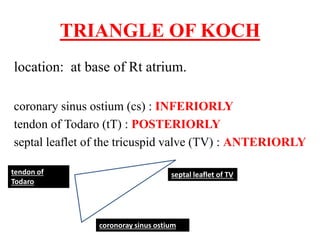
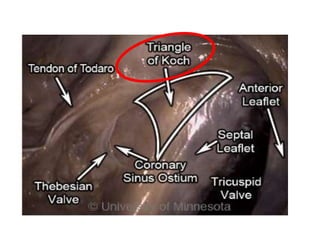
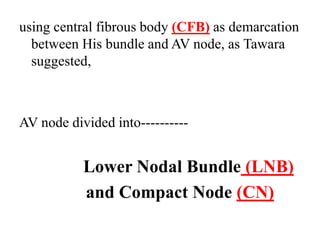
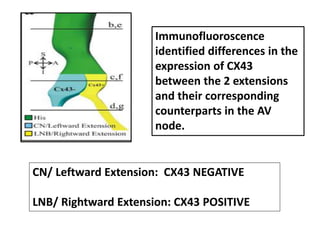
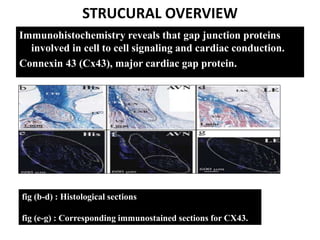
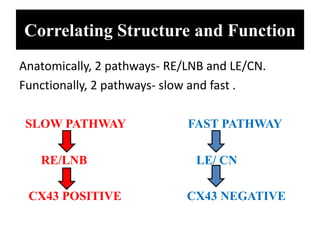
The document summarizes the anatomy and electrophysiology of the human atrioventricular (AV) node. It describes the AV node's location near the triangle of Koch. Immunohistochemistry reveals the AV node is divided into the lower nodal bundle and compact node based on differences in connexin 43 expression. The dual pathway electrophysiology of the AV node involves faster conduction through the connexin 43-negative compact node and slower conduction through the connexin 43-positive lower nodal bundle and extensions. Understanding the molecular compartmentalization of the AV node provides insight into its roles in cardiac conduction and as a potential arrhythmia substrate.