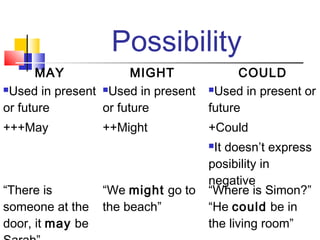
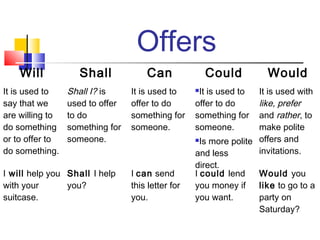
Modal verbs are used to express ideas like possibility, willingness, ability, obligation, certainty and permission. Some common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, ought to, must and have to. Modal verbs are used with other verbs and have consistent forms across subjects. They are used to talk about present and past ability, permission, obligation, advice, possibility, probability and requests.