoeba) or
multiple fission (Plasmodium) and sexually by
conjugation of adults(i.e.hologamy) or fusion of
gametes(i.e.syngamy).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonclassificationofprotozoapasswordajay-210330112458/75/Presentation-on-classification-of-protozoa-5-2048.jpg)