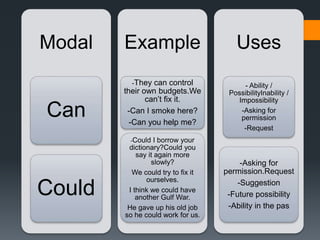
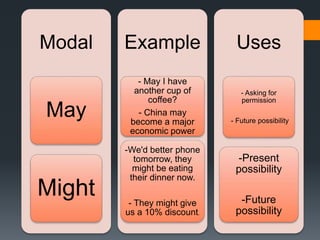
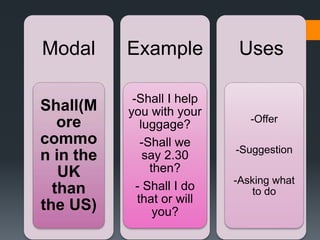
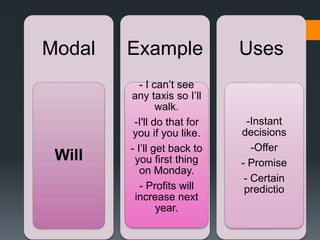
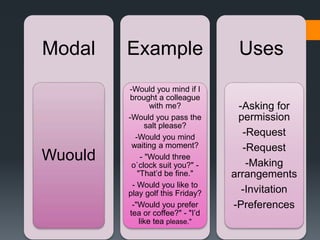
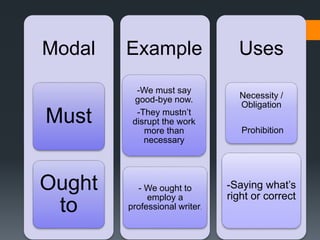
Modals verbs like can, may, must, will are used to express ability, obligation, possibility. Unlike other verbs, modal verbs do not change form or have infinitives/participles. They are used with other verbs to express things like ability, obligation, or possibility. Common mistakes include using an additional auxiliary verb when a modal is used, like "do I must come?" Modal verbs have specific uses - can is ability/possibility, may is permission/possibility, will is for instant decisions and predictions.