Embed presentation
Downloaded 76 times




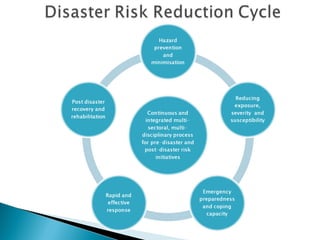
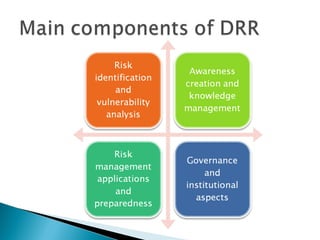
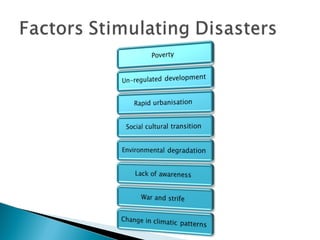

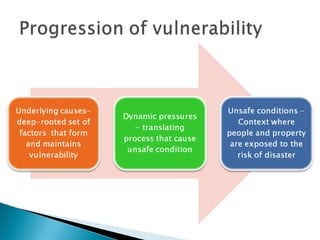








The document discusses reducing vulnerability to hydro-climatic disasters through disaster risk reduction initiatives in Guyana. It emphasizes understanding the relationship between hazards, vulnerability, and risk; evaluating existing disaster risk reduction programs; and promoting knowledge sharing to build resilient communities. Key points include identifying vulnerable populations, dynamics that propagate disasters in Guyana, challenges in effective disaster response, and measures to mitigate water-related disasters through a multi-sectoral approach incorporating disaster risk management into water resource management frameworks.
















