Embed presentation

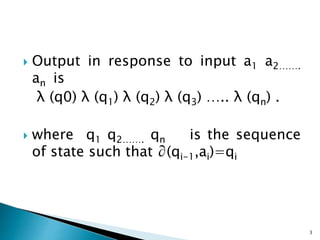


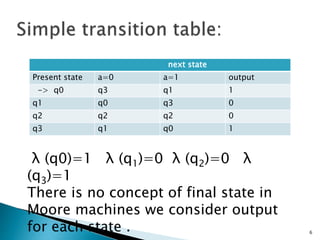
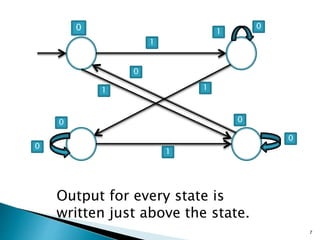

The document discusses Moore automata, which is a type of finite state machine where the next state is determined by the current state alone, independently of the input. In a Moore automata, the output at a given time depends only on the current state of the machine. It consists of 6 tuples: a finite set of states Q, input alphabet set Σ, output alphabet set Δ, transition function δ mapping state-input pairs to the next state, and output function λ mapping each state to an output. The output in response to an input string is determined by the sequence of states entered and the corresponding outputs according to λ. A Moore machine always produces an output for the empty input string based on the initial state.







