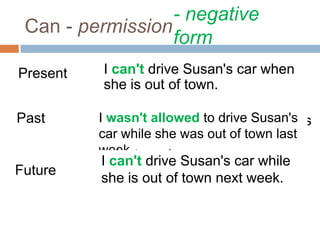
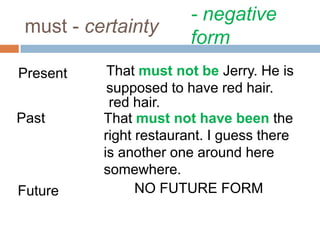
The document discusses modal verbs in English. Modal verbs are special verbs that behave differently than regular verbs. Some key points about modal verbs include: 1) they do not take "-s" in the third person, 2) "not" is used to make them negative, and 3) many cannot be used in past or future tenses. Common modal verbs are defined and examples are provided for can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would. Their uses relate to ability, permission, possibility, necessity, advice, and more.