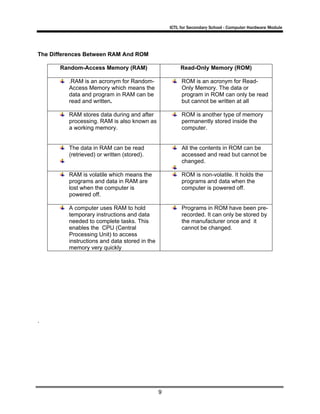
This document provides information about computer hardware components including input devices, output devices, and storage devices. It contains definitions and examples of each type of device. The document is divided into three activities that describe input devices for text, graphics, audio and video; output devices such as displays, printers, and audio equipment; and primary and secondary storage as well as different storage mediums. Worksheets with questions are included to help students identify and understand the different computer hardware components and their functions.