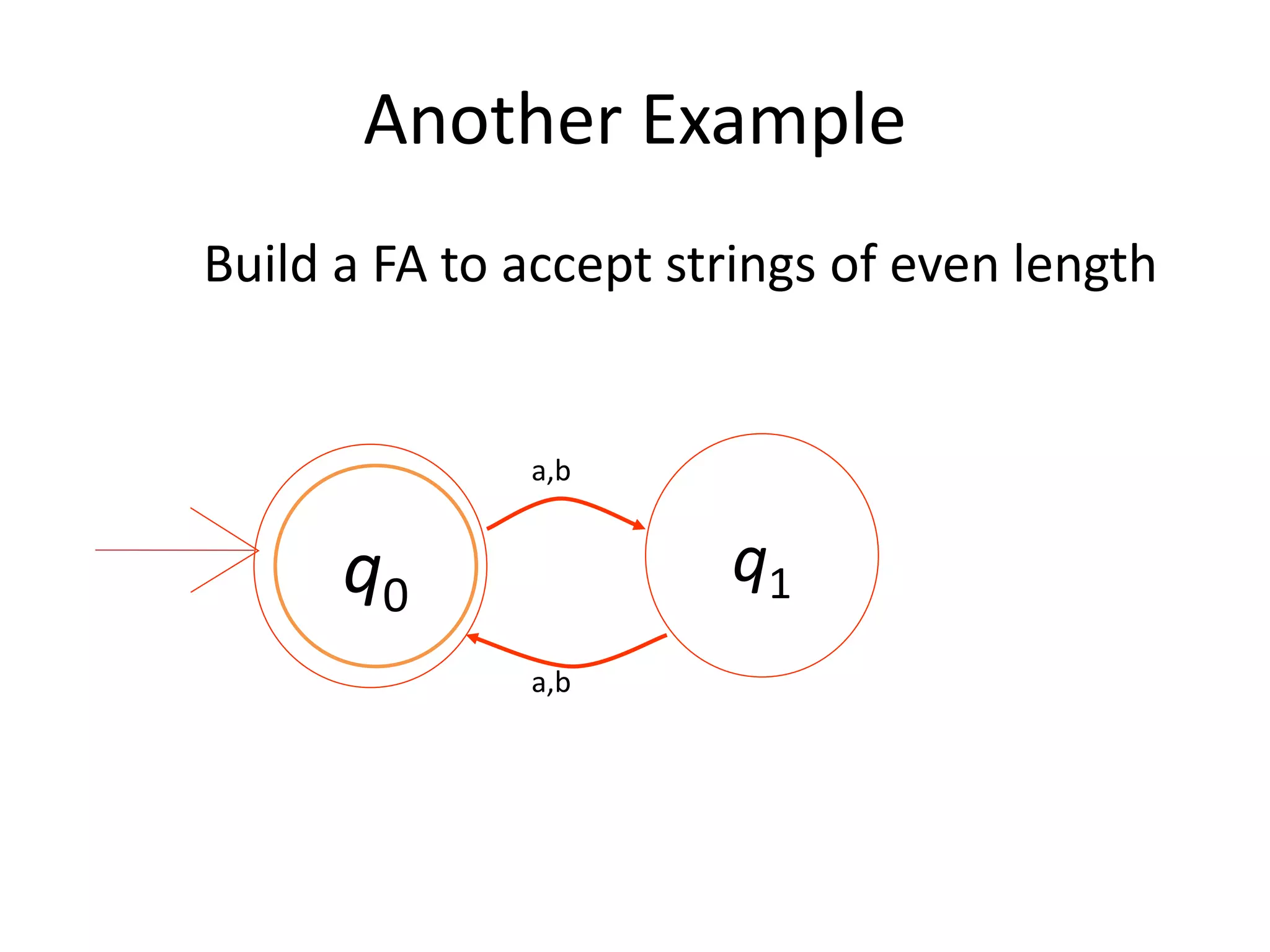
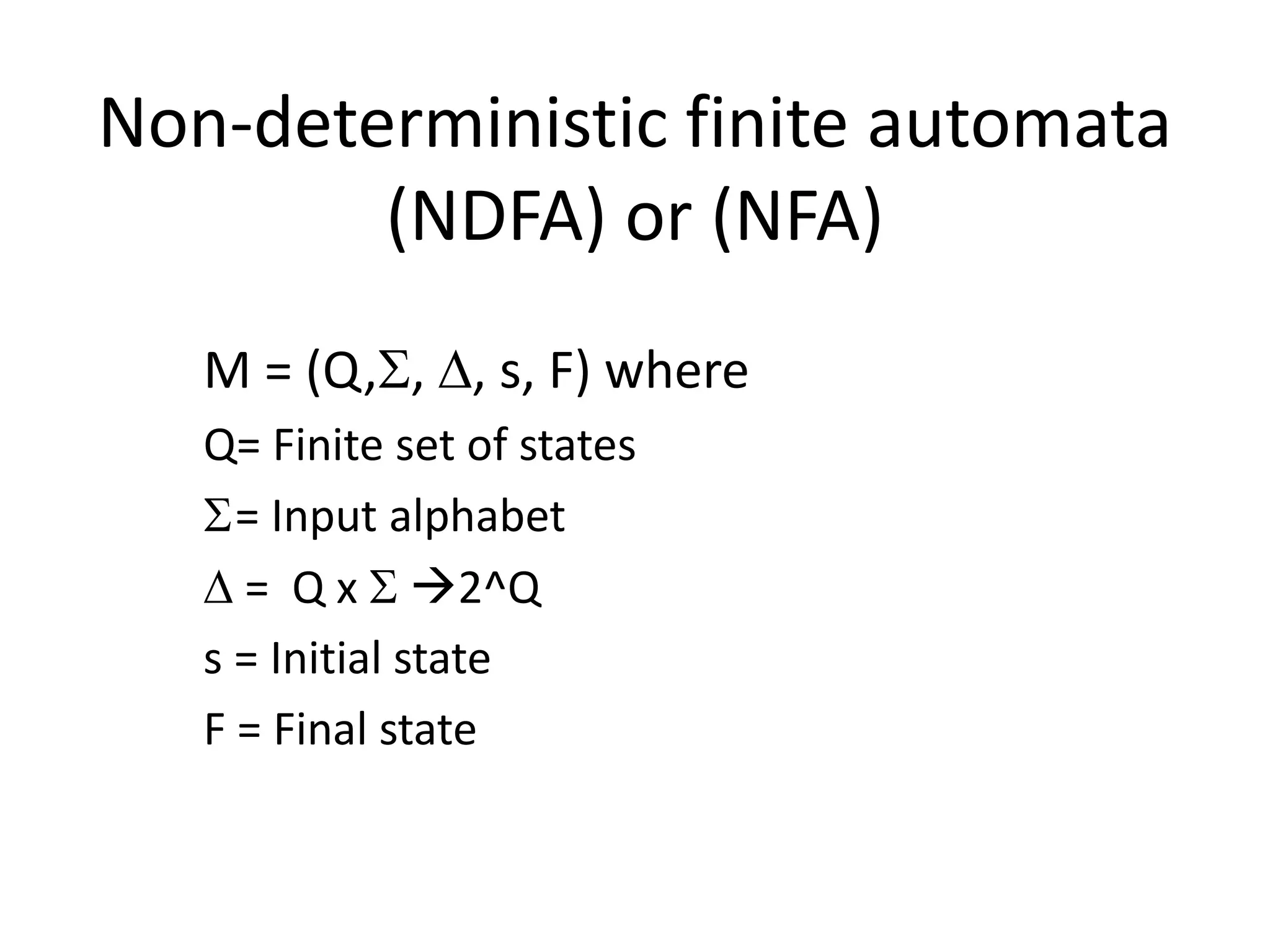
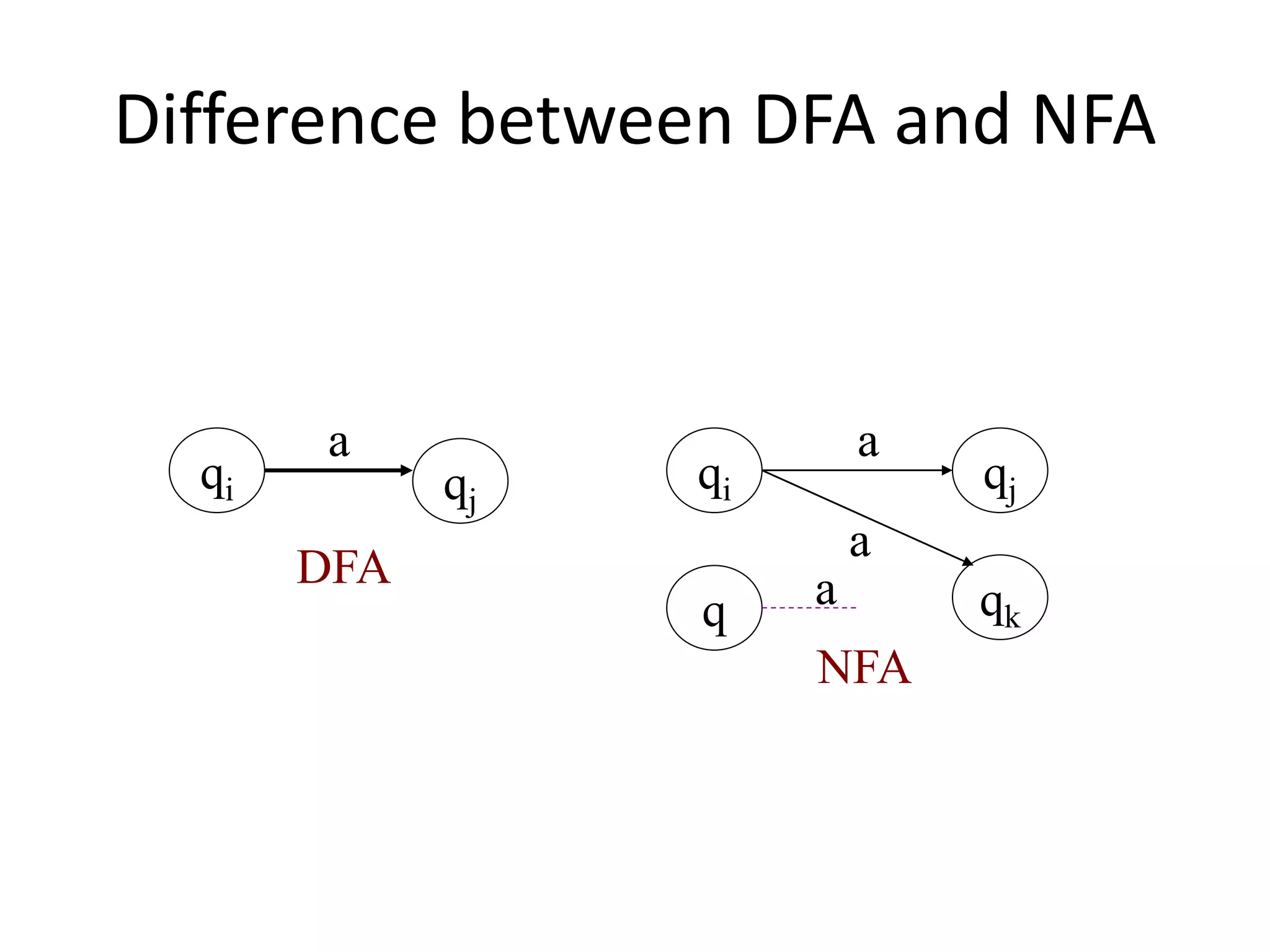
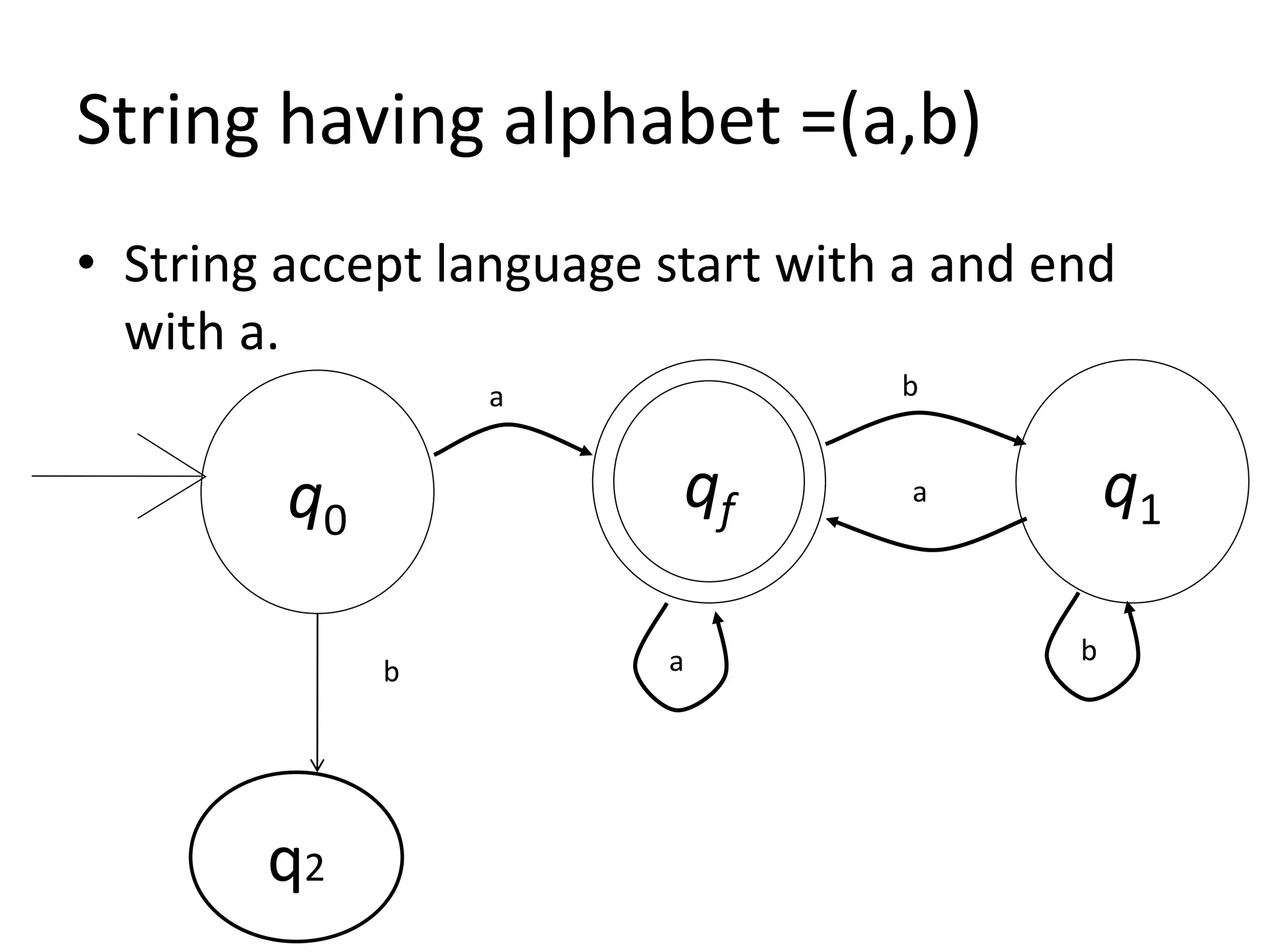
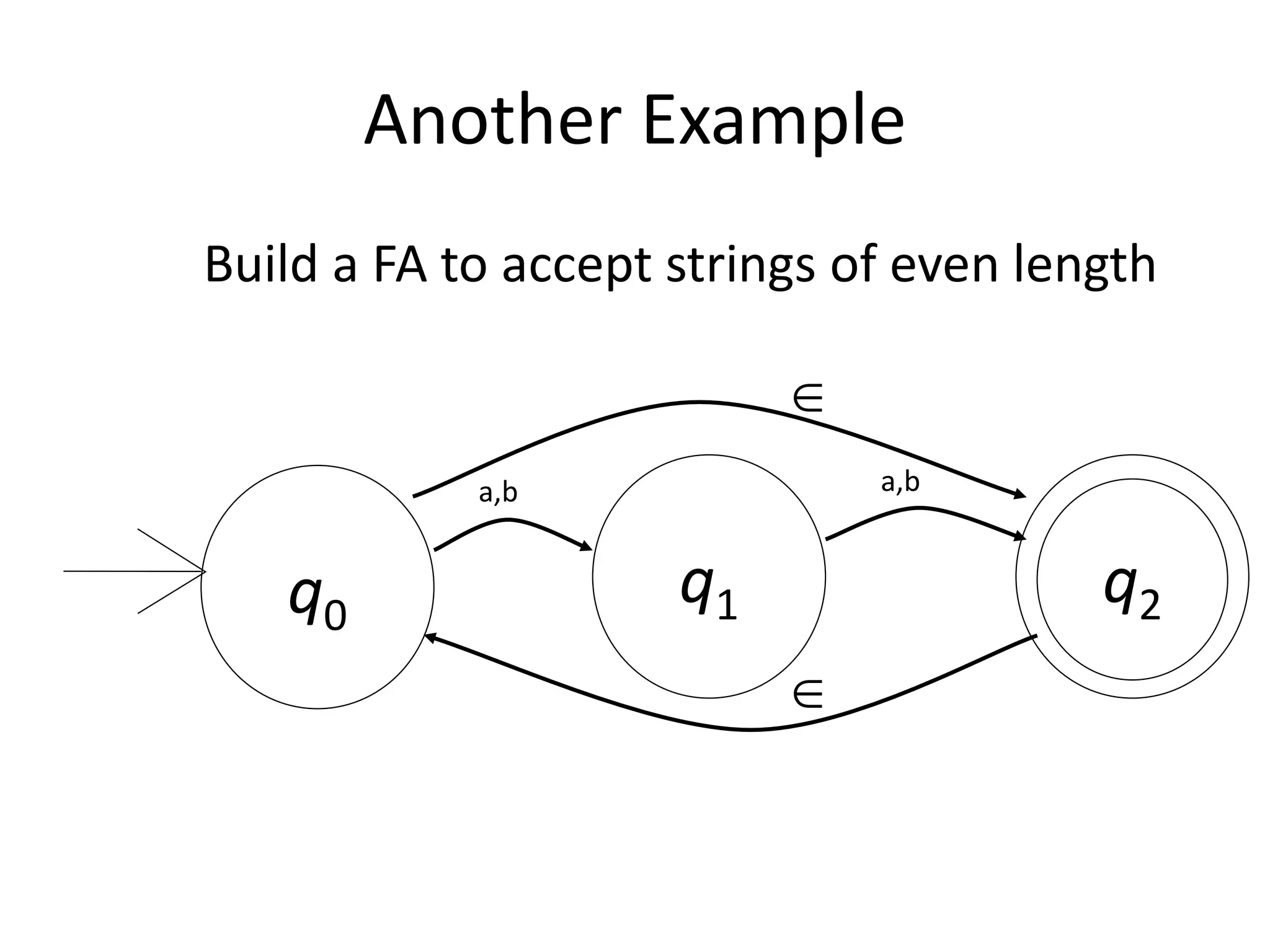
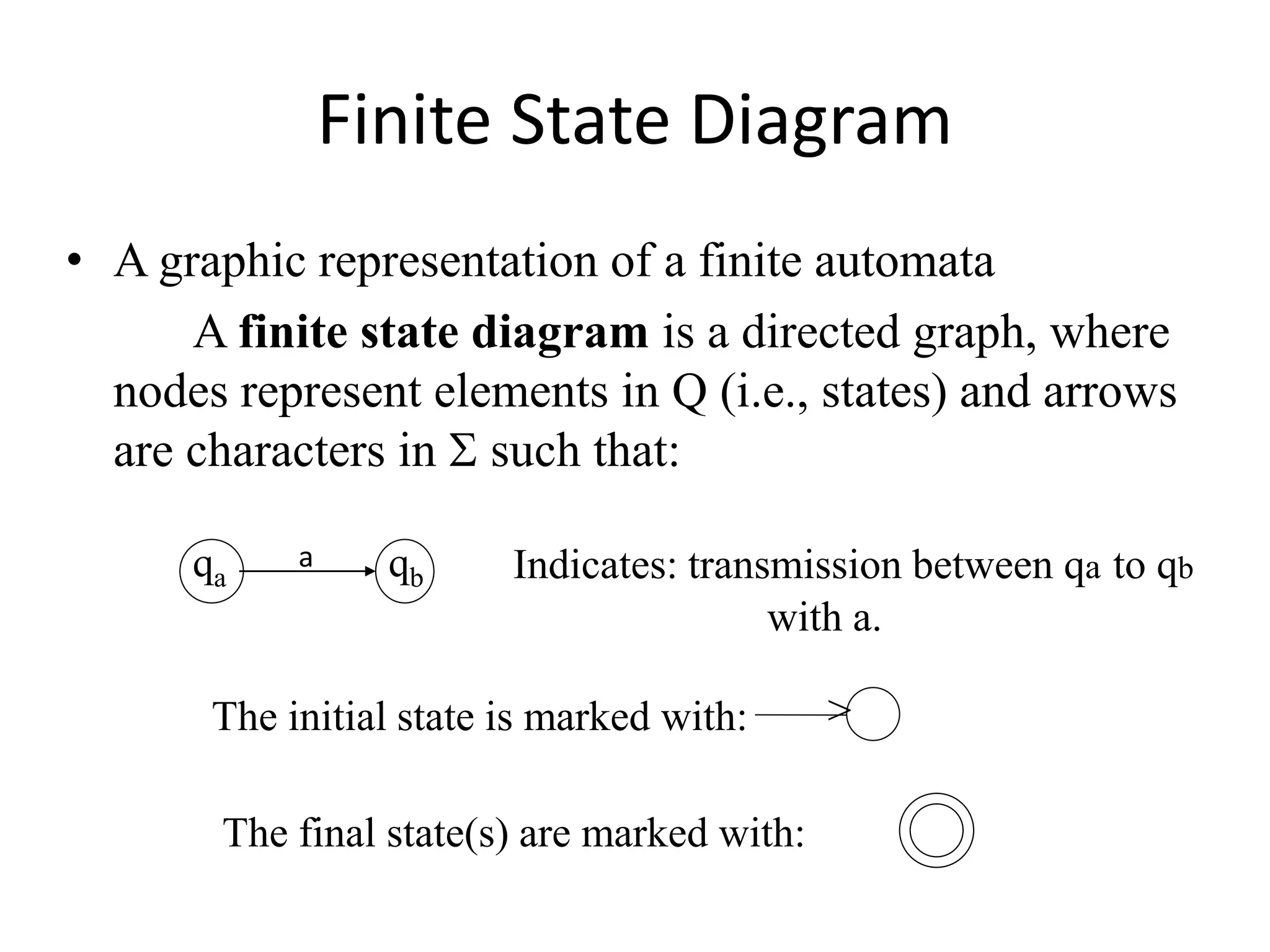
This document discusses finite automata, including:
- Finite automata are machines that recognize patterns in input sequences.
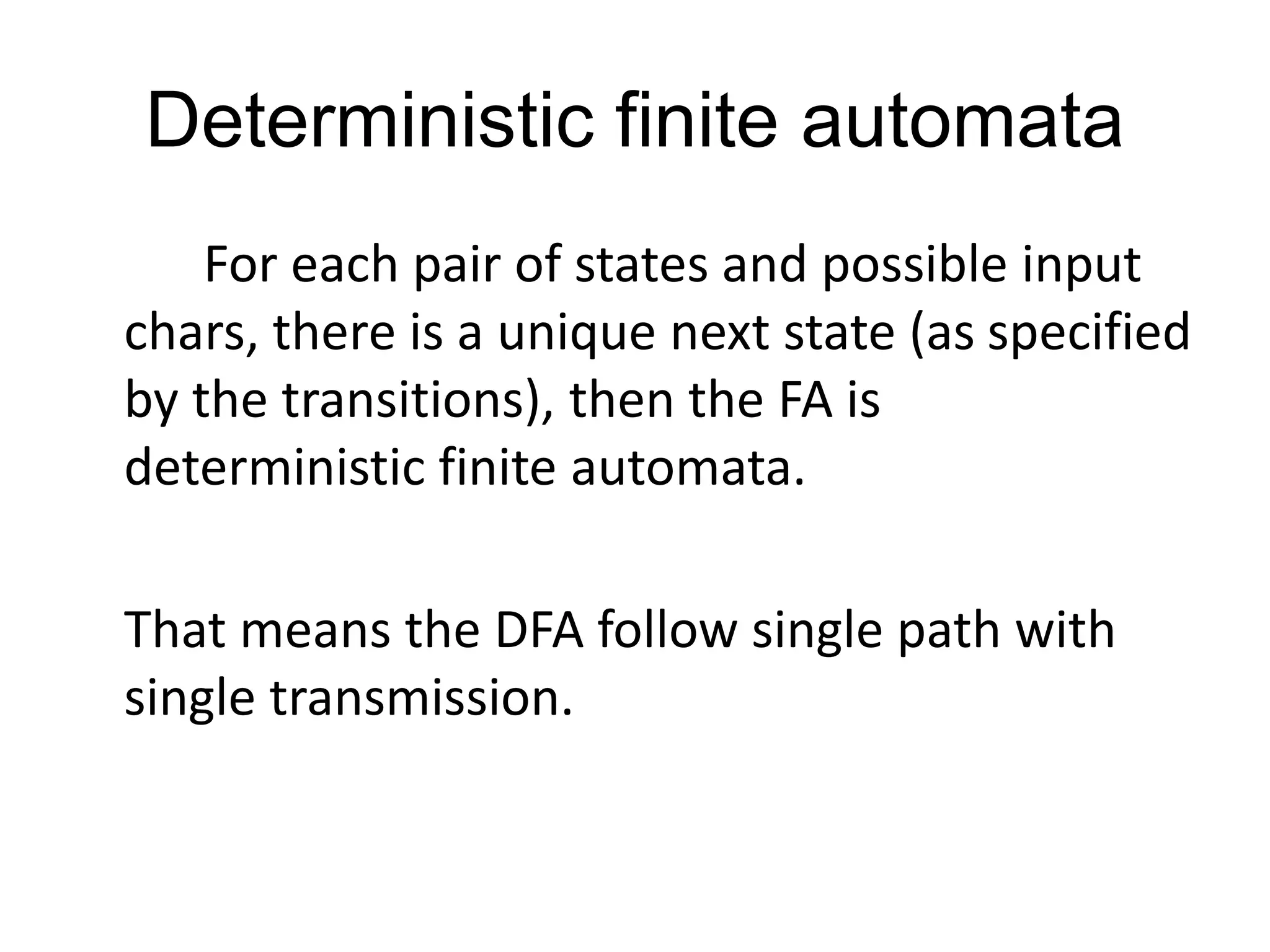
- There are two main types: deterministic finite automata (DFAs) and non-deterministic finite automata (NFAs).
- DFAs have a single transition between states for each input, while NFAs may have multiple possible next states for each input.


![Example
Set of strings over {a,b} that contain “bb”
q2q0 q1
a b
a
b
a
b
d a b
q0 q0 q1
q1 q0 q2
q2 q2 q2
}2{
},{
}2,1,0{
qF
ba
qqqQ
],1[],0[ *
qaabq ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finiteautomata-170619174558/75/Finite-automata-8-2048.jpg)