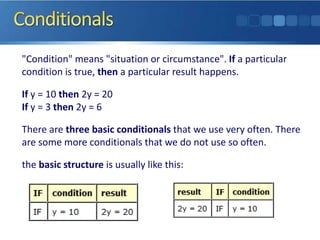
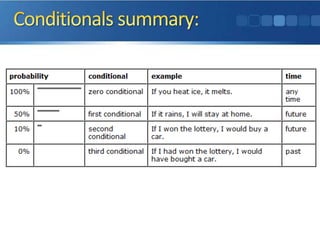
If a condition is true, then a particular result happens. There are three basic conditionals used often: zero conditional which refers to simple present facts; first conditional which refers to possible future events; and second conditional which refers to unlikely or imaginary future events. The third conditional refers to hypothetical or unrealistic past events.