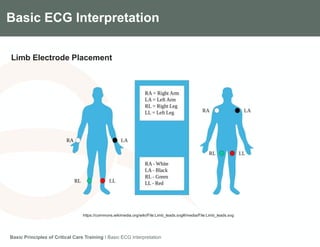
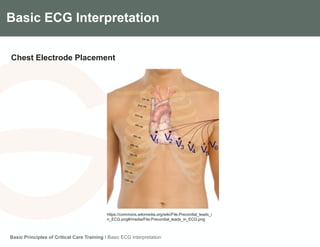
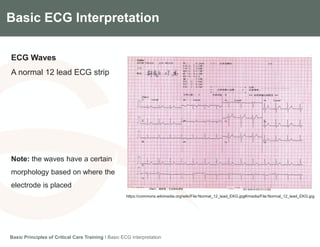
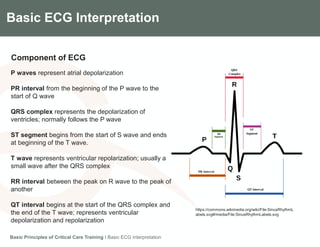
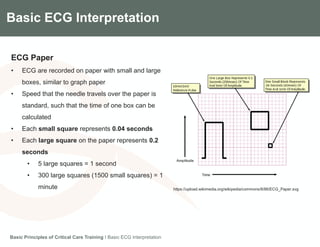
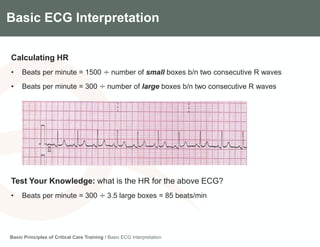
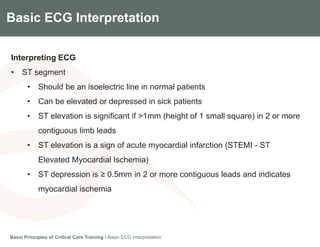
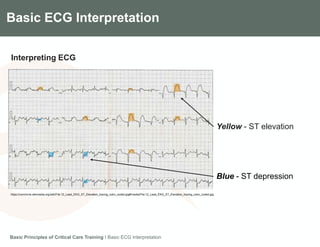
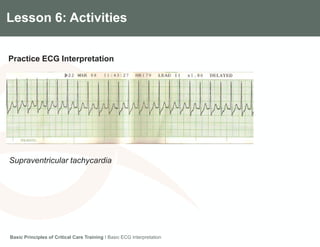
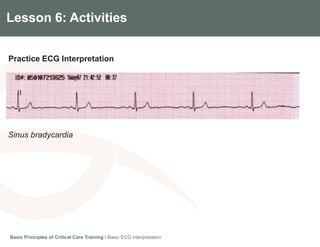
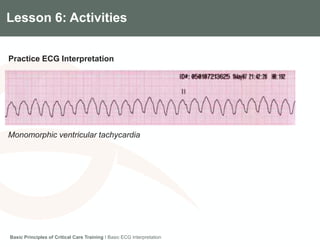
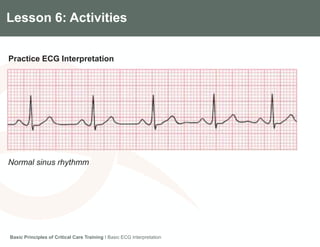
This document provides an overview of basic ECG interpretation. It describes the components of an ECG like waves, intervals, and segments. It explains how to calculate heart rate and determine rhythm. The document outlines how to interpret an ECG by examining the P wave, PR interval, QRS complex, ST segment, and T wave. It emphasizes following steps to document an interpretation and practicing on sample ECGs.