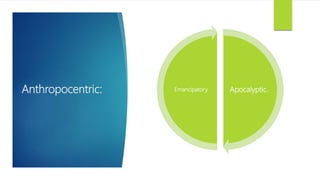
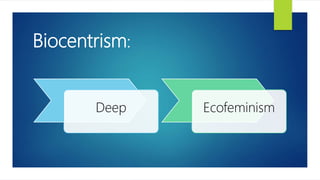
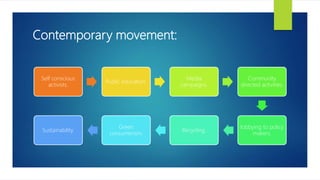
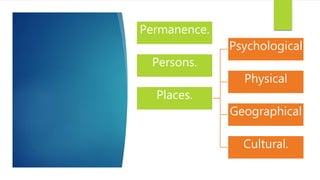
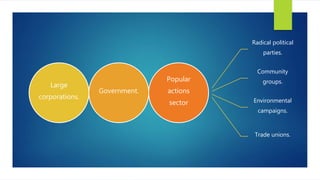
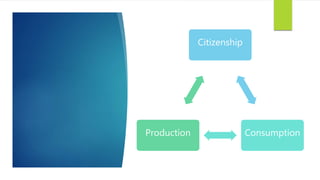
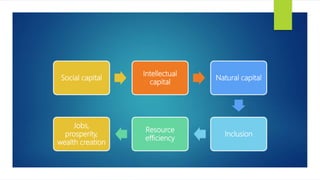
The document discusses various approaches to sustainable development, outlining different schools of environmentalism such as anthropocentric, apocalyptic, emancipatory, biocentric, deep ecology, and ecofeminism. It highlights the political and ethical movement aimed at improving the natural environment by changing harmful human activities, emphasizing strategies like recycling and alternative energy. Contemporary movements involve self-conscious activism, public education, and community engagement to promote sustainability.