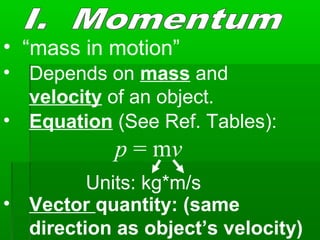
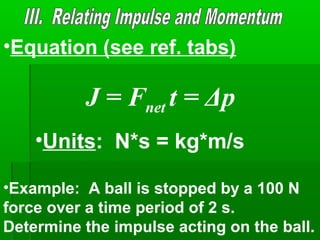
This document defines and provides examples of momentum and impulse. It states that momentum depends on an object's mass and velocity, and can be calculated using the equation p=mv. Impulse is defined as the force applied over time, or the change in an object's momentum. The impulse-momentum theorem states that the impulse acting on an object equals its change in momentum. Examples are provided to illustrate momentum, impulse, and how applying a force over a longer period of time through an airbag can reduce the impact.