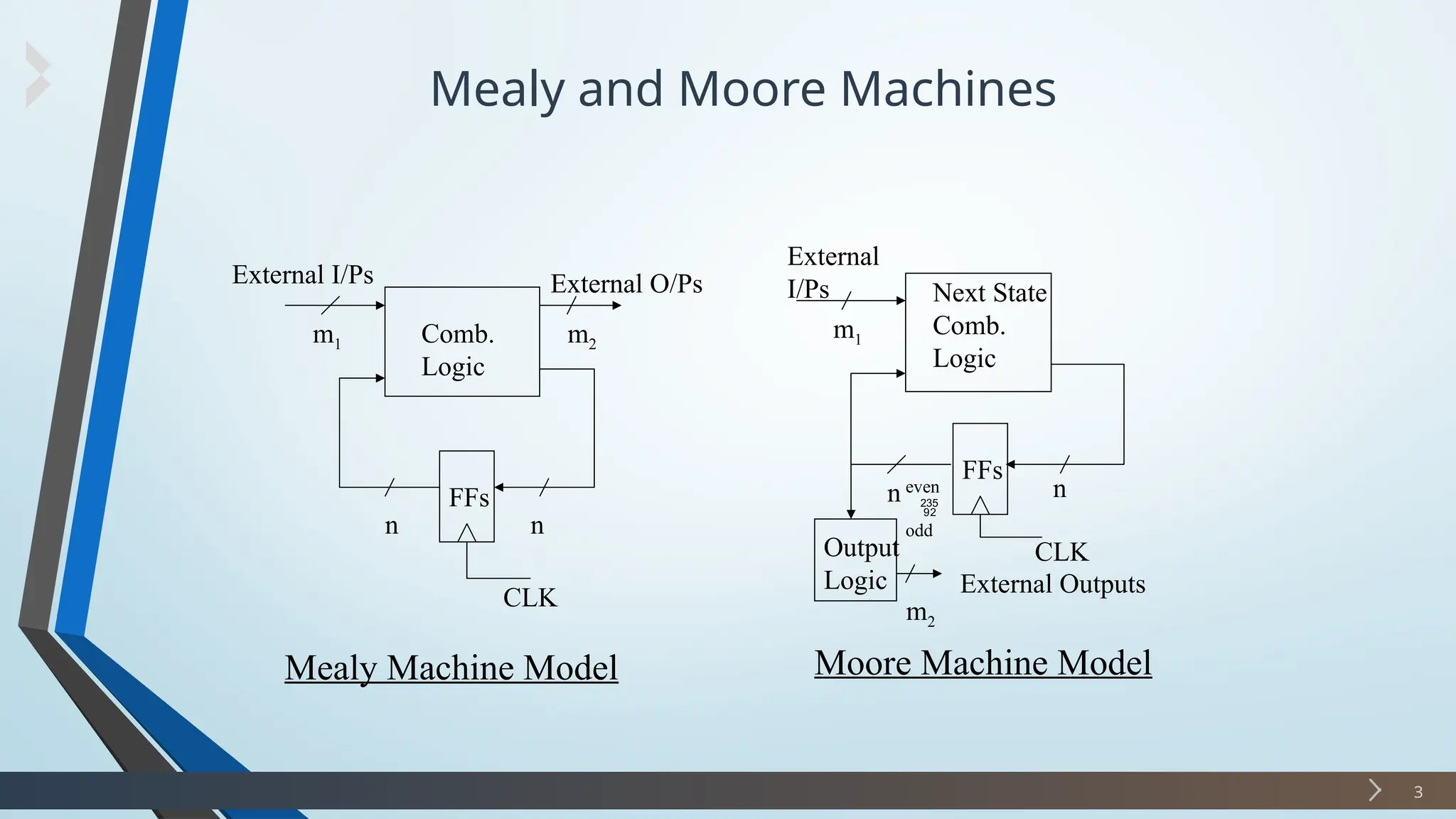
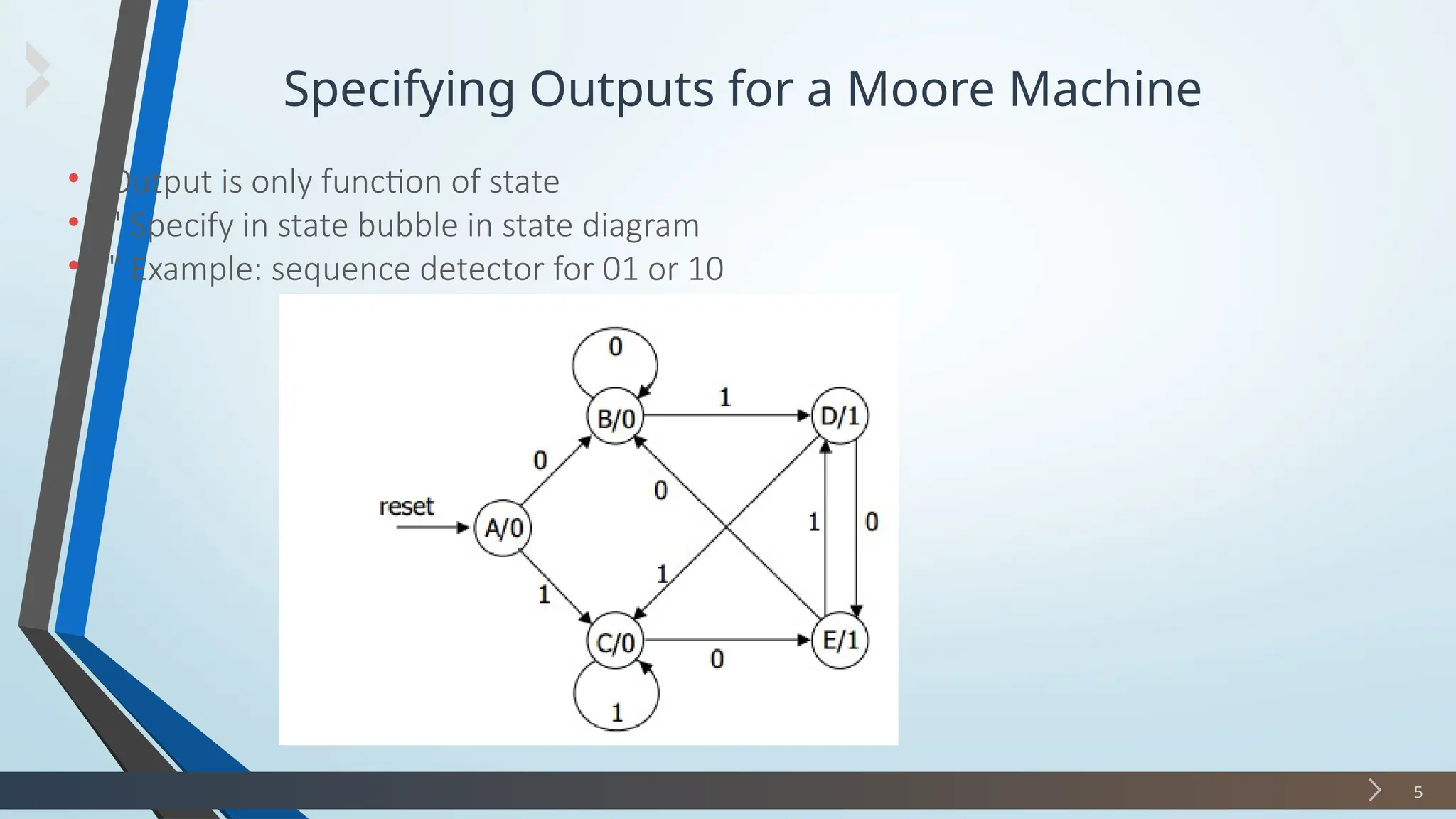
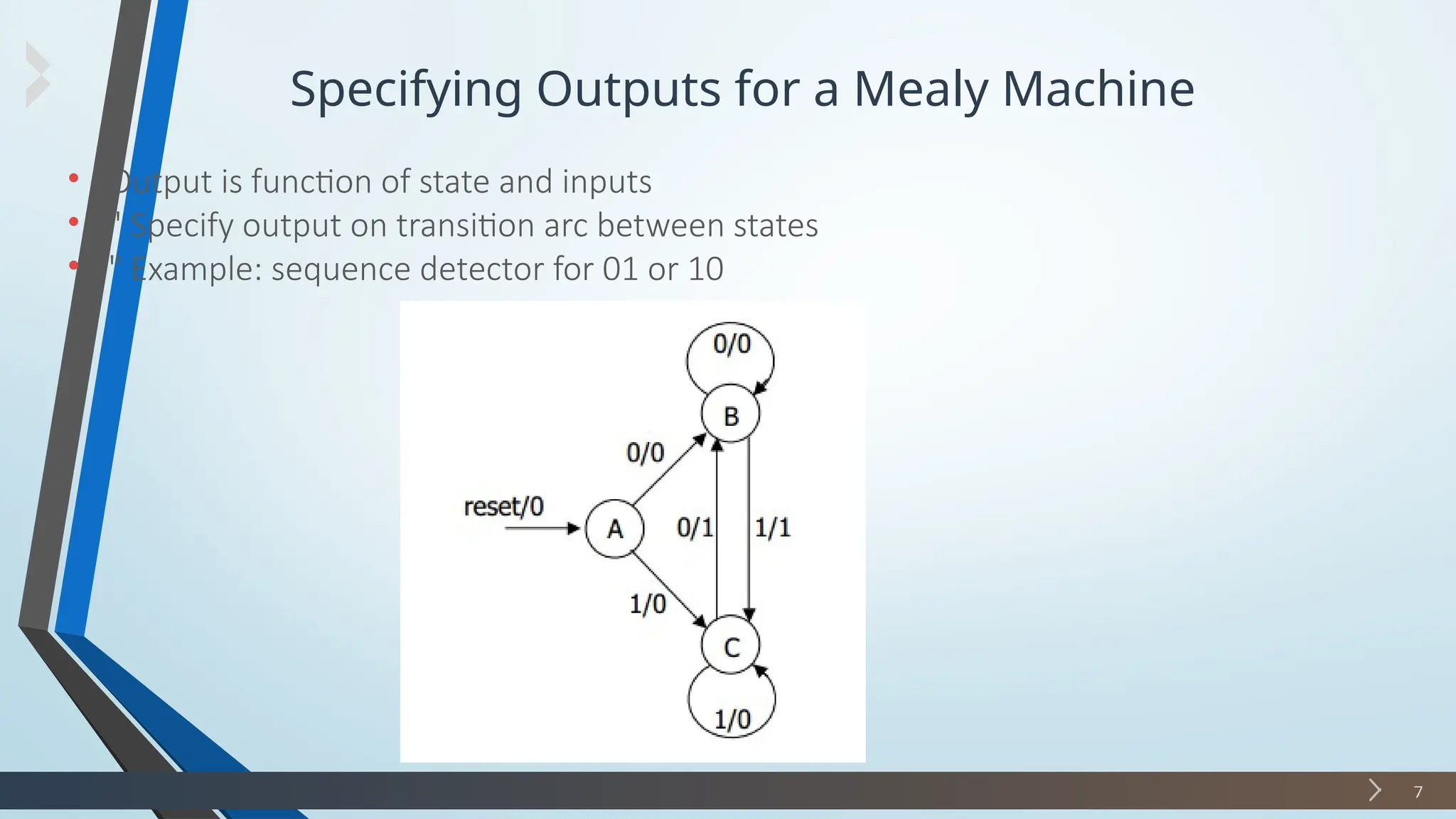
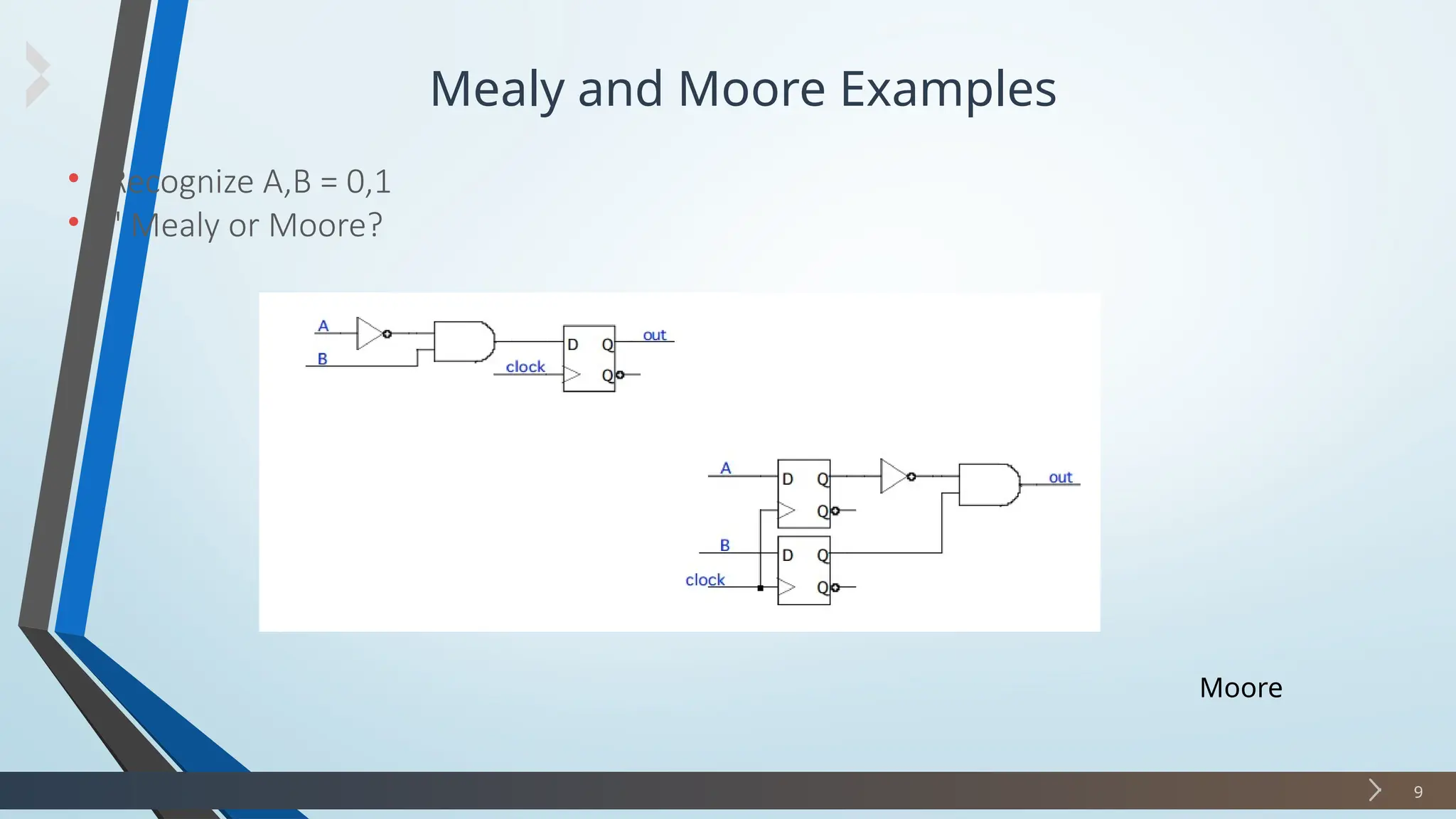
The document discusses finite state machines (FSMs), particularly Mealy and Moore machines, highlighting their differences and applications in digital electronics. It outlines how outputs in Mealy machines depend on both the current state and inputs, while Moore machines' outputs depend solely on their current state. Additionally, it provides examples and steps for designing a sequence detector using these models.