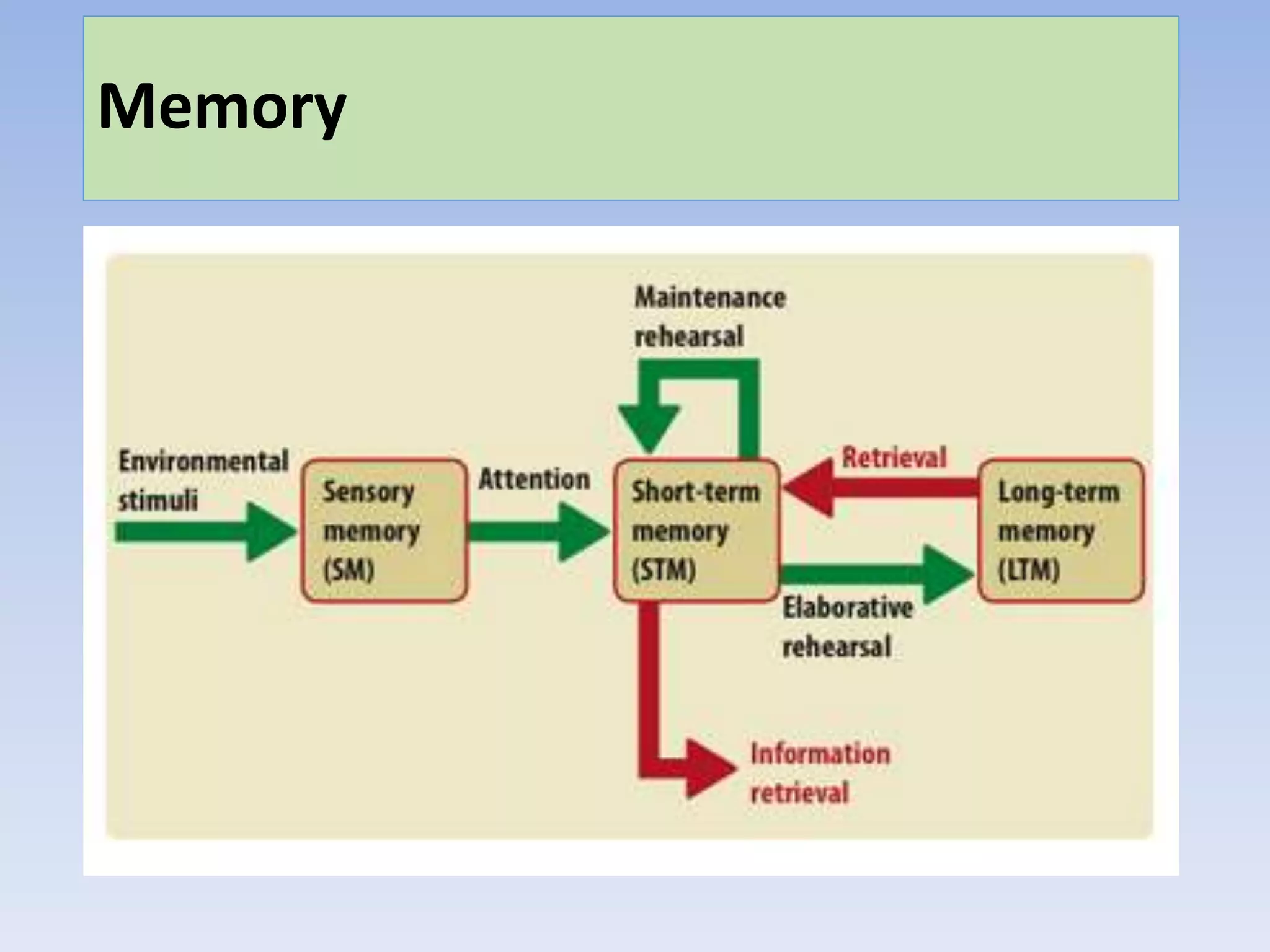
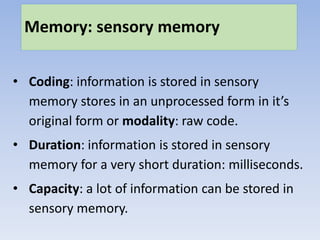
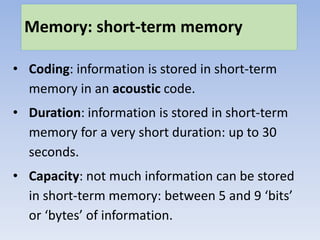
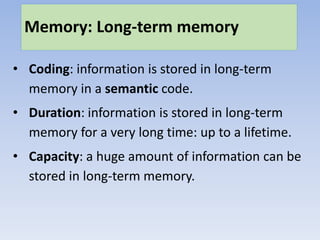
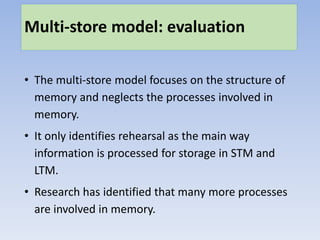
Memory can be divided into three main stores: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Key research has found differences in how information is coded, the duration it can be stored, and storage capacity across these three memory stores. Sensory memory stores information in its raw form for milliseconds. Short-term memory codes information acoustically and can store around 5-9 bits for up to 30 seconds. Long-term memory semantically codes information for retrieval over a lifetime. While this multi-store model is supported by research, it is an oversimplification as memory is more complex with multiple processes involved.