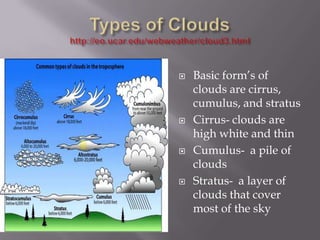
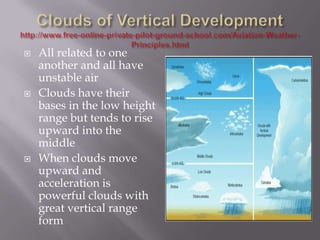
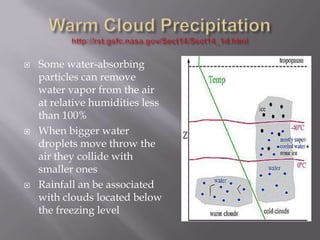
1) When air is compressed or expands, it causes changes in temperature - compression warms air while expansion cools it.
2) Mountains cause air to rise and cool, which can lead to cloud formation and precipitation on the windward side, while the air is dry on the leeward side having lost most moisture.
3) When warm and cold air masses meet, they form fronts where the denser cold air acts as a barrier to the rising warm air, which can produce storms along the front.