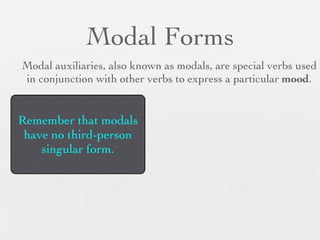
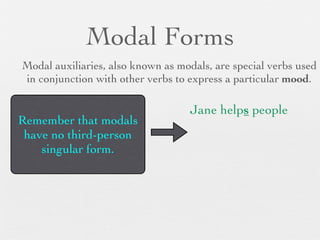
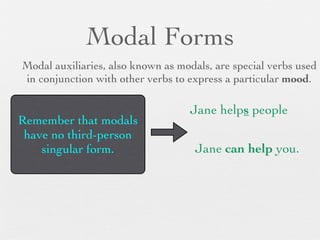
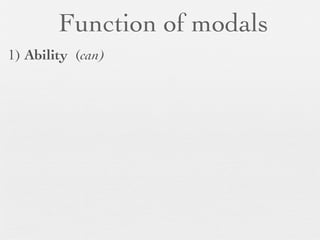
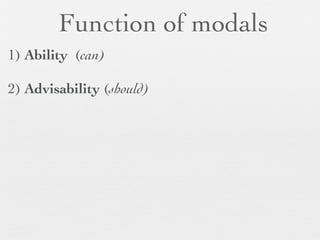
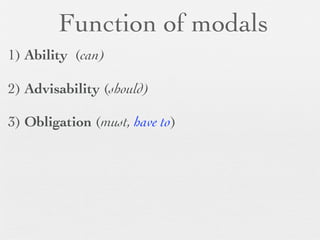
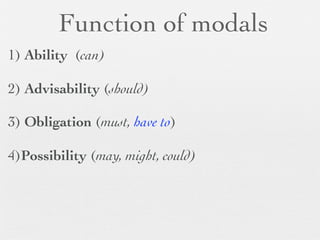
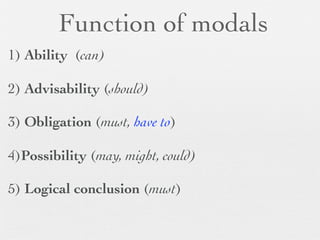
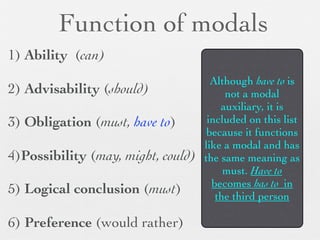
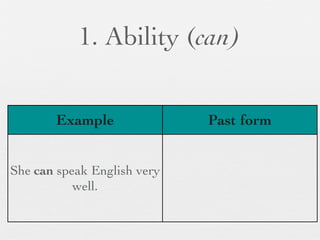
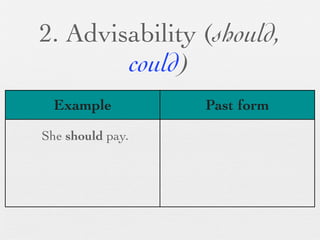
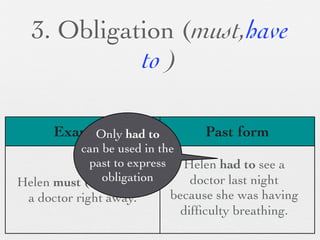
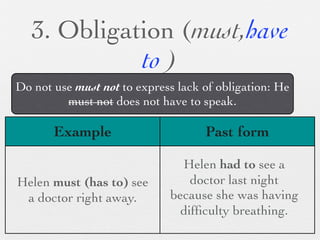
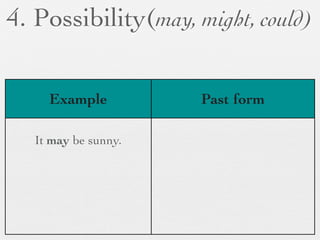
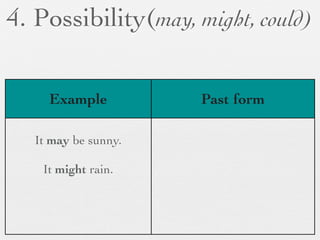
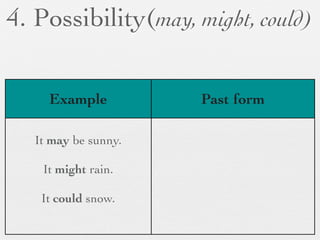
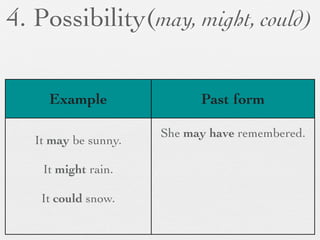
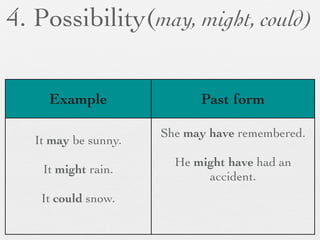
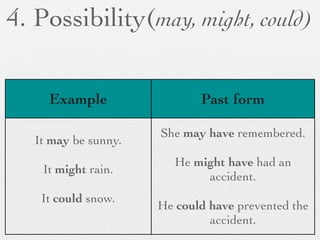
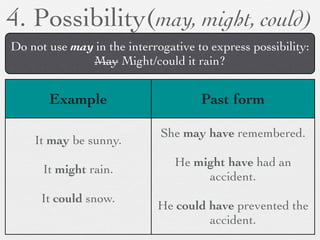
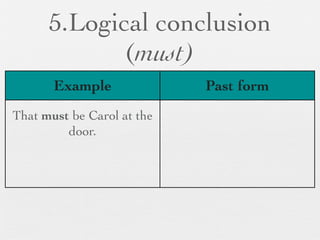
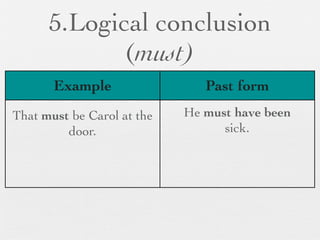
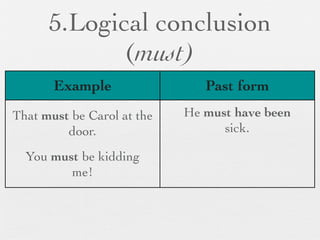
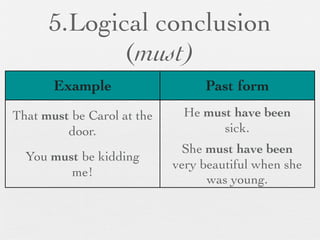
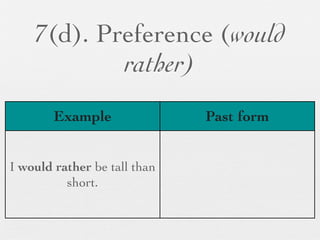
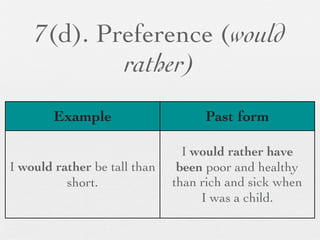
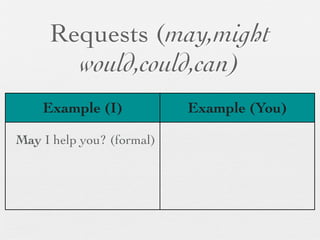
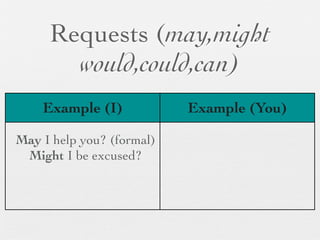
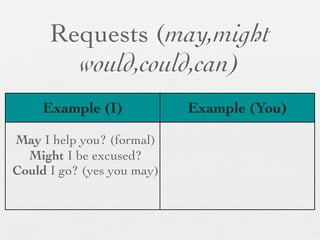
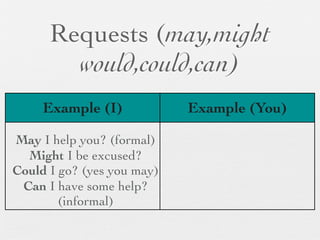
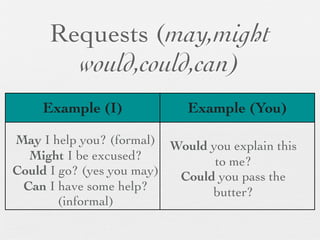
The document discusses modal forms and conditionals. It states that modal auxiliaries, also known as modals, are special verbs used with other verbs to express mood. It provides examples of different types of modals and their functions, including ability, obligation, possibility, preference and requests. It also classifies the most common conditionals into present real conditional, present unreal conditional, and past unreal conditional based on the probability of the if-clause.