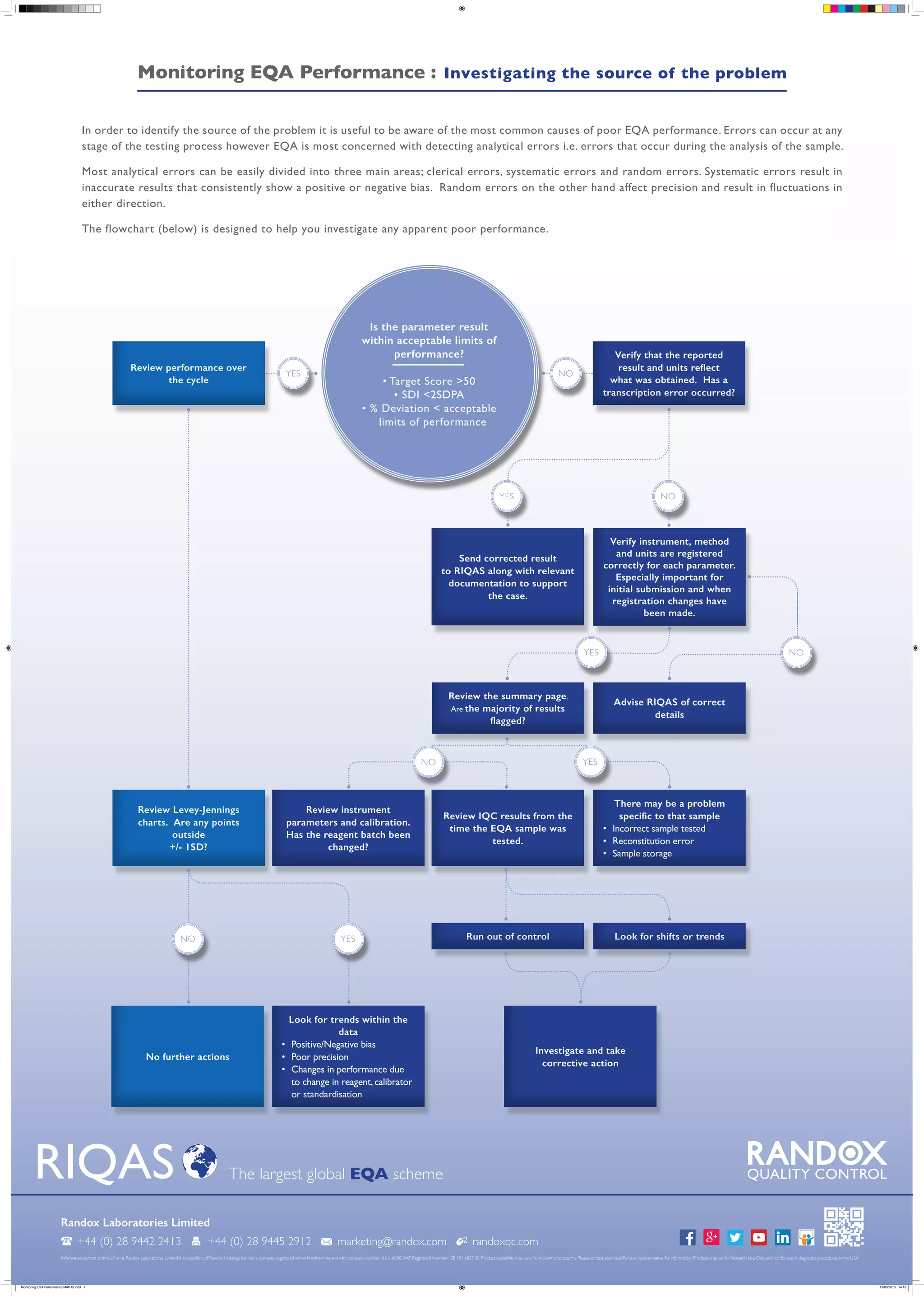
The document outlines a procedure for reviewing performance in an external quality assessment (EQA) program, emphasizing the verification of reported results and the registration of instruments and methods. It details steps for investigating poor performance, including reviewing control charts and data trends, while identifying potential errors and their sources. Common errors include clerical, systematic, and random errors, with a flowchart provided to assist in the investigation process.