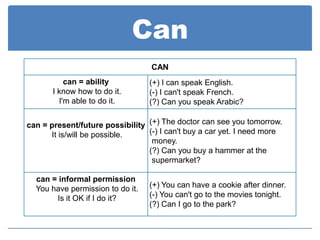
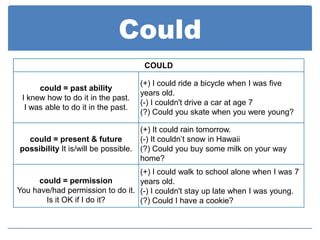
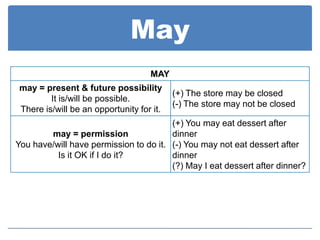
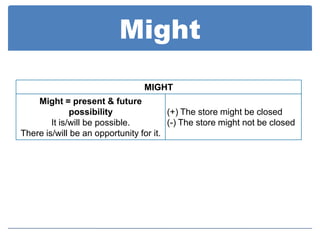
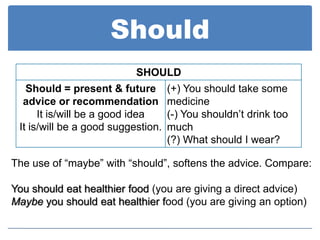
Modal auxiliaries like can, could, may, might, and should are used with main verbs to express meanings like ability, permission, possibility, advice, and recommendation. Modals don't have endings for tense and don't take infinitives or auxiliary verbs like do/does/did. Negation is formed by placing "not" after the modal.