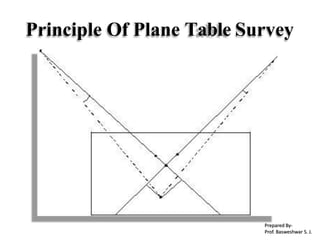
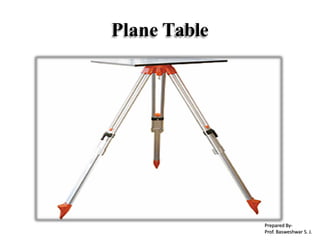
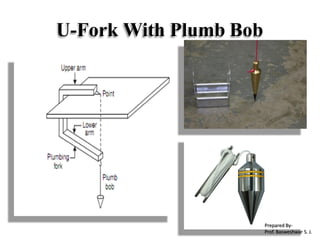
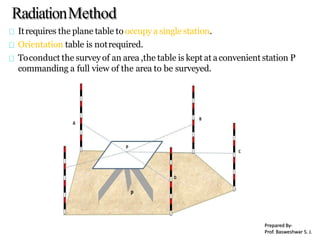
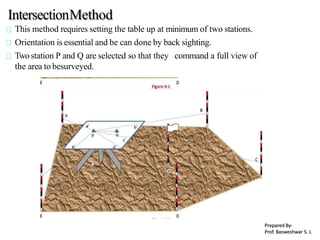
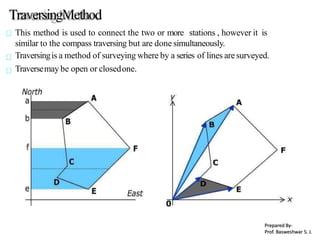
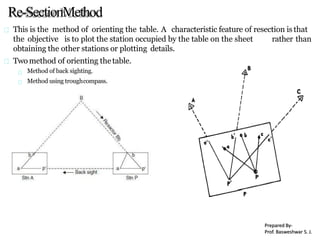
The document outlines the principles and methodologies of plane table surveying, emphasizing its graphical nature and simplicity compared to theodolite surveys, making it suitable for small scale maps. It details essential instruments like the plane table, tripod, and alidade, along with accessories necessary for effective surveying operations. Advantages include real-time plotting and reductions in measurement errors, while disadvantages highlight its inaccuracy for precise work and transportation challenges.