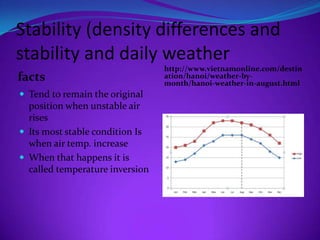
This document contains summaries of various meteorological concepts in 3 sentences or less:
1) It discusses adiabatic temperature changes, how air cools when expanding and warms when compressed, and the differences between dry and wet adiabatic rates.
2) It defines orographic lifting as air being forced to ascend when encountering elevated terrain like mountains, frontal wedging as the interaction between warm and cold air masses at a front, and convergence lifting as the result of air flowing together in the lower atmosphere.
3) It provides short descriptions of cloud types like cirrus, cumulus and stratus clouds based on height and shape, as well as fog, precipitation processes, and the formation of