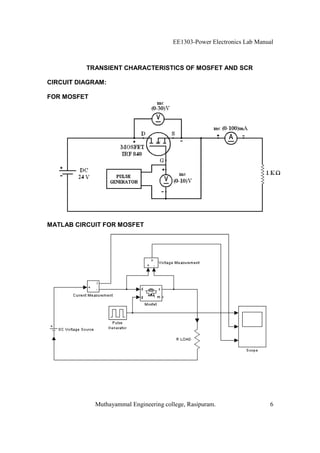
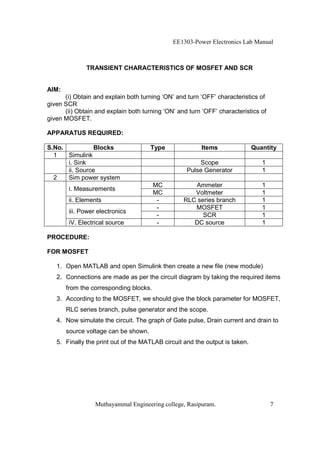
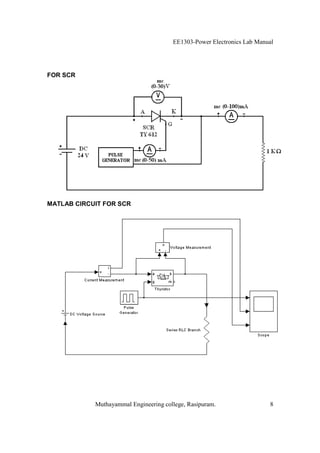
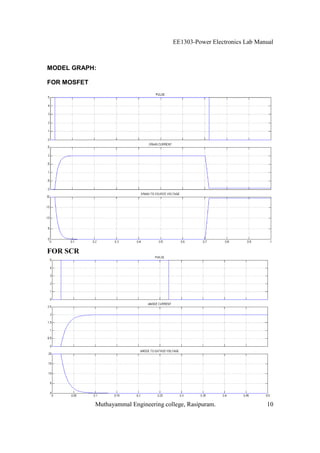
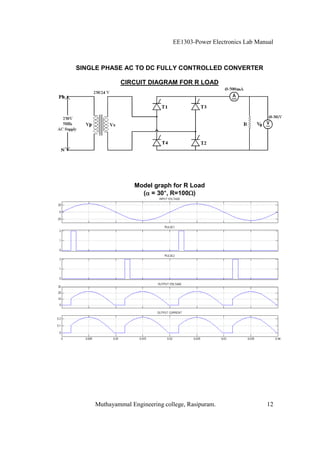
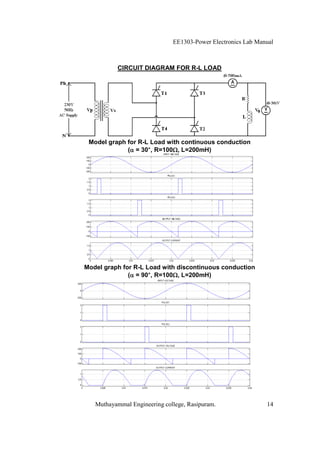
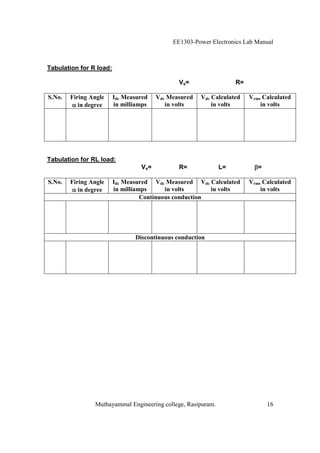
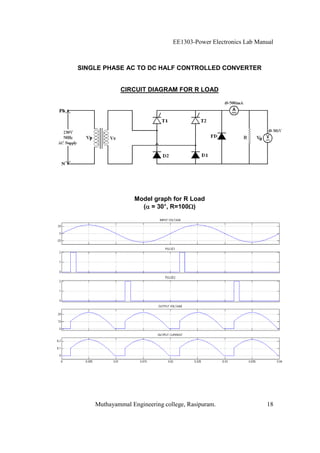
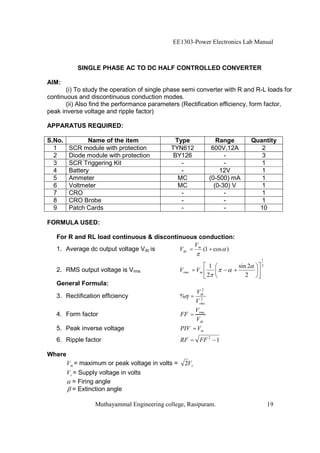
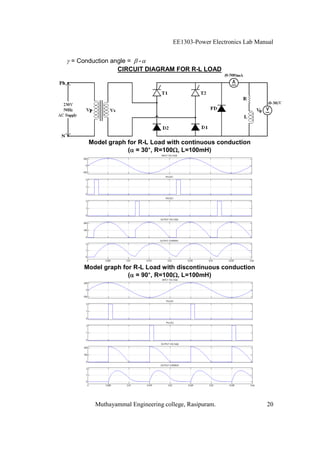
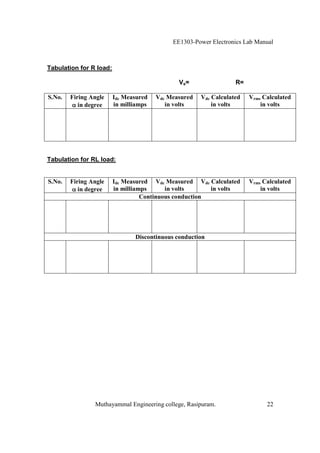
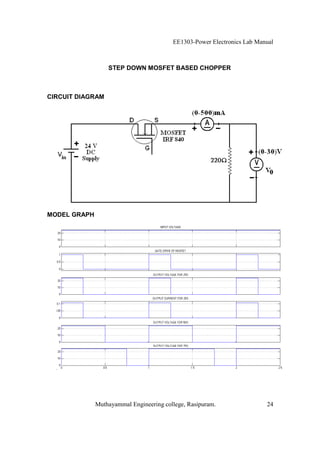
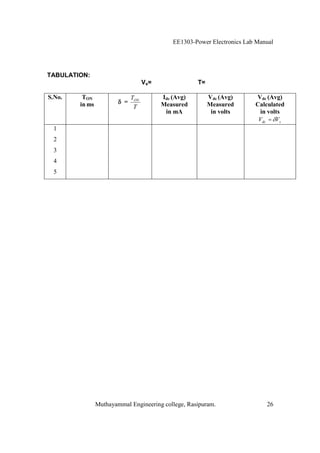
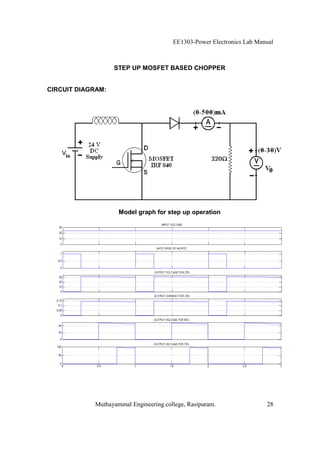
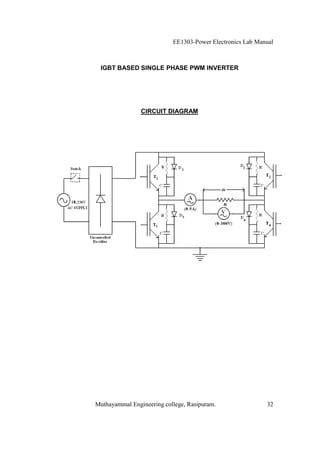
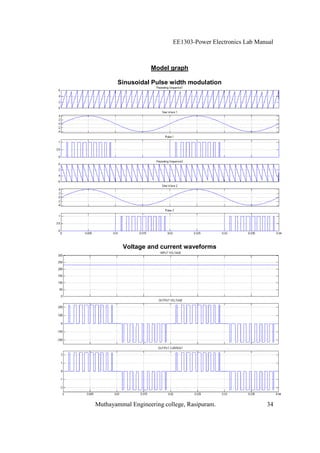
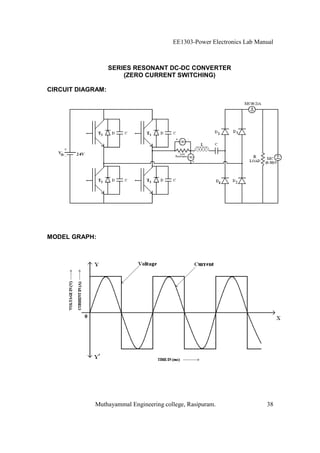
The EE1303 Power Electronics Lab Manual from Muthayammal Engineering College provides detailed instructions for conducting various experiments in power electronics, emphasizing safety protocols, attendance, and record-keeping. It outlines multiple experiments, including the characteristics of different semiconductor devices like SCRs and MOSFETs, and the operations of AC to DC converters, both fully and half-controlled. Each experiment includes aims, required apparatus, procedures, and formulas for analyzing electrical characteristics and performance parameters.