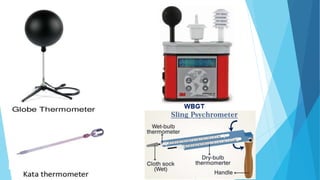
Heat stress is a condition where the body's ability to cool itself is exceeded by the amount of internal and external heat it experiences. It is measured using factors like air temperature, humidity, velocity, and radiant heat. The human heat balance equation accounts for radiant, conductive, evaporative, stored, and metabolic heat. Several heat stress indices exist, including effective temperature, corrected effective temperature, predicted 4-hour sweat rate, Belding-Hatch index, Oxford index, and wet bulb globe temperature, with each taking different climatic and individual factors into account to assess heat stress levels and safety limits.