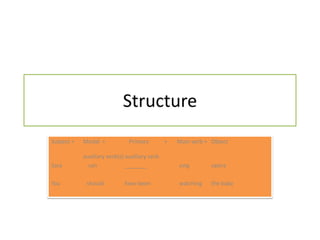
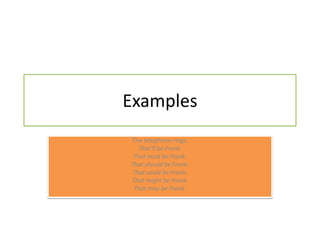
Modal verbs are special verbs that behave differently than regular verbs. Some key differences are that modal verbs do not take "-s" in the third person and use "not" to form negatives. Common modal verbs include can, could, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will, and would. Modal verbs are used to express attitudes like obligation, permission, possibility, and logical deduction. Their meaning depends on the context, and one modal verb can have multiple meanings.