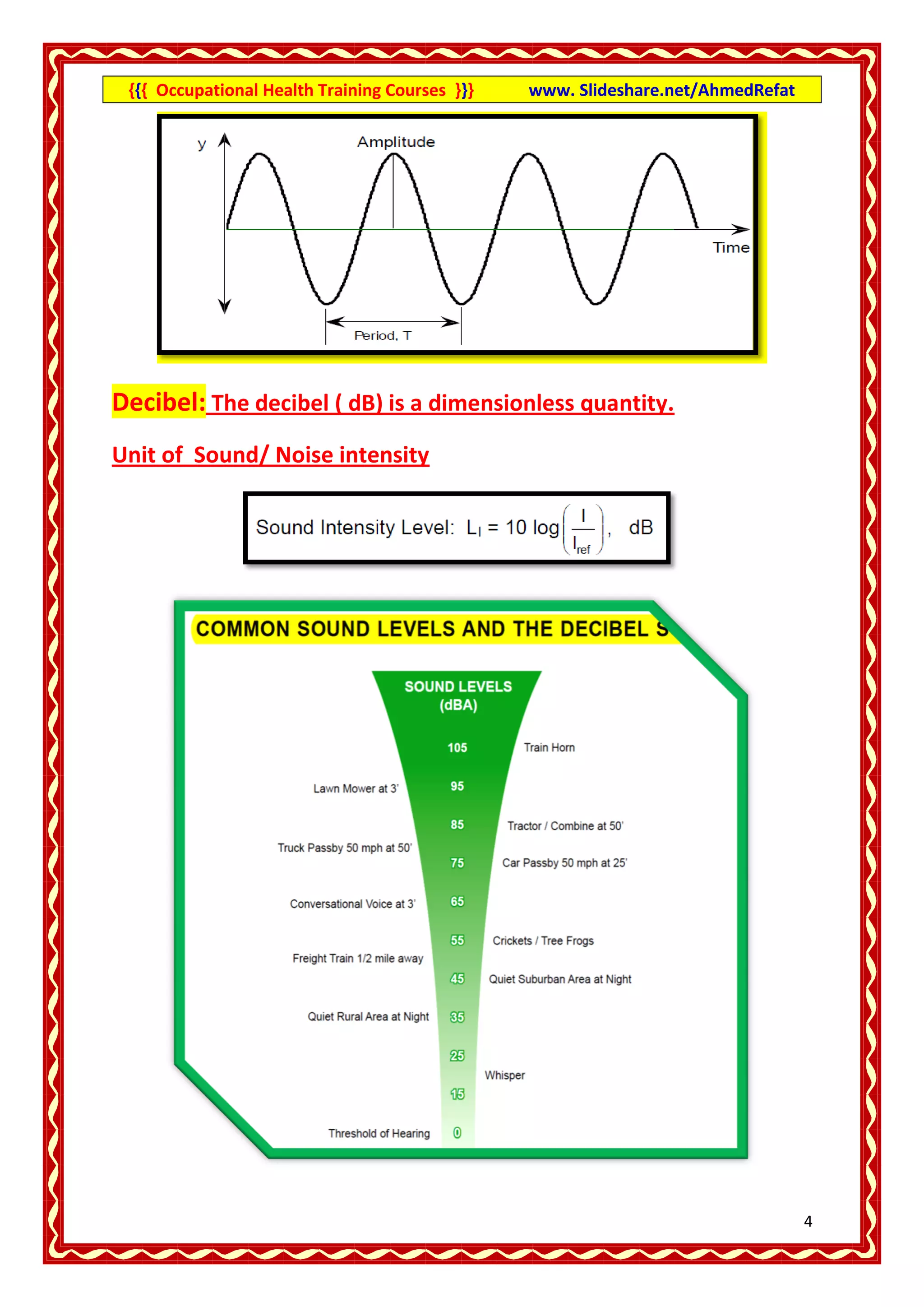
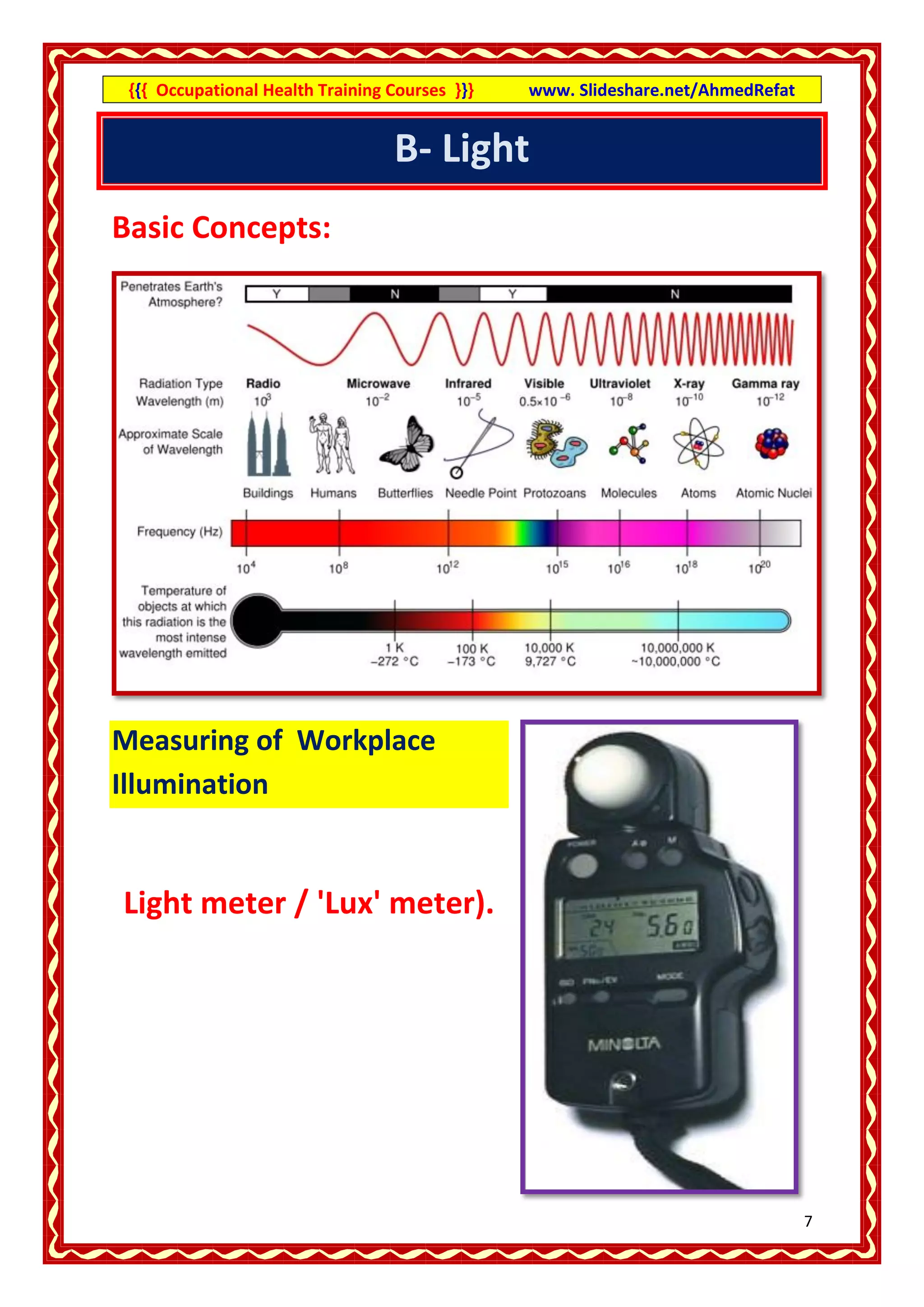
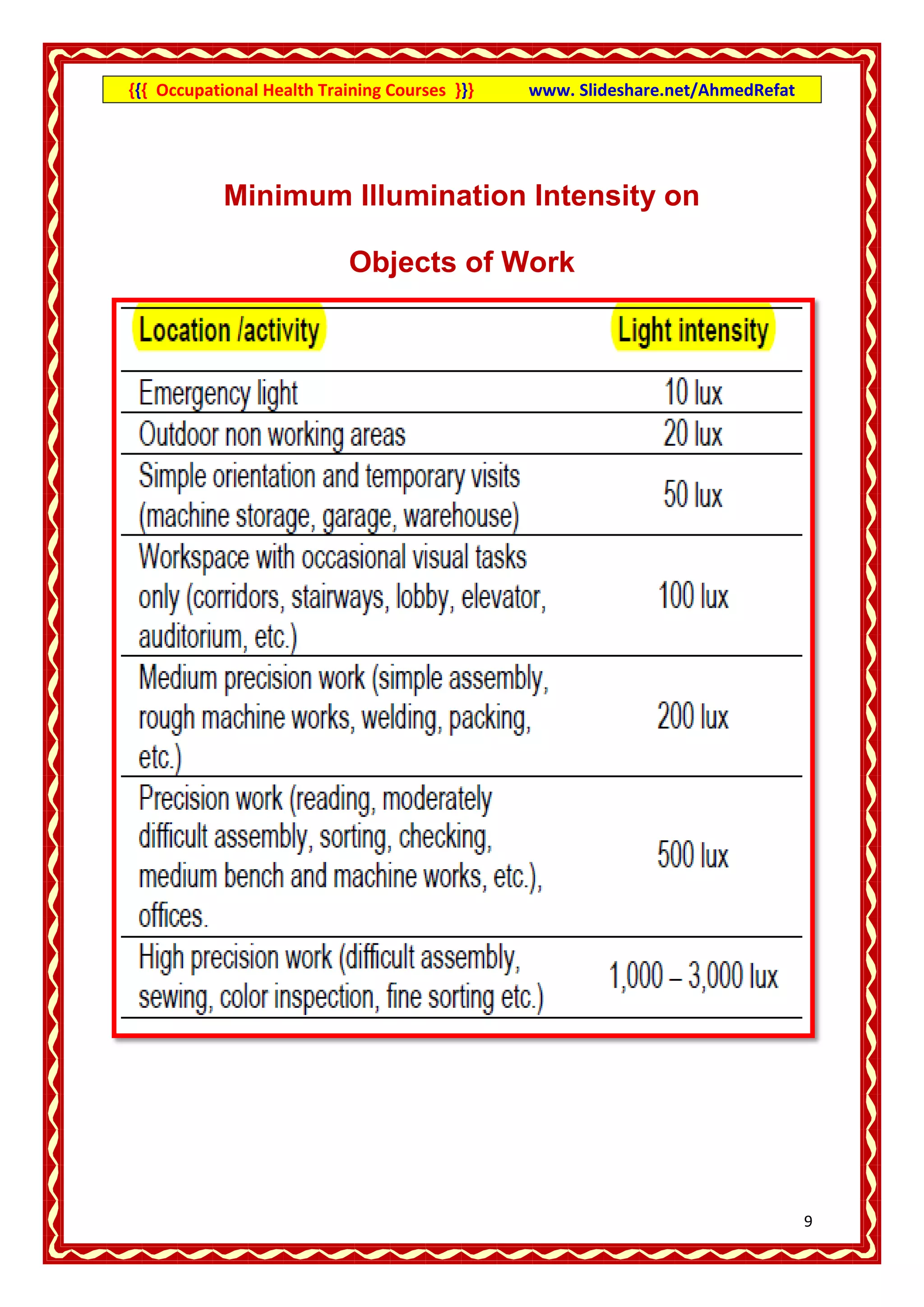
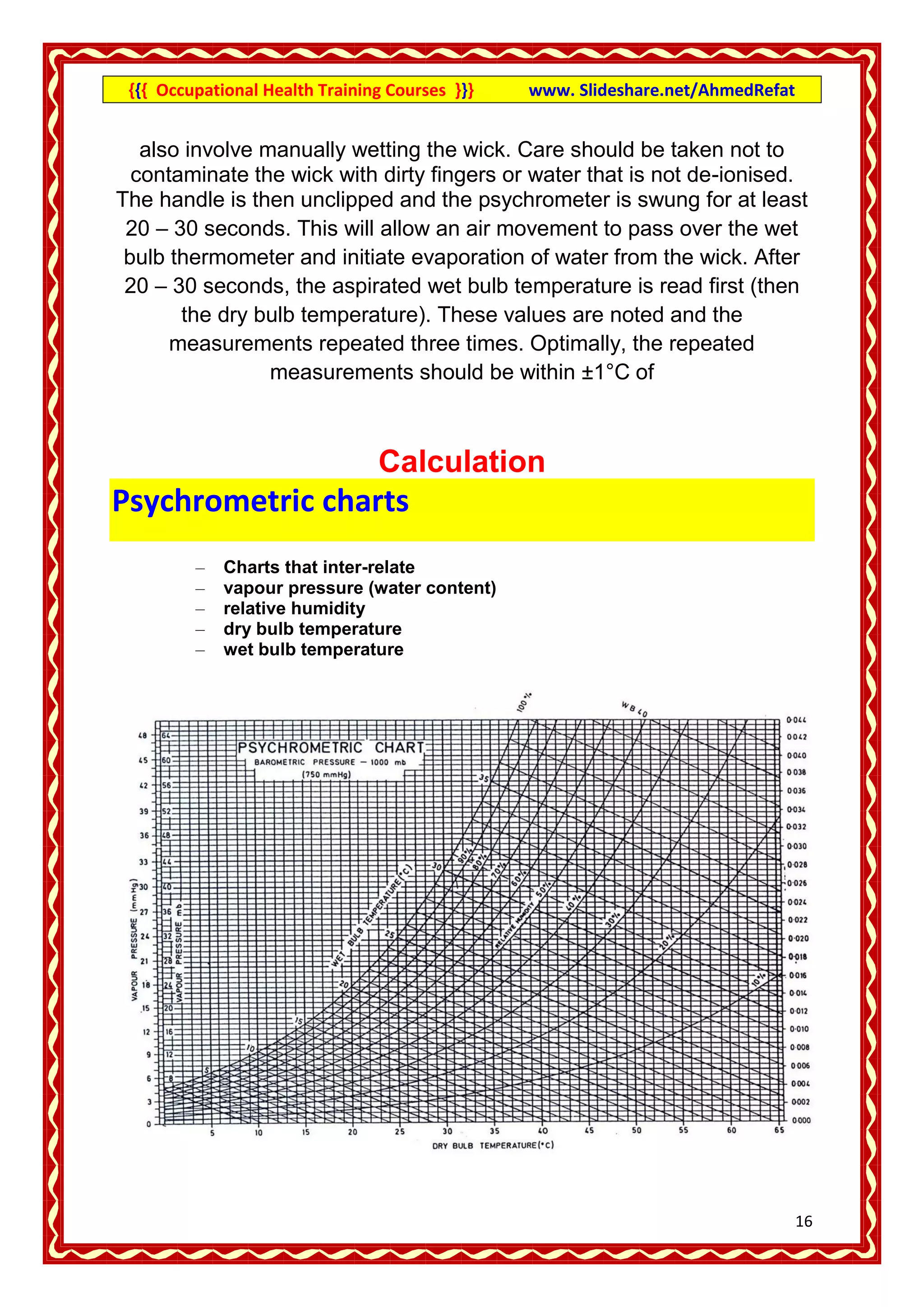
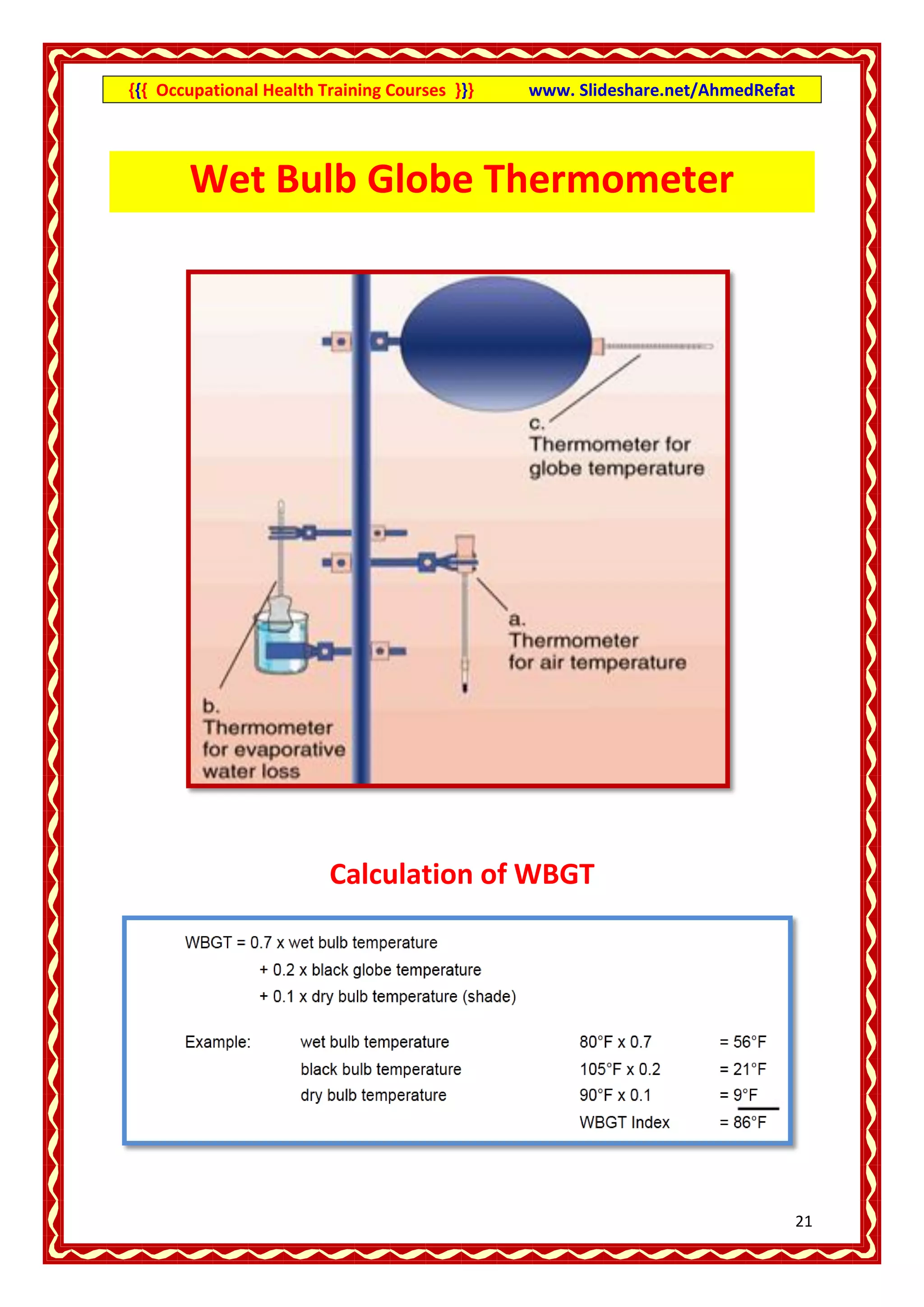
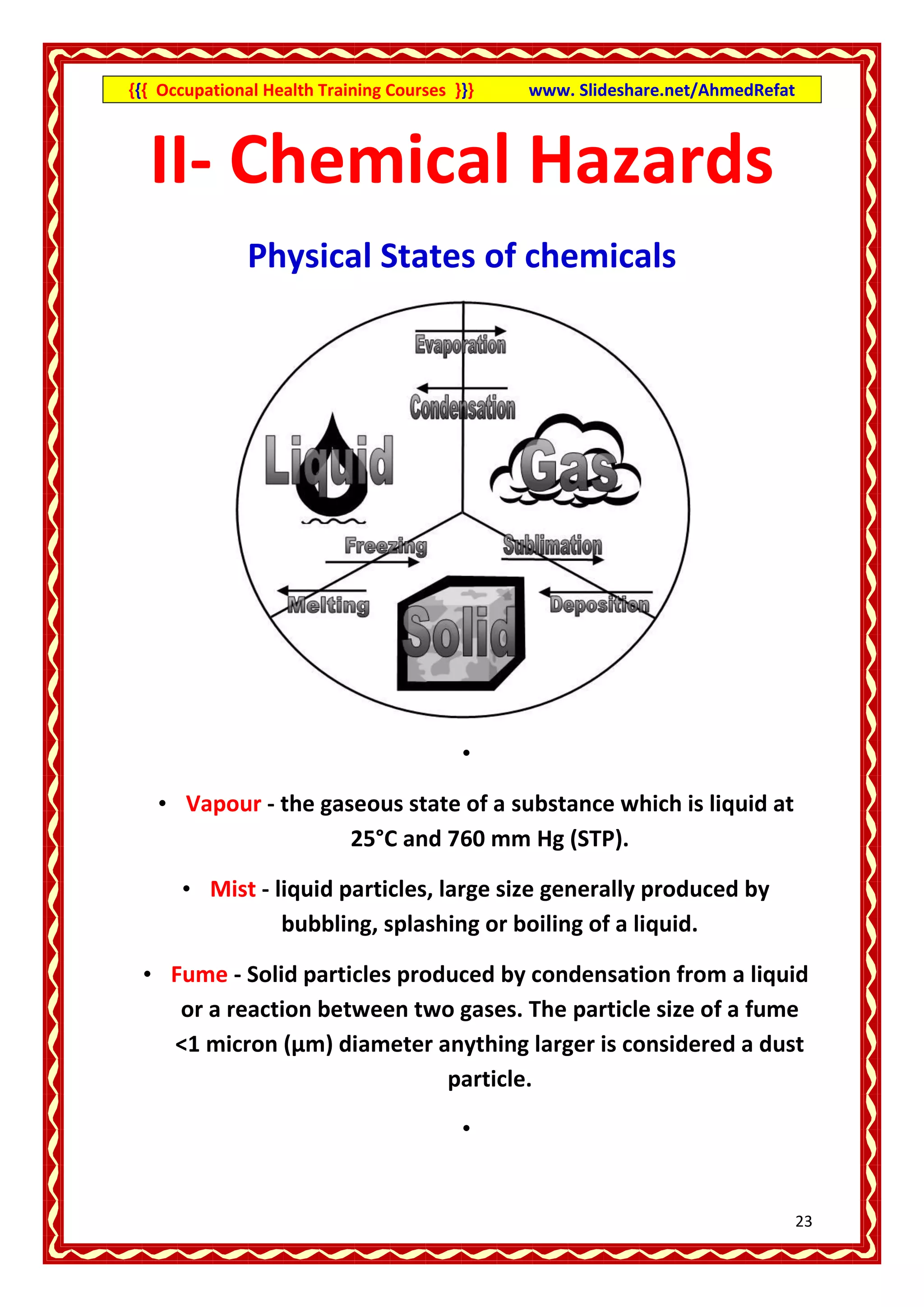
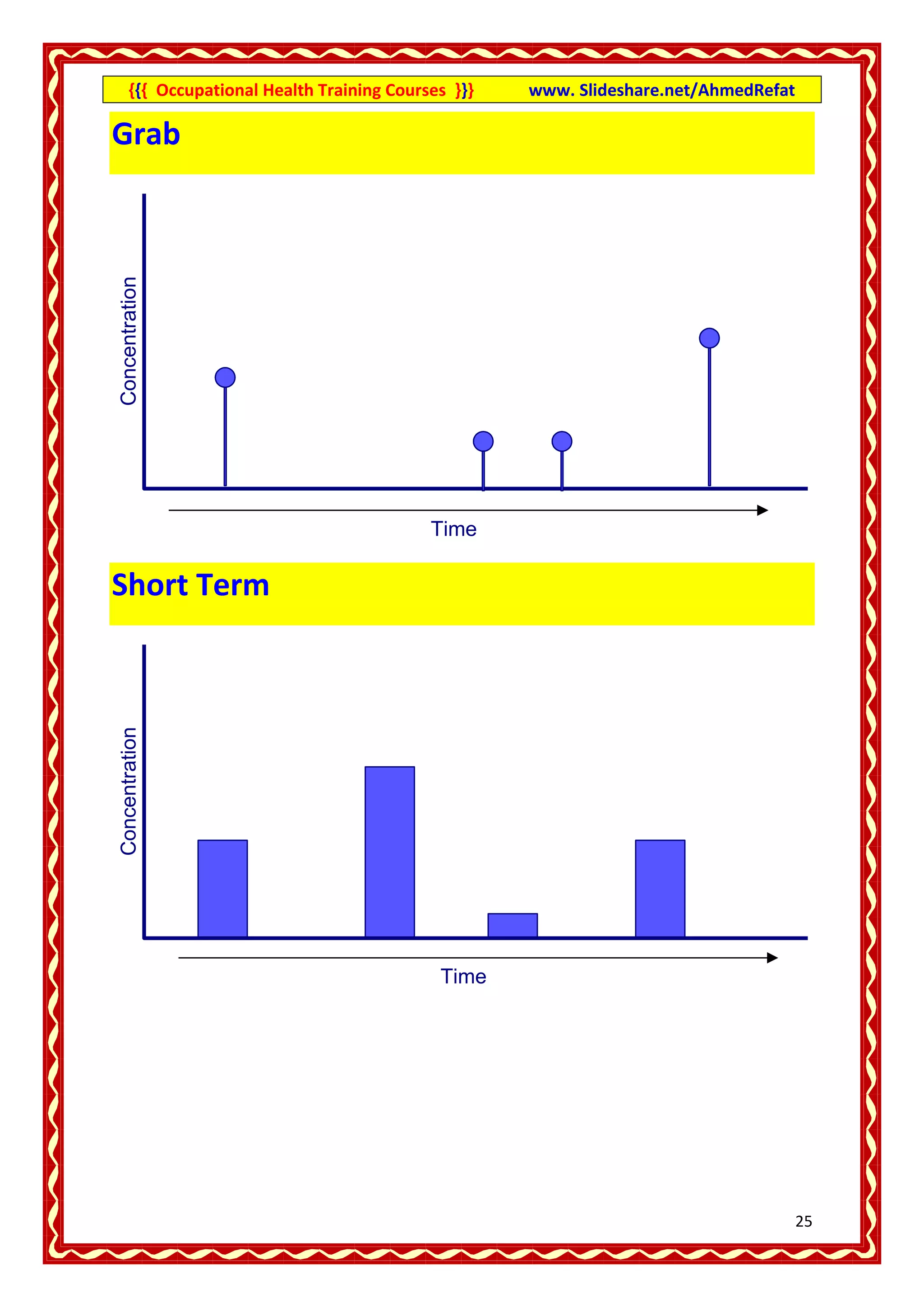
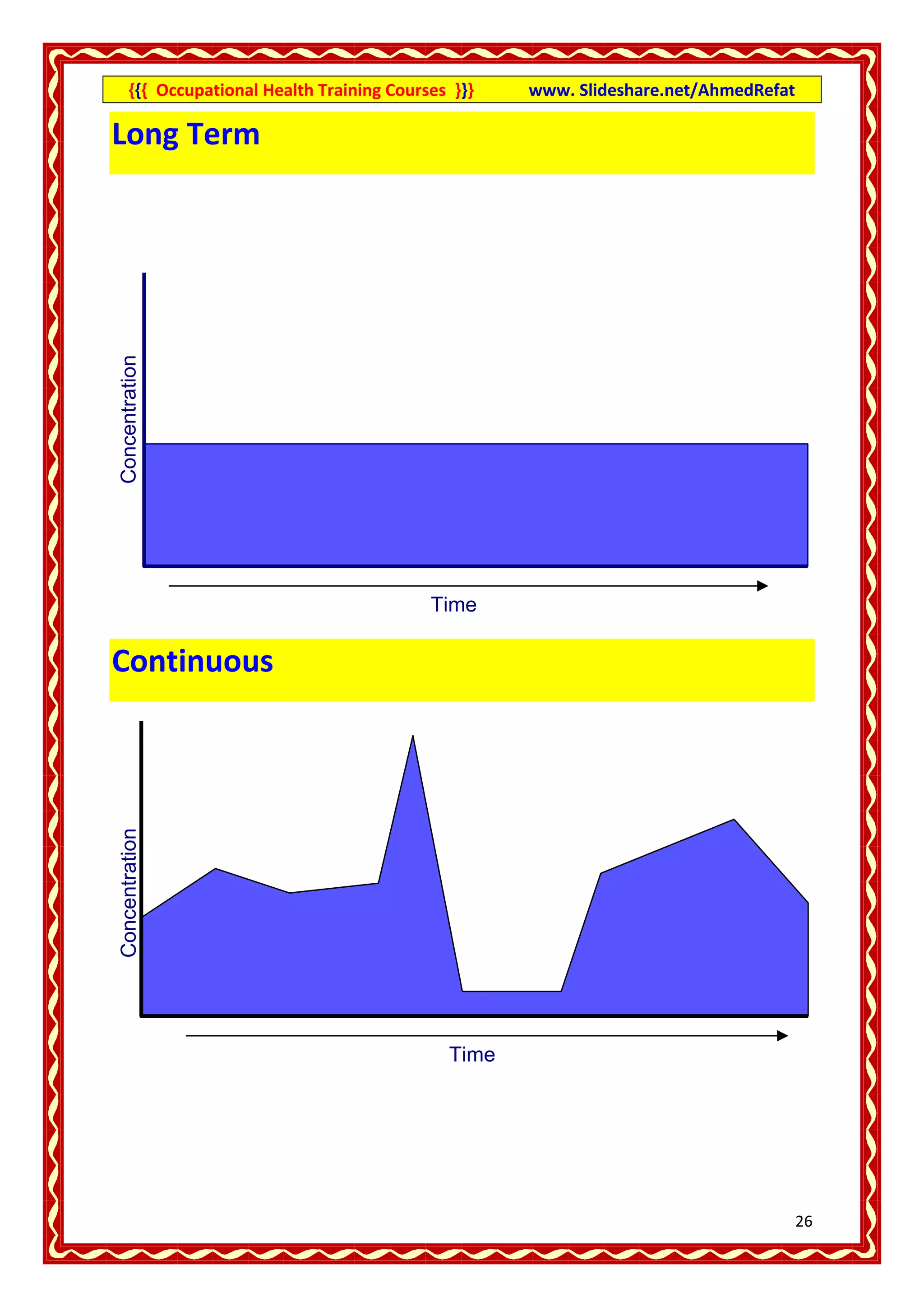
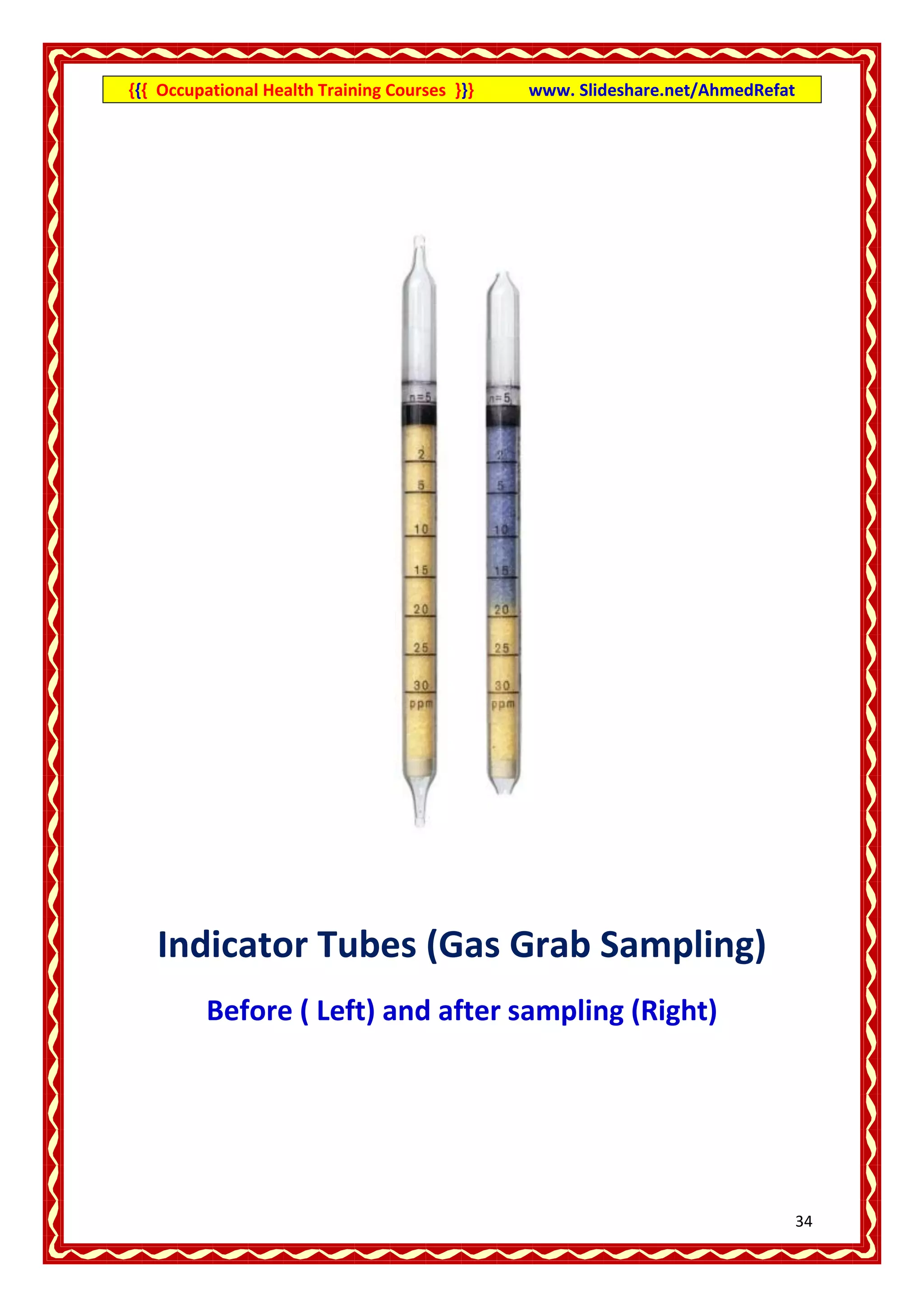
This document provides an overview of occupational health training courses focusing on assessment of workplace hazards. It discusses measuring physical hazards like noise, light, heat and thermal environment. Noise is measured using a sound level meter in decibels while light is measured in lux units using a lux meter. Heat stress and strain are also explained. Methods for measuring chemicals hazards like vapors, fumes and dust are outlined. Sampling techniques including grab, short term and long term sampling are covered. Hygiene standards used to evaluate exposure levels like TLVs are also mentioned.