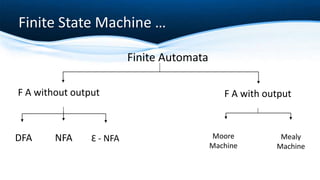
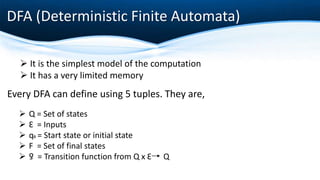
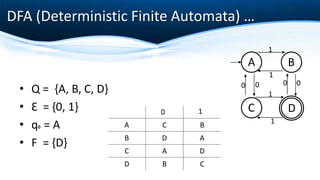
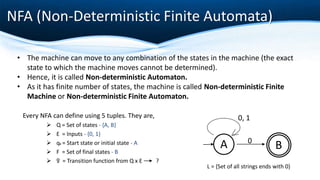
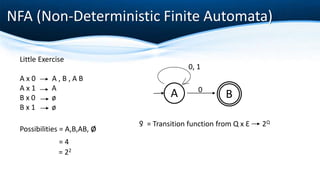
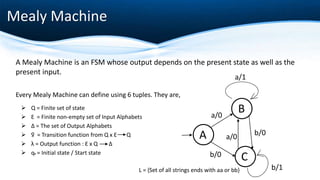
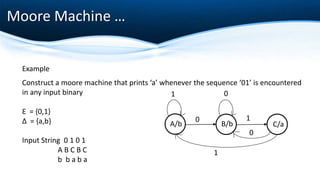
The document outlines key concepts of formalization machines, specifically focusing on finite state machines (FSM) including deterministic (DFA) and non-deterministic (NFA) automata, as well as Mealy and Moore machines. It explains their structures using tuples and provides examples to illustrate their functioning. Additionally, it discusses the transition functions, input alphabets, and output behaviors of these machines.